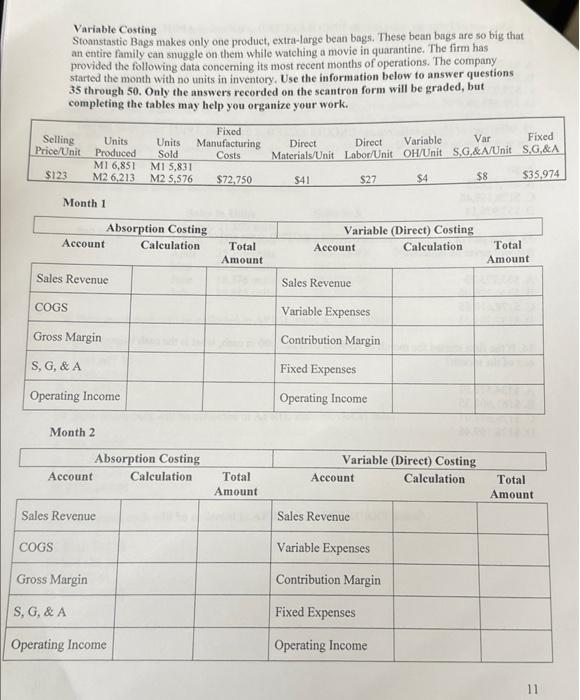
41. Calculate the S,G,\&A under ABSORPTION COSTING in MONTH 2. A. $80,322.07 B. $85,426,07 C. $80,582,00 D. $76,893.70 42. Calculate the TOTAL VARIABLE EXPENSE under VARIABLE costing in MONTH 2. A. $466,480 B. $428,872 C. $446,080 D. $77,112 43. Calculate the TOTAL FIXED EXPENSE under VARIABLE costing in MONTH 2 A. $101,963.29 B. $105,035.70 C. $96,607.36 D. $108,724.00 44. Calculate the OPERATING INCOME under ABSORPTION COSTING for MONTH 2. A. $137,804.71 B. $144,576.88 C. $131,044.00 D. $138,499.04 45. Calculate the OPERATING INCOME under VARIABLE COSTING for MONTH 2. A. $131,044.00 B. $137,804.71 C. $144,576.88 D. $138,499.04 46. Calculate the number of units in ending inventory at the end of MONTH 2. A. 1020 units B. 1275 units C. 637 units D. 1657 units Variable Costing Stoanstastic Bags makes only one product, extra-large bean bags. These bean bags are so big that an entire family can snuggle on them while watching a movie in quarantine. The firm has provided the following data conceming its most recent months of operations. The company started the month with no units in inventory. Use the information below to answer questions 35 through 50 . Only the answers recorded on the scantron form will be graded, but completing the tables may help you organize your work. Month 1 Month 2 47. Calculate the change in units of inventory during MONTH 2. A. 4,556 units B. 1020 units C. 637 units D. 1657 units 48. What is the formula to reconcile the difference in Month 2 operating income when using absorption versus variable costing? A. ( UnitsInventory During Month 2 Month1FOH/unit) B. ( UnitsInventory During Month 1 Month1FOH/unit) C. ( UnitsInventory During Month 1 Month2FOH/unit) D. ( UnitsInventory During Month 2 Month2FOH/unit) 49. The difference in operating income under these two methods is caused by: A. A difference in the way we expense fixed manufacturing OH. B. A difference in the way we expense variable manufacturing OH. C. A difference in the way we expense fixed S,G, \& A. D. A difference in the way we expense variable S, G, \& A. 50. If a firm produces more units than it sells during the period then which of the following is true: A. Absorption Costing Income = Variable Costing Income B. Absorption Costing Income Variable Costing Income D. There is not enough information to determine the direction of income difference. Round ALL calculations to the nearest hundredth (two decimal places). 35. Calculate the FOH/unit in MONTH 1 under ABSORPTION COSTING. A. $13,05 /unit B. $10.62 unit C. $11.71 /unit D. $12,48 /unit 36. Calculate the FOH/unit in MONTH 2 under ABSORPTION COSTING. A. $10.62 /unit B. $12.48 /unit C. $13.05 /unit D. $11.71 /unit 37. Calculate the UNIT PRODUCT COST under ABSORPTION COSTING in MONTH 2. A. $83.71 /unit B. $82.62 /unit C. $72.00 /unit D. $85.05 /unit 38. Calculate the UNIT PRODUCT COST under VARIABLE COSTING in MONTH 2. A. $72.00 /unit B. $83.71 /unit C. $85.05 hunit D. $82.62 /unit 39. Calculate the SALES REVENUE in MONTH 2 A. $764,199 B. $685,848 C. $717,213 D. $560,388 40. Calculate the COGS under ABSORPTION COSTING in MONTH 2. A. $466,766,96 B. $81,521.12 C. $485,126.96 D. $444,462.96