Answered step by step
Verified Expert Solution
Question
1 Approved Answer
5.1 The momentum integral equation (5.10) was obtained in the text for a constant viscosity fluid. However, it is also applicable when the viscosity

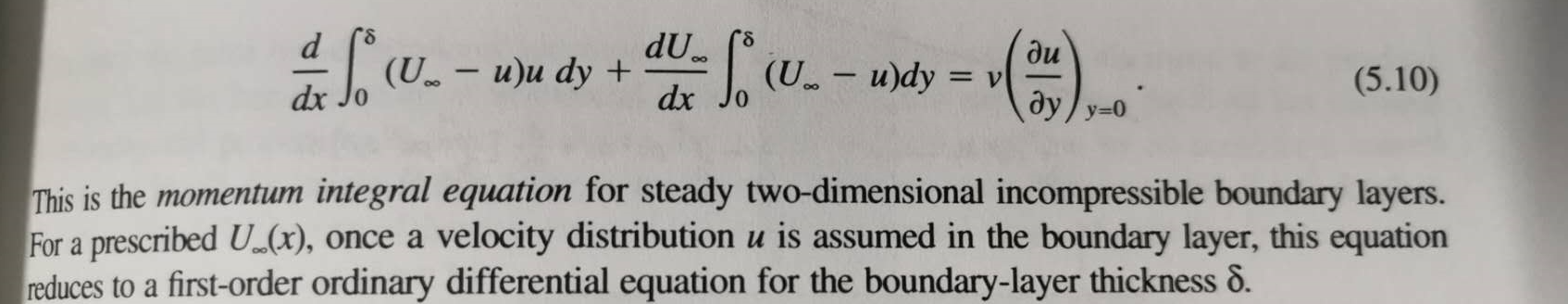
5.1 The momentum integral equation (5.10) was obtained in the text for a constant viscosity fluid. However, it is also applicable when the viscosity is variable. In that case, v in Eq. (5.10) represents the kinematic viscosity at y = 0, that is, at the wall temperature Tw. Explain. d dx fw- du.. (U.. - u)u dy + dx Ufo (U_ - u)dy = v ay y=0 (5.10) This is the momentum integral equation for steady two-dimensional incompressible boundary layers. For a prescribed U..(x), once a velocity distribution u is assumed in the boundary layer, this equation reduces to a first-order ordinary differential equation for the boundary-layer thickness d.
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it
Step: 1

Get Instant Access to Expert-Tailored Solutions
See step-by-step solutions with expert insights and AI powered tools for academic success
Step: 2

Step: 3

Ace Your Homework with AI
Get the answers you need in no time with our AI-driven, step-by-step assistance
Get Started


