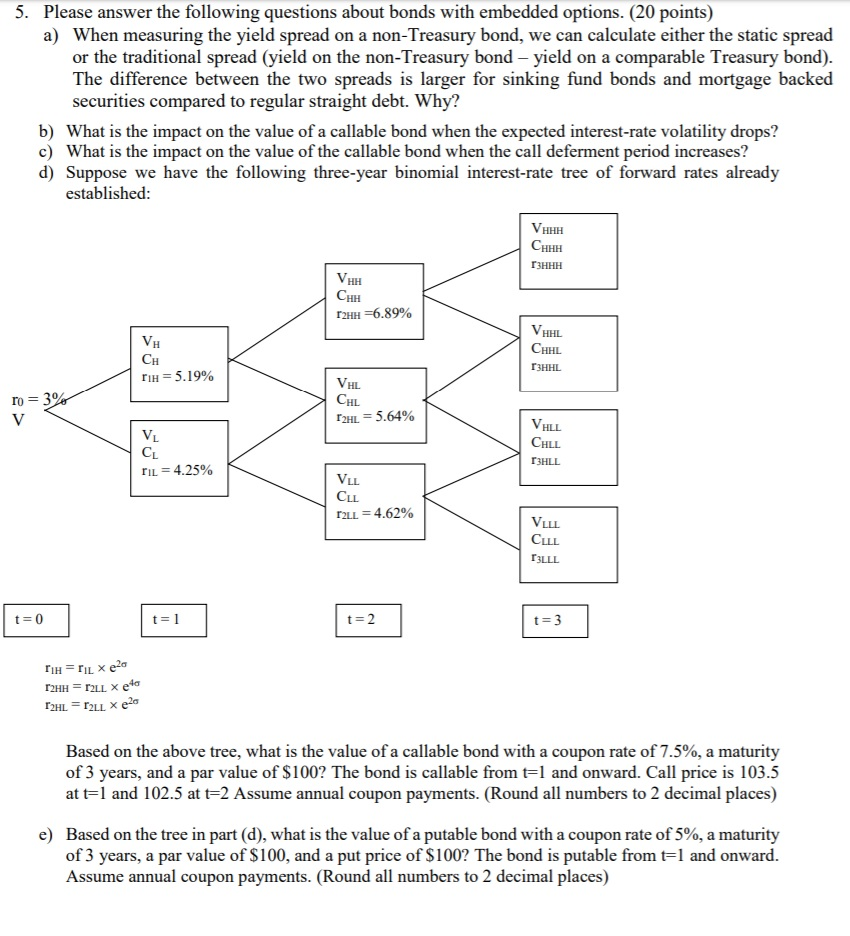
5. Please answer the following questions about bonds with embedded options. (20 points) a) When measuring the yield spread on a non-Treasury bond, we can calculate either the static spread or the traditional spread (yield on the non-Treasury bond - yield on a comparable Treasury bond). The difference between the two spreads is larger for sinking fund bonds and mortgage backed securities compared to regular straight debt. Why? b) What is the impact on the value of a callable bond when the expected interest-rate volatility drops? c) What is the impact on the value of the callable bond when the call deferment period increases? d) Suppose we have the following three-year binomial interest-rate tree of forward rates already established: VHHH CHHH 3HHH VAH CHH r2HH-6.89% VHAL CHHL CH 13HHL rih = 5.19% VHL CHL ro = 3 V r2HL = 5.64% VALL CHLL [3HLL TIL = 4.25% VLL CLL r2LL = 4.62% VILL CLLL T3LLL t=3 TH=riL x 20 T2HH = TALL X etc T2HL = r2LL X e26 Based on the above tree, what is the value of a callable bond with a coupon rate of 7.5%, a maturity of 3 years, and a par value of $100? The bond is callable from t=l and onward. Call price is 103.5 at t=1 and 102.5 at t=2 Assume annual coupon payments. (Round all numbers to 2 decimal places) e) Based on the tree in part (d), what is the value of a putable bond with a coupon rate of 5%, a maturity of 3 years, a par value of $100, and a put price of $100? The bond is putable from t=1 and onward. Assume annual coupon payments. (Round all numbers to 2 decimal places) 5. Please answer the following questions about bonds with embedded options. (20 points) a) When measuring the yield spread on a non-Treasury bond, we can calculate either the static spread or the traditional spread (yield on the non-Treasury bond - yield on a comparable Treasury bond). The difference between the two spreads is larger for sinking fund bonds and mortgage backed securities compared to regular straight debt. Why? b) What is the impact on the value of a callable bond when the expected interest-rate volatility drops? c) What is the impact on the value of the callable bond when the call deferment period increases? d) Suppose we have the following three-year binomial interest-rate tree of forward rates already established: VHHH CHHH 3HHH VAH CHH r2HH-6.89% VHAL CHHL CH 13HHL rih = 5.19% VHL CHL ro = 3 V r2HL = 5.64% VALL CHLL [3HLL TIL = 4.25% VLL CLL r2LL = 4.62% VILL CLLL T3LLL t=3 TH=riL x 20 T2HH = TALL X etc T2HL = r2LL X e26 Based on the above tree, what is the value of a callable bond with a coupon rate of 7.5%, a maturity of 3 years, and a par value of $100? The bond is callable from t=l and onward. Call price is 103.5 at t=1 and 102.5 at t=2 Assume annual coupon payments. (Round all numbers to 2 decimal places) e) Based on the tree in part (d), what is the value of a putable bond with a coupon rate of 5%, a maturity of 3 years, a par value of $100, and a put price of $100? The bond is putable from t=1 and onward. Assume annual coupon payments. (Round all numbers to 2 decimal places)







