Answered step by step
Verified Expert Solution
Question
1 Approved Answer
51 F1 M1 P1 12 O bar 0 SLPM FM1 0 SLPM FM2 5 ber 11 L1 R1 V1 13 0 bar v2 M2
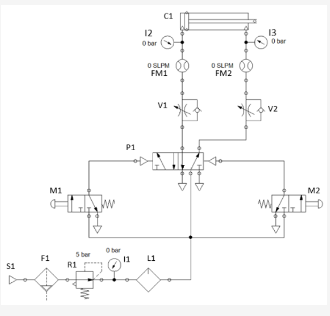
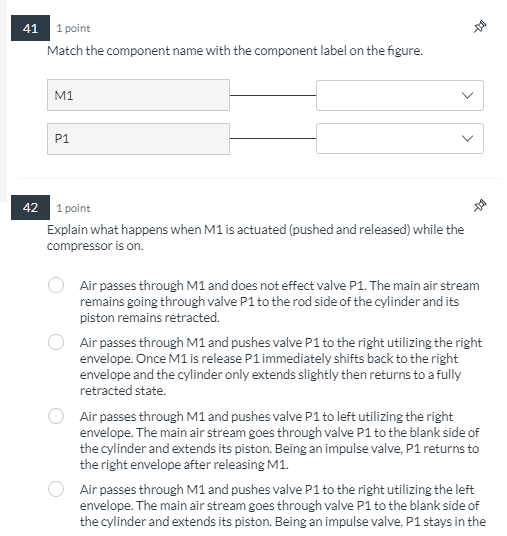



51 F1 M1 P1 12 O bar 0 SLPM FM1 0 SLPM FM2 5 ber 11 L1 R1 V1 13 0 bar v2 M2 41 1 point Match the component name with the component label on the figure. M1 P1 42 1 point Explain what happens when M1 is actuated (pushed and released) while the compressor is on. Air passes through M1 and does not effect valve P1. The main air stream remains going through valve P1 to the rod side of the cylinder and its piston remains retracted. Air passes through M1 and pushes valve P1 to the right utilizing the right envelope. Once M1 is release P1 immediately shifts back to the right envelope and the cylinder only extends slightly then returns to a fully retracted state. Air passes through M1 and pushes valve P1 to left utilizing the right envelope. The main air stream goes through valve P1 to the blank side of the cylinder and extends its piston. Being an impulse valve, P1 returns to the right envelope after releasing M1. Air passes through M1 and pushes valve P1 to the right utilizing the left envelope. The main air stream goes through valve P1 to the blank side of the cylinder and extends its piston. Being an impulse valve, P1 stays in the 43 1 point With the cylinder fully extended, what happens when M2 is actuated (pushed and released) while the compressor is on? P1 Shifts to the right and stays (utilizing the left envelope). Cylinder C1 remains fully extended. P1 Shifts to the left and stays (utilizing the right envelope). Cylinder C1 retracts fully then extends fully and stops. P1 Shifts to the left and stays (utilizing the right envelope). Cylinder C1 retracts fully and stops. Nothing happens 44 1 point Why is it possible to use a momentary Push-Button with valves M1 and M2 instead of detent (permanent) Push-Button? Because P1 needs a constant supply of air to remain actuated. Because P1 needs only an impulse of air to cause it to change positions. Because M1 and M2 are normally closed. Because M1 controls extension only and M2 controls retraction only 45 1 point Complete the following steps and then answer the questions: In the simulation software assigned by your instructor, within your Week1_Lab1_LastName_FirstName project file open a new diagram named Ex7. Build the circuit using the components shown or their equivalents. Start the simulation. What happens when M1 lever is pushed and released? C1 Extends C1 Retracts C1 Does Nothing 46 1 point What happens when M2 lever is pushed and released? C1 Extends C1 Retracts C1 Does Nothing 46 1 point What happens when M2 lever is pushed and released? C1 Extends C1 Retracts C1 Does Nothing 47 1 point Why is P1 called an impulse valve? Because its commands don't need to be permanently supplied with air to stay maintained in a position (envelope). An air impulse pushes it in a position and it stays there until pushed in the opposite direction Because its commands need to be permanently supplied with air to stay maintained in a position (envelope). An air impulse pushes it in a position and it stays there the air supply is stopped Because its reaction to any impulse that it receives both electrical and pneumatic is unpredictable. P1 is not called an impulse valve.
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it
Step: 1

Get Instant Access to Expert-Tailored Solutions
See step-by-step solutions with expert insights and AI powered tools for academic success
Step: 2

Step: 3

Ace Your Homework with AI
Get the answers you need in no time with our AI-driven, step-by-step assistance
Get Started


