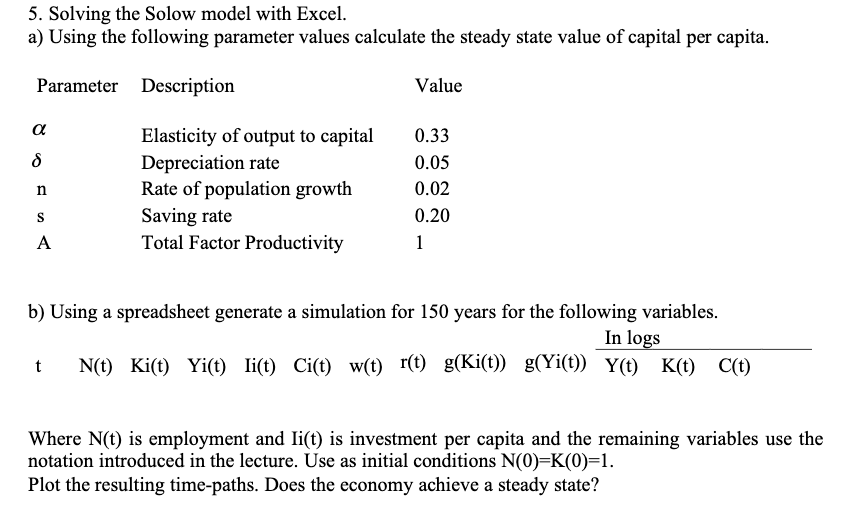

5. Solving the Solow model with Excel. a) Using the following parameter values calculate the steady state value of capital per capita. Parameter Description Value a 8 n Elasticity of output to capital Depreciation rate Rate of population growth Saving rate Total Factor Productivity 0.33 0.05 0.02 0.20 1 S A b) Using a spreadsheet generate a simulation for 150 years for the following variables. In logs t N(t) Ki(t) Yit) li(t) Cit) f(t) f(t) g(Kit)) g(Yi(t)) Yt) Kt) C(t) Where N(t) is employment and lit) is investment per capita and the remaining variables use the notation introduced in the lecture. Use as initial conditions N(O)=K(0)=1. Plot the resulting time-paths. Does the economy achieve a steady state? c) Consider the effects of an increase in the saving rate, from 20% to 60%. Plot the resulting time- paths, assuming the economy remains in the steady state described in b) for the first 10 periods and then the change in saving occurs. Does the change in saving have any permanent effects in the growth rates of the economy? Does it have permanent effects on the levels of capital and production? d) Repeat the same exercise changing the saving rate from 20% to 10%. What is the golden rule level of saving? Explain the evolution of consumption in this and the previous case (comparing then with the benchmark of a 20% saving rate). 5. Solving the Solow model with Excel. a) Using the following parameter values calculate the steady state value of capital per capita. Parameter Description Value a 8 n Elasticity of output to capital Depreciation rate Rate of population growth Saving rate Total Factor Productivity 0.33 0.05 0.02 0.20 1 S A b) Using a spreadsheet generate a simulation for 150 years for the following variables. In logs t N(t) Ki(t) Yit) li(t) Cit) f(t) f(t) g(Kit)) g(Yi(t)) Yt) Kt) C(t) Where N(t) is employment and lit) is investment per capita and the remaining variables use the notation introduced in the lecture. Use as initial conditions N(O)=K(0)=1. Plot the resulting time-paths. Does the economy achieve a steady state? c) Consider the effects of an increase in the saving rate, from 20% to 60%. Plot the resulting time- paths, assuming the economy remains in the steady state described in b) for the first 10 periods and then the change in saving occurs. Does the change in saving have any permanent effects in the growth rates of the economy? Does it have permanent effects on the levels of capital and production? d) Repeat the same exercise changing the saving rate from 20% to 10%. What is the golden rule level of saving? Explain the evolution of consumption in this and the previous case (comparing then with the benchmark of a 20% saving rate)








