Answered step by step
Verified Expert Solution
Question
1 Approved Answer
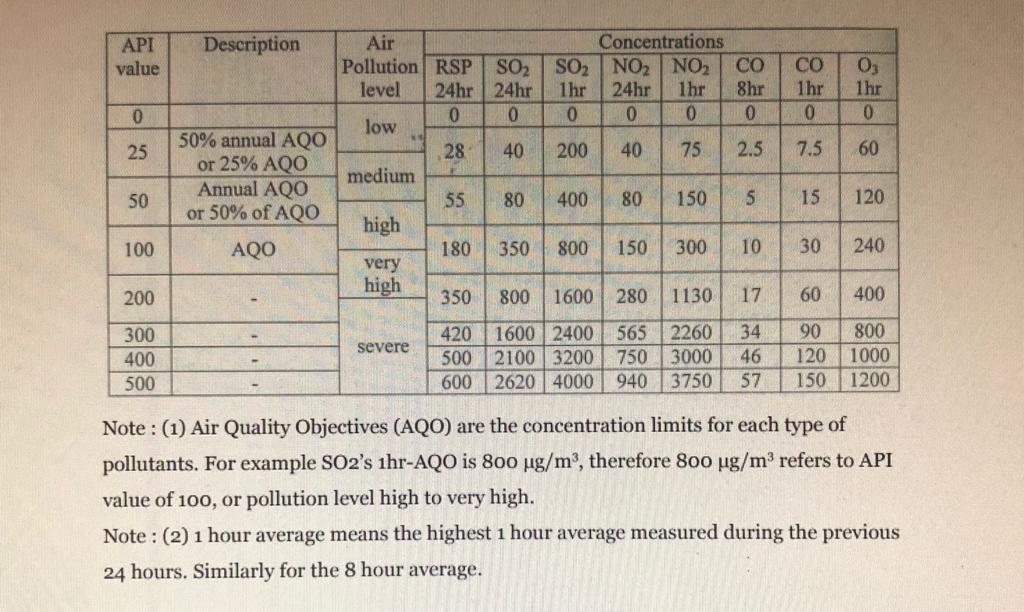
4. Study the equations for the two air pollution indices and answer the questions. Air Pollution Index (before 2013) 5 pollutants are included in



![a. [20 points] Calculate the API and AQHI. Which category is each of them referring to? b. [8 points] Why is](https://dsd5zvtm8ll6.cloudfront.net/si.experts.images/questions/2022/10/6357c3c4e437b_1666696142432.jpg)
4. Study the equations for the two air pollution indices and answer the questions. Air Pollution Index (before 2013) 5 pollutants are included in the calculation of the Air Pollution Index (API). They are respirable suspended particulates (RSP), SO2, NO2, CO and O3. First a sub-API is calculated for each of these pollutants. Some pollutants are calculated twice, for different averaging times. This leads to 8 sub-APIs show in here (all values are in g/m, except for CO which has units of mg/m), API value 0 25 50 100 --- 200 300 400 500 Description 50% annual AQO or 25% AQO Annual AQO or 50% of AQO AQO Air Concentrations Pollution RSP SO SO2 NO NO level 24hr 24hr 1hr 24hr 1hr 0 10 0 0 0 low 28 40 200 40 75 medium high very high severe 55 180 80 350 400 80 800 150 150 CO 8hr 0 2.5 5 300 10 CO 1hr 0 7.5 15 30 03 1hr 0 60 120 240 350 800 1600 280 1130 17 60 400 90 800 420 1600 2400 565 2260 34 500 2100 3200 750 3000 46 120 1000 600 2620 4000 940 3750 57 150 1200 Note: (1) Air Quality Objectives (AQO) are the concentration limits for each type of pollutants. For example SO2's 1hr-AQO is 800 g/m, therefore 800 g/m refers to API value of 100, or pollution level high to very high. Note: (2) 1 hour average means the highest 1 hour average measured during the previous 24 hours. Similarly for the 8 hour average. The sub-index can be found by piecewise linear interpolation, Ip = Ip,bp + -Cp,bp -Cp,bp (Ip.bp+1 - Ip.bp) where Ip = sub-index for pollutant p concp Cp.bp+1 - - concp = concentration of pollutant p Cp,bp concentration of pollutant p at a breakpoint (refer to table) Ip,bp sub-API for pollutant p at the same breakpoint (refer to table) For example, 100 g/m of RSP would give 100-55 IRSP = 50+ (100-50) = = 68 180 55 The highest sub-index for each category becomes the API for that station. These are the concentrations of Mongkok on a certain day are listed in here. RSP (24 hr) = 108.8 g/m 03 (1 hr) = 200.0 g/m 03 (3 hr) = 162.0 g/m PM2.5 (3 hr) = 40.2 g/m CUHK ESSC3800 Global Environmental Change - Assignment 1 PM10 (3 hr) = 70 g/m NO2 (24 hr) = 101.1 g/m NO2 (3 hr) = 130.2 g/m NO2 (1 hr) = 151.2 g/m SO2 (24 hr) = 12.1 g/m SO2 (1 hr) = 18.7 g/m SO2 (3 hr) = 14.8 g/m CO (8 hr) = 1265 g/m CO (1 hr) = 2021.5 g/m Air Quality Health Index The AQHI of the current hour is calculated from the sum of the percentage added health risk (%AR) of daily hospital admissions attributable to the 3-hour moving average concentrations of four criteria air pollutants: %AR=%AR (NO2) + % AR (SO2) + %AR (03) + %AR (PM) %AR(NO2) = [exp (B(NO2) x C(NO2)) - 1] x 100% %AR(SO2) = [exp (B(SO2) x C(SO2)) - 1] x 100% %AR(O3) = [exp (B(03) x C(O3)) - 1] 100% X %AR(PM10) = [exp (B(PM10) x C(PM10)) - 1] x 100% %AR(PM2.5) = [exp (B(PM2.5) x C(PM2.5)) - 1] x 100% where (1) %AR (PM) = %AR (PM10) or %AR (PM2.5), whichever is higher (2) C(NO2), C(SO2), C(O3), C(PM10) and C(PM2.5) are the 3-hour moving average concentration of the respective pollutants in g/m (3) is the health risk factor for each pollutant, B(NO2) = 0.0004462559 B(SO2) = 0.0001393235 B(03) = 0.0005116328 B(PM10) = 0.0002821751 B(PM2.5) = 0.0002180567 a. [20 points] Calculate the API and AQHI. Which category is each of them referring to? b. [8 points] Why is it necessary to have different averaging times for API? Should we have a lower standard (higher pollutant concentration limitation) for 1 hr or 24 hr CUHK ESSC3800 Global Environmental Change - Assignment 1 averages and why? c. [12 points] What are the pros and cons for each of these indices? Discuss your opinion. Do you think one of them is better or both of them are good/bad in reflecting the health effects of the pollutants? d. [3 points] Which index can be updated later when newer data are given? Which variables will be updated? 3
Step by Step Solution
★★★★★
3.49 Rating (156 Votes )
There are 3 Steps involved in it
Step: 1
a To calculate the API we need to find the subAPI for each pollutant and then determine the highest subAPI for each category which becomes the API for that station Using the given concentrations RSP 2...
Get Instant Access to Expert-Tailored Solutions
See step-by-step solutions with expert insights and AI powered tools for academic success
Step: 2

Step: 3

Ace Your Homework with AI
Get the answers you need in no time with our AI-driven, step-by-step assistance
Get Started


