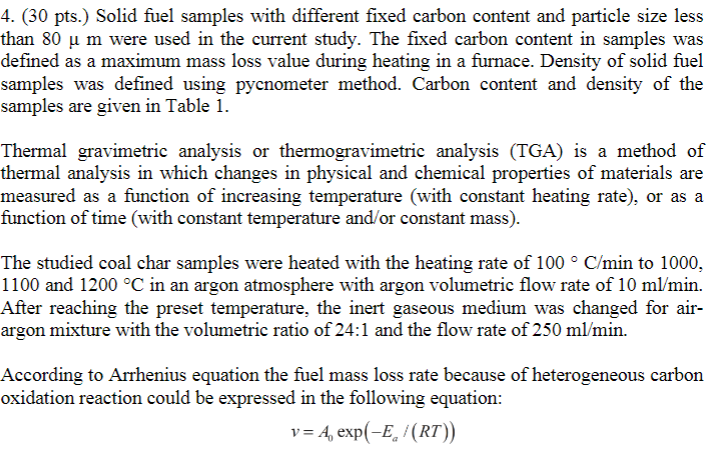
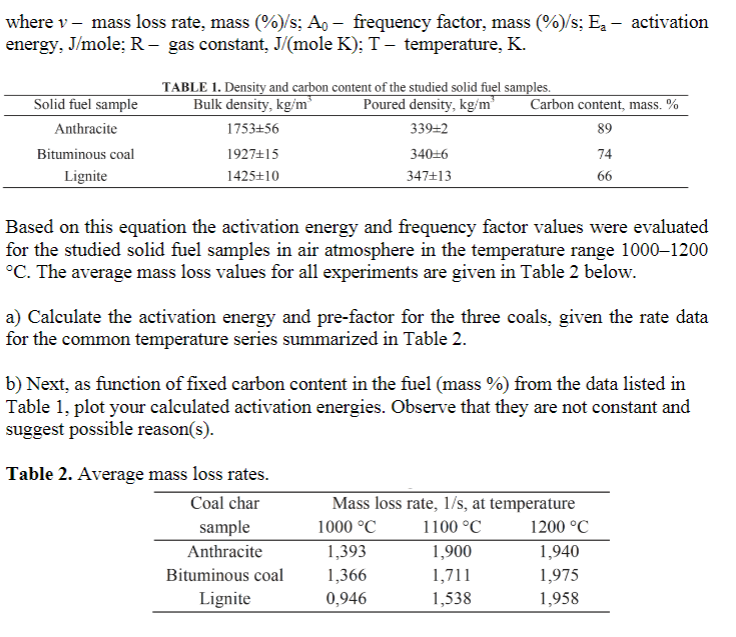
4. (30 pts.) Solid fuel samples with different fixed carbon content and particle size less than 80 u m were used in the current study. The fixed carbon content in samples was defined as a maximum mass loss value during heating in a furnace. Density of solid fuel samples was defined using pycnometer method. Carbon content and density of the samples are given in Table 1. Thermal gravimetric analysis or thermogravimetric analysis (TGA) is a method of thermal analysis in which changes in physical and chemical properties of materials are measured as a function of increasing temperature (with constant heating rate), or as a function of time (with constant temperature and/or constant mass). The studied coal char samples were heated with the heating rate of 100 C/min to 1000, 1100 and 1200 C in an argon atmosphere with argon volumetric flow rate of 10 ml/min. After reaching the preset temperature, the inert gaseous medium was changed for air- argon mixture with the volumetric ratio of 24:1 and the flow rate of 250 ml/min. According to Arrhenius equation the fuel mass loss rate because of heterogeneous carbon oxidation reaction could be expressed in the following equation: v=4, exp(-E /(RT)) where v - mass loss rate, mass (%)/s: Ap - frequency factor, mass (%)/s: Ex - activation energy, J/mole; R- gas constant, J/(mole K); T - temperature, K. Solid fuel sample Anthracite Bituminous coal Lignite TABLE 1. Density and carbon content of the studied solid fuel samples. Bulk density, kg/m Poured density, kgm Carbon content, mass. % 1753+56 339=2 89 1927+15 340=6 74 1425+10 347+13 66 Based on this equation the activation energy and frequency factor values were evaluated for the studied solid fuel samples in air atmosphere in the temperature range 1000-1200 C. The average mass loss values for all experiments are given in Table 2 below. a) Calculate the activation energy and pre-factor for the three coals, given the rate data for the common temperature series summarized in Table 2. b) Next, as function of fixed carbon content in the fuel (mass %) from the data listed in Table 1, plot your calculated activation energies. Observe that they are not constant and suggest possible reason(s). Table 2. Average mass loss rates. Coal char sample Anthracite Bituminous coal Lignite Mass loss rate, 1/s, at temperature 1000 C 1100 C 1200 C 1,393 1,900 1,940 1,366 1,711 1,975 0,946 1,538 1,958








