Answered step by step
Verified Expert Solution
Question
1 Approved Answer
5.05.2. Bellman-Ford algorithm (2. part 2). Consider the scenario shown below. The figure below shows the (old) DV ate (before receiving the new DWs
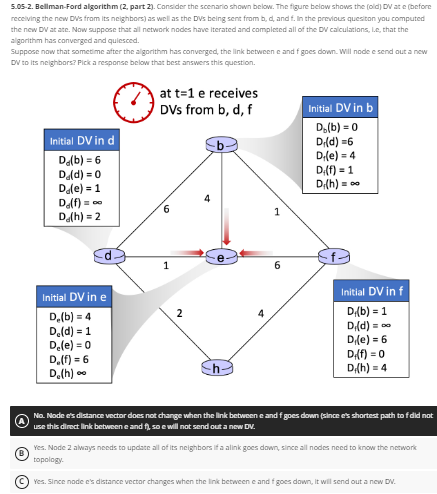
5.05.2. Bellman-Ford algorithm (2. part 2). Consider the scenario shown below. The figure below shows the (old) DV ate (before receiving the new DWs from its neighbors) as well as the DVs being sent from b, d, and f. In the previous quesiton you computed the new DV at ate. Now suppose that all network nodes have iterated and completed all of the DV calculations, le, that the algorithm has converged and quiesced. Suppose now that sometime after the algorithm has converged, the link between e and f goes down. Will node e send out a new DV to its neighbors? Pick a response below that best answers this question. (3) Initial DV in d D.(b) = 6 Du(d)=0 Dule) = 1 De(f)= 0 D (h) = 2 Initial DV in e D.(b) = 4 D.(d) = 1 De(e) = 0 D(f)= 6 D. (h) at t=1 e receives DVs from b, d, f 1 2 4 6 Initial DV in b D(b)=0 D,(d)=6 Di(e) = 4 D; (f)= 1 Di(h) = Initial DV in f D.(b) = 1 D,(d) Di(e) = 6 D.(f) = 0 D.(h) = 4 No. Node e's distance vector does not change when the link between e and f goes down (since e's shortest path tof did not use this direct link between e and f, soe will not send out a new DV. Yes. Node 2 always needs to update all of its neighbors if a alink goes down, since all nodes need to know the network topology. Yes. Since node e's distance vector changes when the link between e and f goes down, it will send out a new DV. 5.05-2. Bellman-Ford algorithm (2, part 2). Consider the scenario shown below. The figure below shows the (old) DV at e (before receiving the new DVs from its neighbors) as well as the DVS being sent from b, d, and f. In the previous quesiton you computed the new DV at ate. Now suppose that all network nodes have iterated and completed all of the DV calculations, le, that the algorithm has converged and quiesced. Suppose now that sometime after the algorithm has converged, the link between e and f goes down. Will node e send out a new DV to its neighbors? Pick a response below that best answers this question. (3) Initial DV in d D.(b) = 6 Du(d) = 0 Dole) = 1 Do(f) = D (h) = 2 Initial DV in e D.(b) = 4 D.(d) = 1 De(e) = 0 D(f) = 6 D. (h) at t=1 e receives DVS from b, d, f 1 2 4 6 Initial DV in b D(b)=0 Di(d)=6 Di(e) = 4 Di(f) = 1 Di(h) = Initial DV in f D.(b) = 1 D,(d) Di(e) = 6 D.(f) = 0 D.(h) = 4 No. Node e's distance vector does not change when the link between e and f goes down (since e's shortest path tof did not use this direct link between e and f, soe will not send out a new DV. Yes. Node 2 always needs to update all of its neighbors ifa alink goes down, since all nodes need to know the network topology. Yes. Since node e's distance vector changes when the link between e and f goes down, it will send out a new DV.
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it
Step: 1
The detailed answer for the above question is provided below Solu...
Get Instant Access to Expert-Tailored Solutions
See step-by-step solutions with expert insights and AI powered tools for academic success
Step: 2

Step: 3

Ace Your Homework with AI
Get the answers you need in no time with our AI-driven, step-by-step assistance
Get Started


