Answered step by step
Verified Expert Solution
Question
1 Approved Answer
4. Is overshoot consistent with purchasing power parity? Explain why or why not. Explain the role overshoot has in resolving the inflexibility of prices

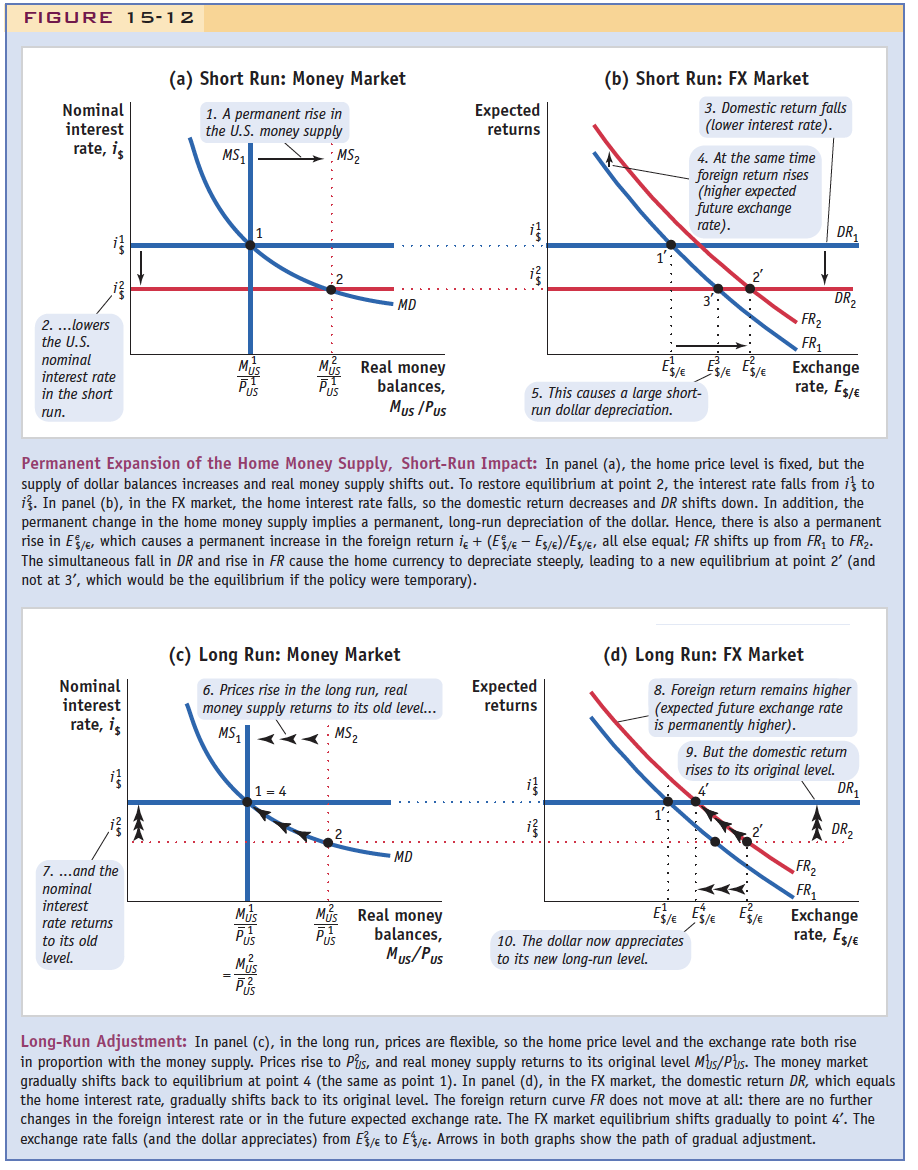
4. Is overshoot consistent with purchasing power parity? Explain why or why not. Explain the role overshoot has in resolving the inflexibility of prices in the short-run? You may want to use Fig. 15-12 as a reference. (10 pts.). FIGURE 15-12 Nominal interest rate, is 2. ...lowers the U.S. i nominal interest rate in the short run. Nominal interest rate, is i 7. ...and the nominal interest (a) Short Run: Money Market 1. A permanent rise in the U.S. money supply MS rate returns to its old level. Mis PUS MS MS Pus 1-4 MD Real money balances, Mus / Pus (c) Long Run: Money Market 6. Prices rise in the long run, real money supply returns to its old level... MS MS MD Expected returns Real money balances, Mus/Pus i Permanent Expansion of the Home Money Supply, Short-Run Impact: In panel (a), the home price level is fixed, but the supply of dollar balances increases and real money supply shifts out. To restore equilibrium at point 2, the interest rate falls from is to i. In panel (b), in the FX market, the home interest rate falls, so the domestic return decreases and DR shifts down. In addition, the permanent change in the home money supply implies a permanent, long-run depreciation of the dollar. Hence, there is also a permanent rise in E/, which causes a permanent increase in the foreign return i + (E/ - Es/)/Es/e, all else equal; FR shifts up from FR to FR. The simultaneous fall in DR and rise in FR cause the home currency to depreciate steeply, leading to a new equilibrium at point 2' (and not at 3', which would be the equilibrium if the policy were temporary). (b) Short Run: FX Market Expected returns i 5. This causes a large short- run dollar depreciation. 3. Domestic return falls (lower interest rate). 4. At the same time foreign return rises (higher expected future exchange rate). 3'- ES/E ES/E ES/E 10. The dollar now appreciates to its new long-run level. FR FR (d) Long Run: FX Market ES/ ES/E Exchange rate, Es/ 8. Foreign return remains higher (expected future exchange rate is permanently higher). DR [$/ 9. But the domestic return rises to its original level. DR FR FR DR Exchange rate, Es/ Long-Run Adjustment: In panel (c), in the long run, prices are flexible, so the home price level and the exchange rate both rise in proportion with the money supply. Prices rise to Ps, and real money supply returns to its original level Mus/Pus. The money market gradually shifts back to equilibrium at point 4 (the same as point 1). In panel (d), in the FX market, the domestic return DR, which equals the home interest rate, gradually shifts back to its original level. The foreign return curve FR does not move at all: there are no further changes in the foreign interest rate or in the future expected exchange rate. The FX market equilibrium shifts gradually to point 4'. The exchange rate falls (and the dollar appreciates) from Esto E. Arrows in both graphs show the path of gradual adjustment.
Step by Step Solution
★★★★★
3.40 Rating (153 Votes )
There are 3 Steps involved in it
Step: 1
Answer Yes overshooting is consistent with PPP Investors ...
Get Instant Access to Expert-Tailored Solutions
See step-by-step solutions with expert insights and AI powered tools for academic success
Step: 2

Step: 3

Ace Your Homework with AI
Get the answers you need in no time with our AI-driven, step-by-step assistance
Get Started


