Question: 5. The following case study is found in the main text book posted as an ebook on Moodle. Read the examples in the book
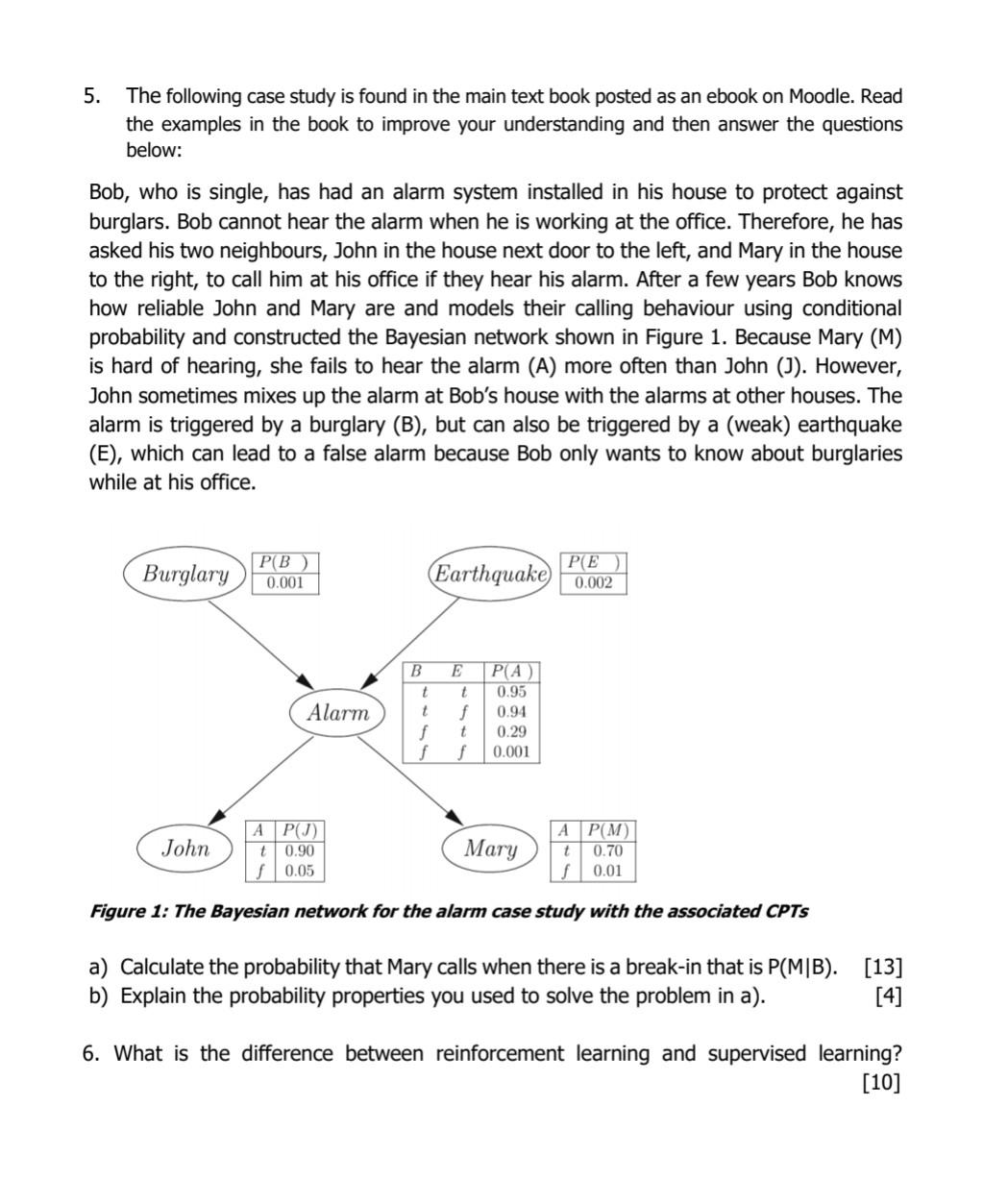
5. The following case study is found in the main text book posted as an ebook on Moodle. Read the examples in the book to improve your understanding and then answer the questions below: Bob, who is single, has had an alarm system installed in his house to protect against burglars. Bob cannot hear the alarm when he is working at the office. Therefore, he has asked his two neighbours, John in the house next door to the left, and Mary in the house to the right, to call him at his office if they hear his alarm. After a few years Bob knows how reliable John and Mary are and models their calling behaviour using conditional probability and constructed the Bayesian network shown in Figure 1. Because Mary (M) is hard of hearing, she fails to hear the alarm (A) more often than John (J). However, John sometimes mixes up the alarm at Bob's house with the alarms at other houses. The alarm is triggered by a burglary (B), but can also be triggered by a (weak) earthquake (E), which can lead to a false alarm because Bob only wants to know about burglaries while at his office. Burglary P(B) 0.001 John Alarm A P(E Earthquake 0.002 B P(A) t t 0.95 t f 0.94 f t 0.29 f f 0.001 E A P(J) 0.90 t t 0.70 f 0.01 f 0.05 Figure 1: The Bayesian network for the alarm case study with the associated CPTS P(M) Mary a) Calculate the probability that Mary calls when there is a break-in that is P(MIB). b) Explain the probability properties you used to solve the problem in a). [13] [4] 6. What is the difference between reinforcement learning and supervised learning? [10] 5. The following case study is found in the main text book posted as an ebook on Moodle. Read the examples in the book to improve your understanding and then answer the questions below: Bob, who is single, has had an alarm system installed in his house to protect against burglars. Bob cannot hear the alarm when he is working at the office. Therefore, he has asked his two neighbours, John in the house next door to the left, and Mary in the house to the right, to call him at his office if they hear his alarm. After a few years Bob knows how reliable John and Mary are and models their calling behaviour using conditional probability and constructed the Bayesian network shown in Figure 1. Because Mary (M) is hard of hearing, she fails to hear the alarm (A) more often than John (J). However, John sometimes mixes up the alarm at Bob's house with the alarms at other houses. The alarm is triggered by a burglary (B), but can also be triggered by a (weak) earthquake (E), which can lead to a false alarm because Bob only wants to know about burglaries while at his office. Burglary P(B) 0.001 John Alarm A P(E Earthquake 0.002 B P(A) t t 0.95 t f 0.94 f t 0.29 f f 0.001 E A P(J) 0.90 t t 0.70 f 0.01 f 0.05 Figure 1: The Bayesian network for the alarm case study with the associated CPTS P(M) Mary a) Calculate the probability that Mary calls when there is a break-in that is P(MIB). b) Explain the probability properties you used to solve the problem in a). [13] [4] 6. What is the difference between reinforcement learning and supervised learning? [10]
Step by Step Solution
3.38 Rating (160 Votes )
There are 3 Steps involved in it
To calculate the probability that Mary calls when there is a breakin denoted as PMB we need to take into account not only the direct effect of the bur... View full answer

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


