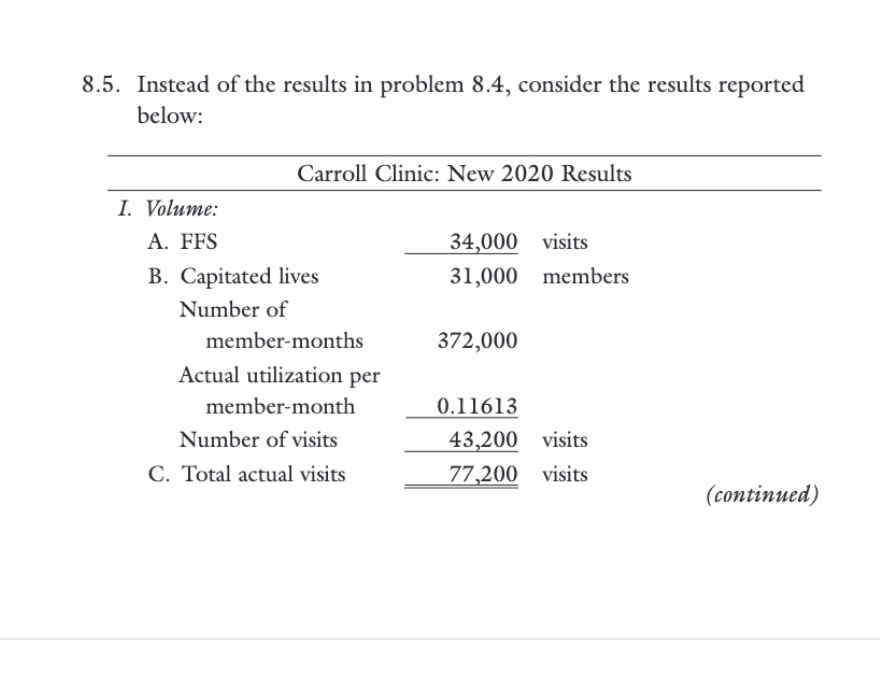


.5. Instead of the results in problem 8.4 , consider the results reported below: II. Revenues: A. FFS B. Capitated lives 372,000 actual member-months C. Total actual revenues $1,975,000 III. Costs: A. Variable Costs: Labor $1,242,000(46,000 hours at $27 /hour ) Supplies 126,000(90,000 units at $1.40/ unit) Total variable costs $1,368,000 Variable cost per visit $17.72($1,368,00077,200) B. Fixed Costs: Overhead, plant, and equipment $525,000 C. Total actual costs $1,893,000 IV. Profit and Loss Statement: Revenues: Costs: Variable: FFS $602,487 Contribution margin $607,000 Assume the results reported in problem 8.4 hold, except that a difference existed among budgeted (static) enrollment and realized enrollment. The corrected results are presented above. a. Construct Carroll's flexible budgets for 2020. (Hint: Because of a change in enrollment, creating three flexible budgets is necessary. See the note to exhibit 8.7.) b. What are the profit variance, revenue variance, and cost variance? penski's Healthcare Finance c. Focus on the revenue side. What is the volume variance? The price variance? Break the volume variance into enrollment and utilization components. How does your answer here differ from your corresponding answer to problem 8.4 ? d. Now consider the cost side. What are the volume and management variances? Break down the management variance into labor, supplies, and fixed costs variances. e. Interpret your results. In particular, focus on the differences between the variance analysis here and the one in problem 8.4. .5. Instead of the results in problem 8.4 , consider the results reported below: II. Revenues: A. FFS B. Capitated lives 372,000 actual member-months C. Total actual revenues $1,975,000 III. Costs: A. Variable Costs: Labor $1,242,000(46,000 hours at $27 /hour ) Supplies 126,000(90,000 units at $1.40/ unit) Total variable costs $1,368,000 Variable cost per visit $17.72($1,368,00077,200) B. Fixed Costs: Overhead, plant, and equipment $525,000 C. Total actual costs $1,893,000 IV. Profit and Loss Statement: Revenues: Costs: Variable: FFS $602,487 Contribution margin $607,000 Assume the results reported in problem 8.4 hold, except that a difference existed among budgeted (static) enrollment and realized enrollment. The corrected results are presented above. a. Construct Carroll's flexible budgets for 2020. (Hint: Because of a change in enrollment, creating three flexible budgets is necessary. See the note to exhibit 8.7.) b. What are the profit variance, revenue variance, and cost variance? penski's Healthcare Finance c. Focus on the revenue side. What is the volume variance? The price variance? Break the volume variance into enrollment and utilization components. How does your answer here differ from your corresponding answer to problem 8.4 ? d. Now consider the cost side. What are the volume and management variances? Break down the management variance into labor, supplies, and fixed costs variances. e. Interpret your results. In particular, focus on the differences between the variance analysis here and the one in problem 8.4









