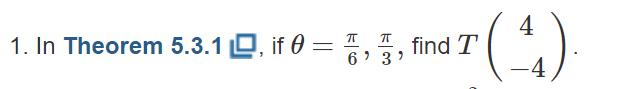Question
4 1. In Theorem 5.3.1 D, if 0= 5,5, II find T 6 3 -4 Theorem 5.3.1. Let T: R? R be the orthogonal
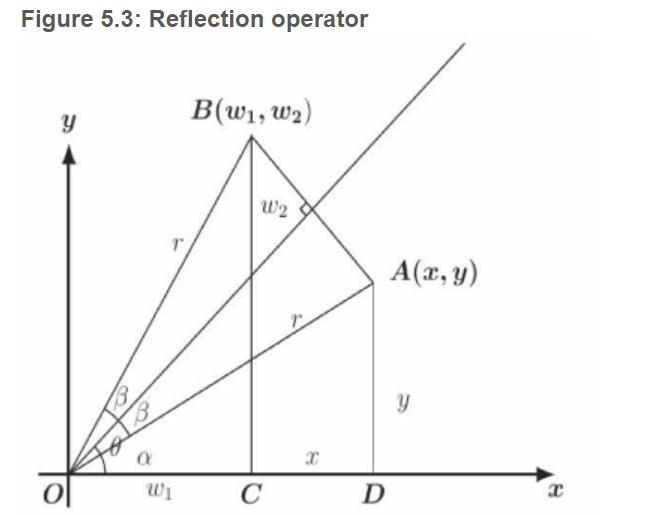
4 1. In Theorem 5.3.1 D, if 0= 5,5, II find T 6 3 -4 Theorem 5.3.1. Let T: R? R be the orthogonal projection on a line I passing through the origin (0, 0) and let the angle between I and the x-axis be 0 (see Figure 5.3 O). Then (5.3.1) r(")-(cos@sine ") (;) cos0 sin 0 cos 0 sin'o ):). Proof From Figure 5.3 D, we see that (5.3.2) (w1, w2) = (r cos 0,r sin 0). We prove the following assertion. (5.3.3) r = x cos 0 +y sin 0. Indeed, by Figure 5.3 D, r = s cos B= s cos(0 - a) and Figure 5.3: Reflection operator B(w1, w2) w2 A(x, y) Wi C D
Step by Step Solution
3.39 Rating (149 Votes )
There are 3 Steps involved in it
Step: 1

Get Instant Access to Expert-Tailored Solutions
See step-by-step solutions with expert insights and AI powered tools for academic success
Step: 2

Step: 3

Ace Your Homework with AI
Get the answers you need in no time with our AI-driven, step-by-step assistance
Get StartedRecommended Textbook for
Elementary Linear Algebra with Applications
Authors: Howard Anton, Chris Rorres
9th edition
471669598, 978-0471669593
Students also viewed these Mathematics questions
Question
Answered: 1 week ago
Question
Answered: 1 week ago
Question
Answered: 1 week ago
Question
Answered: 1 week ago
Question
Answered: 1 week ago
Question
Answered: 1 week ago
Question
Answered: 1 week ago
Question
Answered: 1 week ago
Question
Answered: 1 week ago
Question
Answered: 1 week ago
Question
Answered: 1 week ago
Question
Answered: 1 week ago
Question
Answered: 1 week ago
Question
Answered: 1 week ago
Question
Answered: 1 week ago
Question
Answered: 1 week ago
Question
Answered: 1 week ago
Question
Answered: 1 week ago
Question
Answered: 1 week ago
Question
Answered: 1 week ago
View Answer in SolutionInn App