Answered step by step
Verified Expert Solution
Question
1 Approved Answer
4. Consider the following choices between lotteries: $4000 p = 0.80 L $3000 p = 1.00 = VS. L2 = $0 p = 0.20
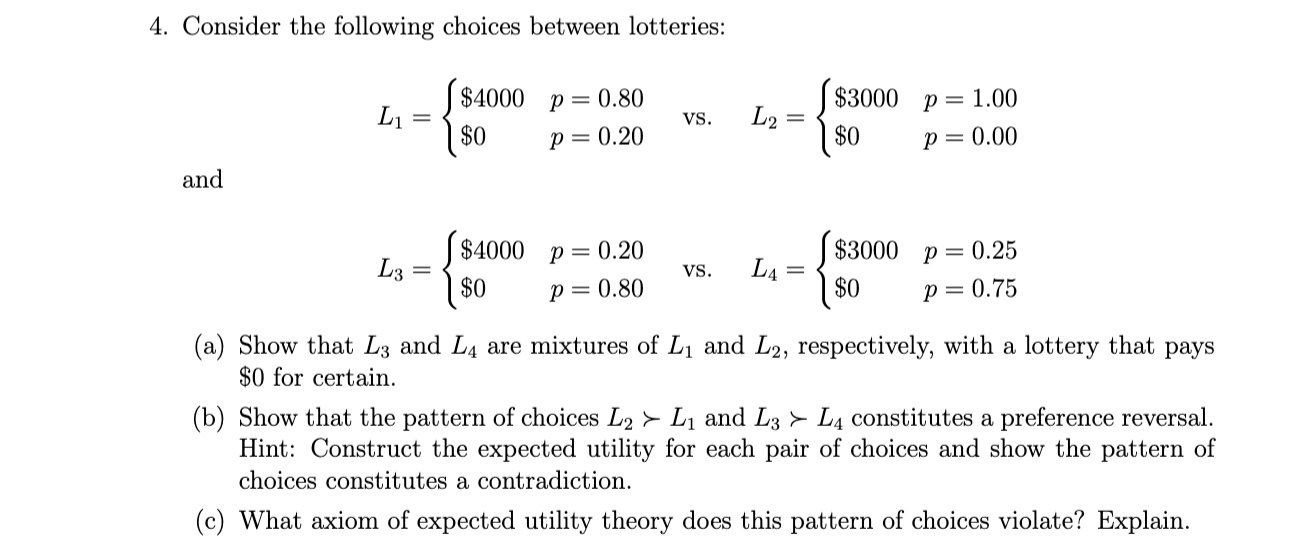

4. Consider the following choices between lotteries: $4000 p = 0.80 L $3000 p = 1.00 = VS. L2 = $0 p = 0.20 $0 p = 0.00 and $4000 p = 0.20 $3000 p = 0.25 L3 = VS. L = $0 p = 0.80 $0 p = 0.75 (a) Show that L3 and L4 are mixtures of L1 and L2, respectively, with a lottery that pays $0 for certain. (b) Show that the pattern of choices L2 > L and L3 > L4 constitutes a preference reversal. Hint: Construct the expected utility for each pair of choices and show the pattern of choices constitutes a contradiction. (c) What axiom of expected utility theory does this pattern of choices violate? Explain. 5. Consider a setting like the mug experiment described in class. An agent has current wealth w and may have 0 or 1 mugs. Let m stand for the number of mugs. An allocation is a (m, w) pair. For instance, (1, 15) means I have a 1 mug and $15, while (0,20) means 0 mugs and $20. Suppose that the agent's utility for allocations is given by u(m, w): u (m) + u (w) where u(m) = = {8 if m = 1 0 if m = 0 for >0 and u(w) = W. 2 (a) Suppose the agent does not own a mug. Compute Willingness-to-Pay (WTP). That is, WTP solves: u(1, w - WTP) = u(0, w). That is, this is the highest price a person would be willing to pay to acquire a mug. (b) Suppose the agent does own a mug. Compute Willingness-to-Accept (WTA). That is, WTA solves: u(1, w) = u(0, w+WTA). That is, this is the lowest price a person would be willing to accept to give up a mug. (c) Calculate WTA - WTP. Explain what this means in a few sentences. Hint: This is a standard utility maximizing agent. Now consider again the same setup as above: an agent has current wealth w and may have m{0,1} mugs. An allocation is a (m, w) pair. Now, suppose that the agent is loss averse with utility for allocations given by v(m, w | r) = v (m | r) + v (w | 12) where v (m|r)= So (m-r) if m>ri -A (0 (rm)) if msn and w- T2 v2 (w|12) = if w>T -A (raw) if wra for > 0,1. The reference point r = (1, 2) is given by the agent's current situation (the status quo). (d) Suppose the agent does not own a mug. Compute WTP. (e) Suppose the agent does own a mug. Compute WTA. (f) Calculate WTA - WTP as a function of A. When is it positive? How does it change as A increases?
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it
Step: 1

Get Instant Access to Expert-Tailored Solutions
See step-by-step solutions with expert insights and AI powered tools for academic success
Step: 2

Step: 3

Ace Your Homework with AI
Get the answers you need in no time with our AI-driven, step-by-step assistance
Get Started


