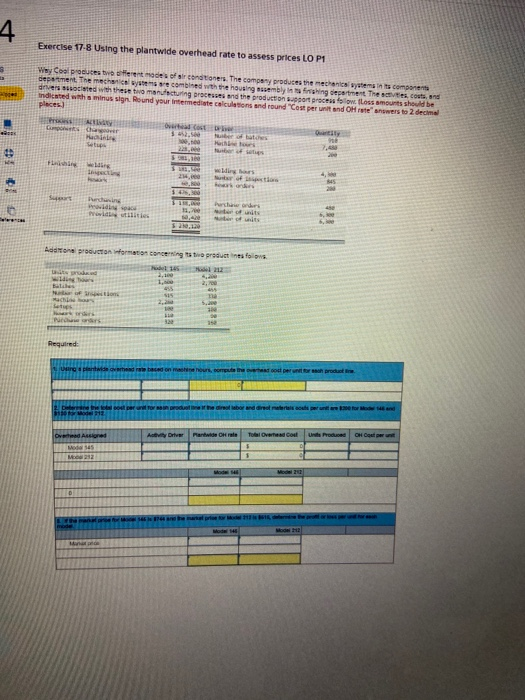
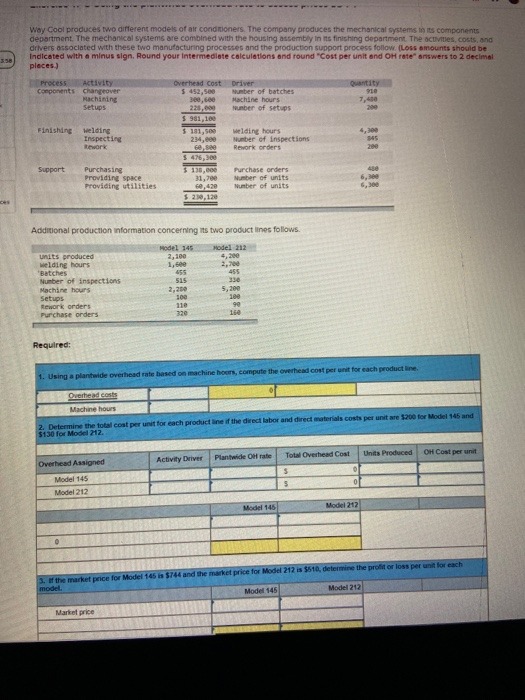
4 Exercise 17-8 Using the plantwide overhead rate to assess prices LO P1 Why Cool produces tweet des of conditioners. The company produces e mechanics we componen department. The mechanical ens recombined with the housing sembly infringement Theres, costs and deve sociated with these toacturing process and the produconor process of floss amounts should be Indicated with a minus sign. Round your intermediate calculations and round"Cost per unit and OH tewers to 2 decimal places) Ga da s. ber 200 Hai ws 13. Purdu Author utilities Add to run wortes concerning redenes fins 145 2 2.100 5,20 Win Bates 455 Notions 15 ma 2. 5. Setups Pows 322 Required pedigerend 2 Determine the cost Model 13 AD Partide Chale Total Overhead out Product CH Ovid Aksioned MG 545 Mo 212 Mode 1 Won H Way Cool produces two different models of air conditioners. The company produces the mechanical systems in its components department. The mechanical systems are combined with the housing assembly in its finishing department. The activities, Cotes, and drivers associated with these two manufacturing processes and the production support process follow (Loss amounts should be Indicated with a minus sign. Round your intermediate calculations and round "Cost per unit and OH rate" answers to 2 decimal places.) Process Activity Components Changeover Machining Setups Quantity 910 7,40 200 Finishing Welding Inspecting Rework Overhead Cost Driver 5 452,500 Number of batches 300,600 Machine hours Number of setups $981,100 $ 181,500 welding hours 234,000 Number of inspections 6. Rework orders $ 476,300 3 130,000 Purchase orders 31,700 Number of units 60.420 Number of units $ 239,120 200 Support Purchasing Providing space Providing utilities 6,30 Additional production information concerning its two product lines follows Model 145 2,100 1, units produced welding hours Batches Number of inspections Machine hours Setups Rework orders Purchase orders Model 212 4,200 2,700 455 330 5,200 515 2,28 100 100 90 16 330 Required: 1. Using a plantwide overhead rate based on machine hours, compute the overhead cost per unit for each product line Dushad costs Machine hours 2. Determine the total cost per unit for each product line of the direct labor and direct materials costs per unitare 200 for Model 145 and $130 for Model 212 Total Overhead Cost Plantwide Otrate Units Produced OH Cost per unit Activity Driver Overhead Assigned Model 145 Model 212 5 5 0 0 Model 145 Model 212 3. If the market price for Model 145 is $744 and the market price for Model 212 is $510, determine the profit or loss per unit for each model Model 145 Model 212 Market price