
#5
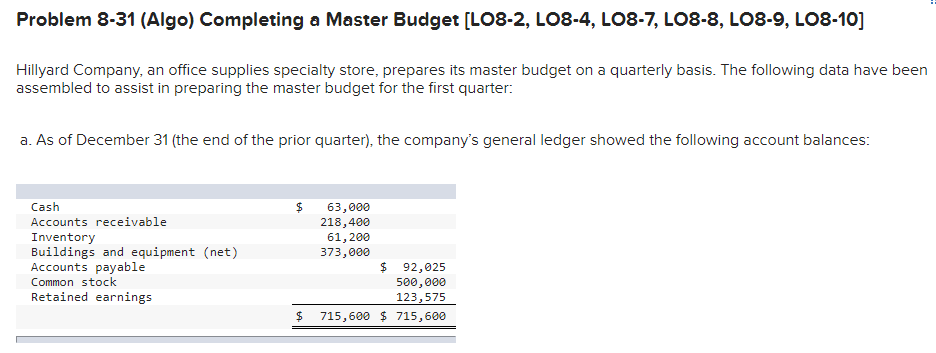


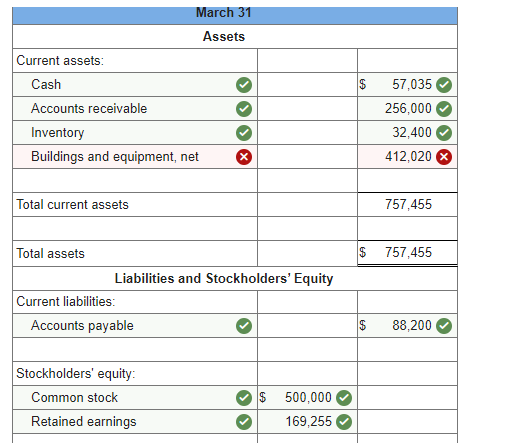
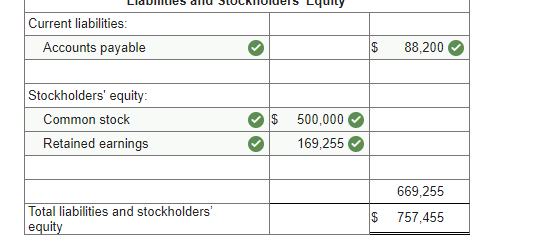
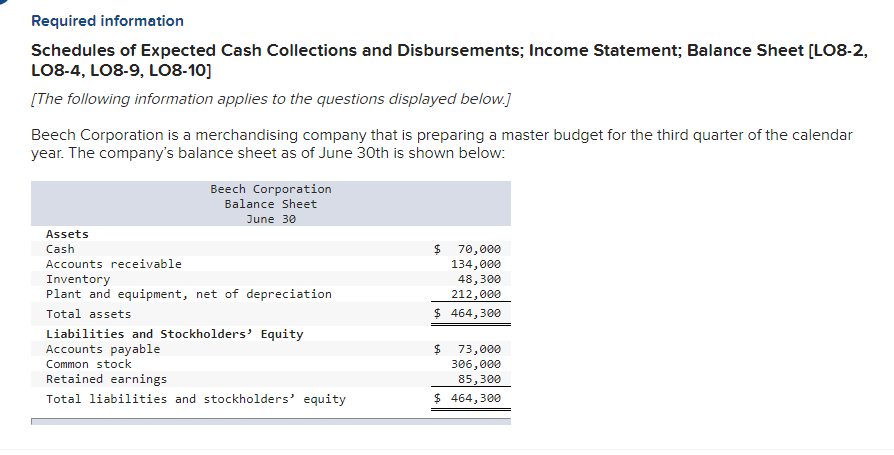
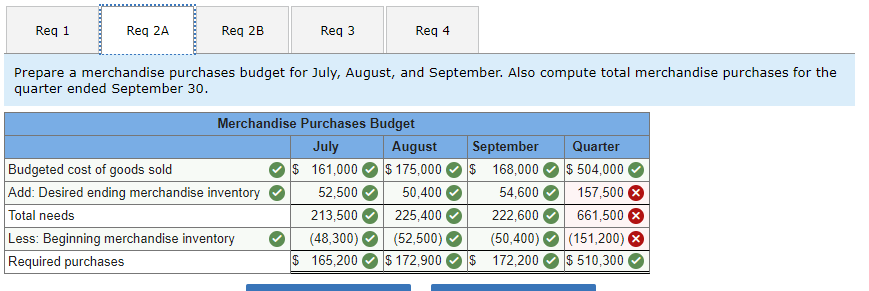
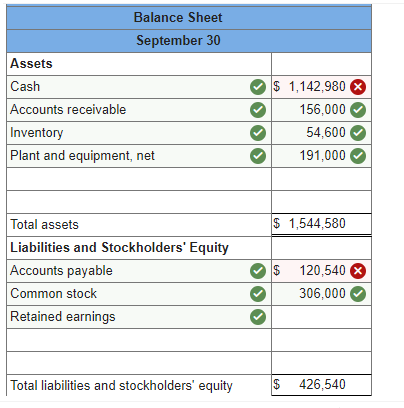
Required information Schedules of Expected Cash Collections and Disbursements; Income Statement; Balance Sheet [LO8-2, LO8-4, LO8-9, LO8-10] [The following information applies to the questions displayed below.) Beech Corporation is a merchandising company that is preparing a master budget for the third quarter of the calendar year. The company's balance sheet as of June 30th is shown below: Beech Corporation Balance Sheet June 30 Assets Cash Accounts receivable Inventory Plant and equipment, net of depreciation Total assets Liabilities and Stockholders' Equity Accounts payable Common stock Retained earnings Total liabilities and stockholders' equity 70,000 134,000 48,300 212,000 464,300 $ 73,000 306,000 85,300 $ 464,300 Exercise 8-12 (Algo) Beech's managers have made the following additional assumptions and estimates: 1. Estimated sales for July, August September, and October will be $230,000, $250,000, $240,000, and $260,000, respectively. 2. All sales are on credit and all credit sales are collected. Each month's credit sales are collected 35% in the month of sale and 65% in the month following the sale. All of the accounts receivable at June 30 will be collected in July. 3. Each month's ending inventory must equal 30% of the cost of next month's sales. The cost of goods sold is 70% of sales. The company pays for 40% of its merchandise purchases in the month of the purchase and the remaining 60% in the month following the purchase. All of the accounts payable at June 30 will be paid in July. 4. Monthly selling and administrative expenses are always $42,000. Each month $7,000 of this total amount is depreciation expense and the remaining $35,000 relates to expenses that are paid in the month they are incurred. 5. The company does not plan to borrow money or pay or declare dividends during the quarter ended September 30. The company does not plan to issue any common stock or repurchase its own stock during the quarter ended September 30. Required: 1. Prepare a schedule of expected cash collections for July, August, and September. 2-a. Prepare a merchandise purchases budget for July, August, and September. Also compute total merchandise purchases for the quarter ended September 30. 2-b. Prepare a schedule of expected cash disbursements for merchandise purchases for July, August, and September. 3. Prepare an income statement that computes net operating income for the quarter ended September 30. 4. Prepare a balance sheet as of September 30. Req 1 Reg 2A Reg 2B Req3 Req 4 Prepare a merchandise purchases budget for July, August, and September. Also compute total merchandise purchases for the quarter ended September 30. Merchandise Purchases Budget July August Budgeted cost of goods sold $ 161,000 $ 175,000 Add: Desired ending merchandise inventory 52,500 50,400 Total needs 213,500 225,400 Less: Beginning merchandise inventory (48,300) (52,500) Required purchases $ 165,200 $ 172,900 September $ 168,000 54,600 222,600 (50,400) $ 172,200 Quarter $ 504,000 157,500 661,500 (151,200) $ 510,300 Balance Sheet September 30 Assets Cash Accounts receivable Inventory Plant and equipment, net $ 1,142,980 156,000 54,600 191,000 $ 1,544,580 Total assets Liabilities and Stockholders' Equity Accounts payable Common stock Retained earnings $ 120,540 306,000 Total liabilities and stockholders' equity $ 426,540 Problem 8-31 (Algo) Completing a Master Budget (LO8-2, LO8-4, LO8-7, LO8-8, LO8-9, LO8-10] Hillyard Company, an office supplies specialty store, prepares its master budget on a quarterly basis. The following data have been assembled to assist in preparing the master budget for the first quarter: a. As of December 31 (the end of the prior quarter), the company's general ledger showed the following account balances: $ Cash Accounts receivable Inventory Buildings and equipment (net) Accounts payable Common stock Retained earnings 63,000 218,400 61,200 373,000 $ 92,025 500,000 123,575 715,600 $ 715,600 $ b. Actual sales for December and budgeted sales for the next four months are as follows: December (actual) January February $ 273,000 $ 408,000 $ 605,000 $ 320,000 $ 216,000 March April c. Sales are 20% for cash and 80% on credit. All payments on credit sales are collected in the month following sale. The accounts receivable at December 31 are a result of December credit sales. d. The company's gross margin is 40% of sales. (In other words, cost of goods sold is 60% of sales.) e. Monthly expenses are budgeted as follows: salaries and wages, $38,000 per month: advertising, $58,000 per month; shipping, 5% of sales; other expenses, 3% of sales. Depreciation, including depreciation on new assets acquired during the quarter, will be $45,780 for the quarter. f. Each month's ending inventory should equal 25% of the following month's cost of goods sold. g. One-half of a month's inventory purchases is paid for in the month of purchase; the other half is paid in the following month. h. During February, the company will purchase a new copy machine for $3,300 cash. During March, other equipment will be purchased for cash at a cost of $81,500. i. During January, the company will declare and pay $45,000 in cash dividends. j. Management wants to maintain a minimum cash balance of $30,000. The company has an agreement with a local bank that allows the company to borrow in increments of $1,000 at the beginning of each month. The interest rate on these loans is 1% per month and for simplicity we will assume that interest is not compounded. The company would, as far as it is able, repay the loan plus accumulated interest at the end of the quarter. Required: Using the data above, complete the following statements and schedules for the first quarter: 1. Schedule of expected cash collections: 2-a. Merchandise purchases budget: 2-b. Schedule of expected cash disbursements for merchandise purchases: 3. Cash budget: 4. Prepare an absorption costing income statement for the quarter ending March 31. 5. Prepare a balance sheet as of March 31. March 31 Assets Current assets: Cash Accounts receivable Inventory Buildings and equipment, net $ O 57,035 256,000 32,400 412,020 >IX Total current assets 757,455 $ 757,455 Total assets Liabilities and Stockholders' Equity Current liabilities: Accounts payable $ 88,200 Stockholders' equity Common stock Retained earnings $ 500,000 169,255 Current liabilities: Accounts payable $ 88,200 Stockholders' equity Common stock Retained earnings $ 500,000 169,255 669,255 Total liabilities and stockholders' equity $ 757,455















