4-0 stainless steel sutures used for orthopedic applications are subjected to a heat treating process. The sutures are drawn through an oven at a rate
4-0 stainless steel sutures used for orthopedic applications are subjected to a heat treating process. The sutures are drawn through an oven at a rate of 0.5 meters per minute. The oven temperature is kept at 700°C. The wire enters the oven at room temperature, 25°C, and exits the oven at 500°C. What is the rate of heat transfer to the wire? Note that a 4-0 suture has a diameter of 0.150 mm. Hint: You will need to use the following table. You can assume that stainless steel and mild steel have similar thermal properties. The answer is 25.5 W.
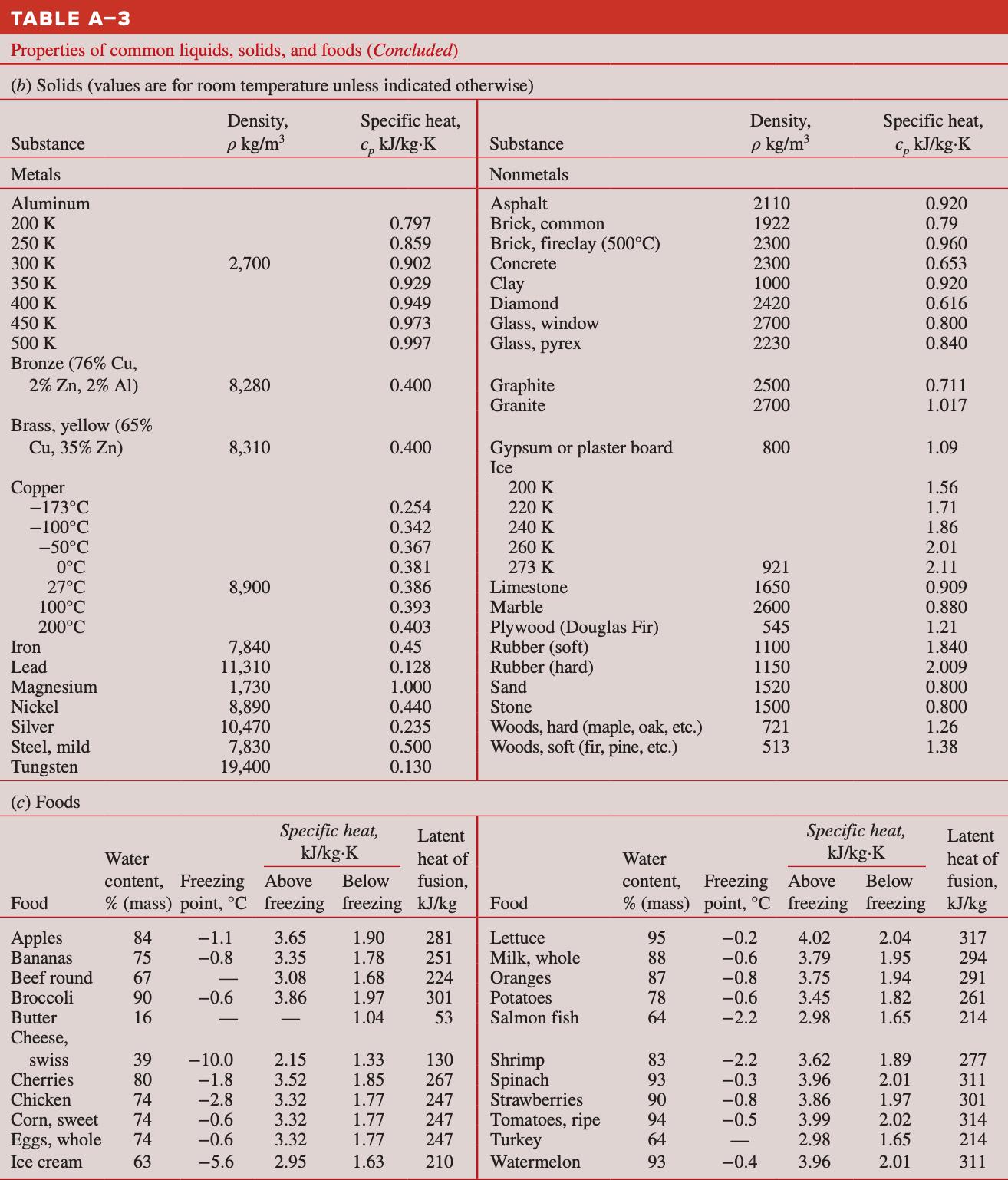
Image transcription text
TABLE A-3 Properties of common liquids, solids, and foods (Concluded) (b) Solids (values are for room temperature unless indicated otherwise)Density, Specific heat, Density, Specific heat, Substance p kg/m3 cp lekg-K Substance p kg/m3 cp kJ/kg-K Metals Nonmetals Aluminum
Asphalt 21 10 0.920 200 K 0.797 Brick, common 1922 0.79 250 K 0.859 Brick, fireclay (500°C) 2300 0.960 300 K 2,700 0.902 Co...
As an example, you can see an example of steel sutures manufactured by Ethicon here: https://www.jnjmedtech.com/en-US/product/surgical-stainless-steel-suture
TABLE A-3 Properties of common liquids, solids, and foods (Concluded) (b) Solids (values are for room temperature unless indicated otherwise) Substance Density, p kg/m Specific heat, c, kJ/kg.K Density, Substance p kg/m Specific heat, c, kJ/kg.K Metals Nonmetals Aluminum Asphalt 2110 0.920 200 K 0.797 Brick, common 1922 0.79 250 K 0.859 Brick, fireclay (500C) 2300 0.960 300 K 2,700 0.902 Concrete 2300 0.653 350 K 0.929 Clay 1000 0.920 400 K 0.949 Diamond 2420 0.616 450 K 0.973 Glass, window 2700 0.800 500 K 0.997 Glass, pyrex 2230 0.840 Bronze (76% Cu, 2% Zn, 2% Al) 8,280 0.400 Graphite 2500 0.711 Granite 2700 1.017 Brass, yellow (65% Cu, 35% Zn) 8,310 0.400 Gypsum or plaster board 800 1.09 Ice Copper 200 K 1.56 -173C 0.254 220 K 1.71 -100C 0.342 240 K 1.86 -50C 0.367 260 K 2.01 0C 0.381 273 K 921 2.11 27C 8,900 0.386 Limestone 1650 0.909 100C 0.393 Marble 2600 0.880 200C 0.403 Plywood (Douglas Fir) 545 1.21 Iron 7,840 0.45 Rubber (soft) 1100 1.840 Lead 11,310 0.128 Rubber (hard) 1150 2.009 Magnesium 1,730 1.000 Sand 1520 0.800 Nickel 8,890 0.440 Stone 1500 0.800 Silver 10,470 0.235 Woods, hard (maple, oak, etc.) 721 1.26 Steel, mild 7,830 0.500 Woods, soft (fir, pine, etc.) 513 1.38 Tungsten 19,400 0.130 (c) Foods Water Specific heat, kJ/kg.K Latent heat of Water content, Freezing Above Below fusion, content, Freezing Specific heat, kJ/kg.K Above Below Latent heat of fusion, Food % (mass) point, C freezing freezing kJ/kg Food % (mass) point, C freezing freezing kJ/kg Apples Bananas Beef round Broccoli Butter Cheese, swiss 39 Cherries Chicken Corn, sweet Eggs, whole Ice cream 21626 207773 84 -1.1 3.65 1.90 281 Lettuce 95 -0.2 4.02 2.04 317 75 -0.8 3.35 1.78 251 Milk, whole 88 -0.6 3.79 1.95 294 67 3.08 1.68 224 Oranges 87 -0.8 3.75 1.94 291 90 -0.6 3.86 1.97 301 Potatoes 78 -0.6 3.45 1.82 261 1.04 53 Salmon fish 64 -2.2 2.98 1.65 214 -10.0 2.15 1.33 130 Shrimp 80 -1.8 3.52 1.85 267 Spinach 74 -2.8 3.32 1.77 247 Strawberries 74 -0.6 3.32 1.77 247 Tomatoes, ripe 74 -0.6 3.32 1.77 247 Turkey 63 -5.6 2.95 1.63 210 Watermelon 332113 83 -2.2 3.62 1.89 277 93 -0.3 3.96 2.01 311 90 -0.8 3.86 1.97 301 94 -0.5 3.99 2.02 314 64 2.98 1.65 214 93 -0.4 3.96 2.01 311
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it
Step: 1

See step-by-step solutions with expert insights and AI powered tools for academic success
Step: 2

Step: 3

Ace Your Homework with AI
Get the answers you need in no time with our AI-driven, step-by-step assistance
Get Started


