Question
5.3) MATLAB Exercises 1. Extend the factorial function defined above, such that it checks for a positive input argument. 2. Write a function that calculates
5.3) MATLAB Exercises 1. Extend the factorial function defined above, such that it checks for a positive input argument. 2. Write a function that calculates a random walk trajectory based on the iteration xi+1 = xi +  , where
, where  is a uniformly distributed random variable between -1 and 1. Plot the resulting trajectory. (Please change A for
is a uniformly distributed random variable between -1 and 1. Plot the resulting trajectory. (Please change A for  in the formula in order to check previous calculus are correct it was my mistake on previous instructions) 3. Change the sorting algorithm given below such that it sorts the elements in descending order. Compare the speed of your function with the built-in MATLAB function sort.
in the formula in order to check previous calculus are correct it was my mistake on previous instructions) 3. Change the sorting algorithm given below such that it sorts the elements in descending order. Compare the speed of your function with the built-in MATLAB function sort.
4. Approximation of . The area of a circle is given by A = r^2 where r is the radius. Assume a circle with r = 0.5 embedded in a unit square. A point in the unit square is defined by p = (x,y) where 0 x,y 1. If we draw ntot times two uniformly distributed random numbers (x,y) and count how often the corresponding points falls into the circle (ncirc), we get an approximation of the circle area by ncirc tot and by that of the number . Write a function which approximates by the described method. How many draws do you need to get the rst three digits right?
Note: I forgot to put  on instructions on part 2 replace in formula of part 2 where is A for epsilon (
on instructions on part 2 replace in formula of part 2 where is A for epsilon ( ) in order to proceed to part 4 check if all previous results stay the same then proceed to part 4.
) in order to proceed to part 4 check if all previous results stay the same then proceed to part 4.
function y=calculate_factorial(n)
% check whether input argument is negative if (n1 n=n-1; y=y*n; % calculate the factorial value end end end
SCREENSHOT OF CODE:
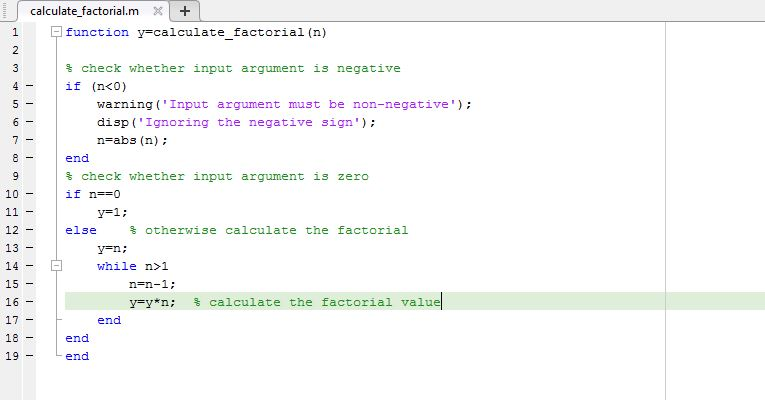
SAMPLE OUTPUT:
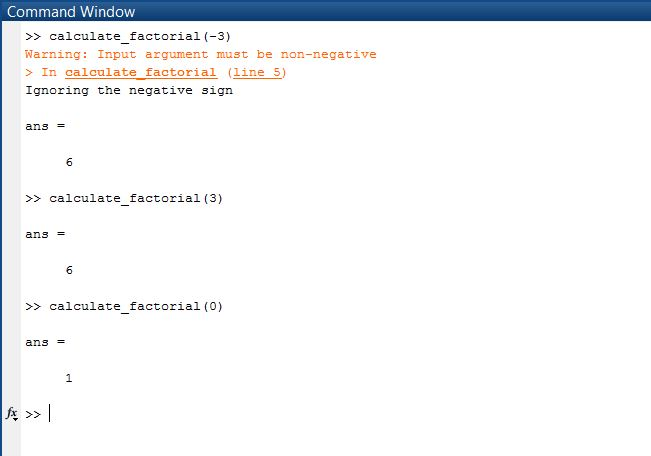
part 2)
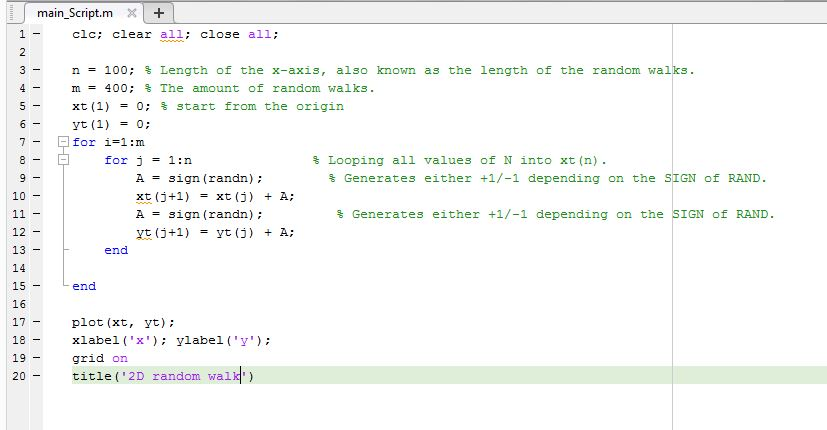
clc; clear all; close all;
n = 100; % Length of the x-axis, also known as the length of the random walks. m = 400; % The amount of random walks. xt(1) = 0; % start from the origin yt(1) = 0; for i=1:m for j = 1:n % Looping all values of N into xt(n). A = sign(randn); % Generates either +1/-1 depending on the SIGN of RAND. xt(j+1) = xt(j) + A; A = sign(randn); % Generates either +1/-1 depending on the SIGN of RAND. yt(j+1) = yt(j) + A; end end
plot(xt, yt); xlabel('x'); ylabel('y'); grid on title('2D random walk')
=============================== SCREENSHOT OF CODE
============================================ SAMPLE OUTPUT
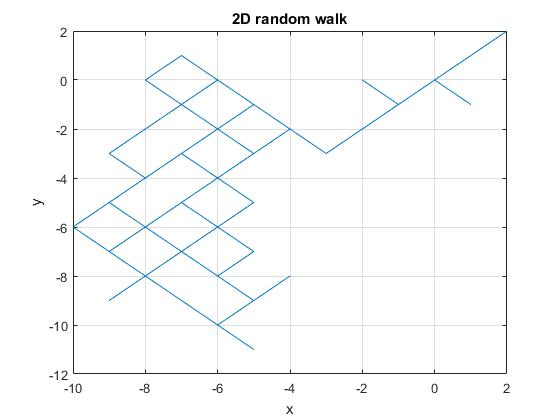
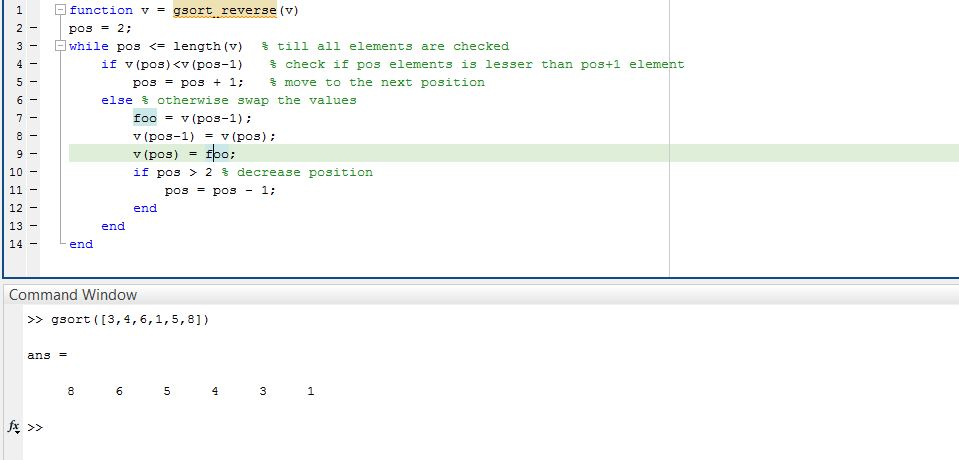
part 3 descending order
function v = gsort_reverse(v) pos = 2; while pos 2 % decrease position pos = pos - 1; end end end
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it
Step: 1

Get Instant Access to Expert-Tailored Solutions
See step-by-step solutions with expert insights and AI powered tools for academic success
Step: 2

Step: 3

Ace Your Homework with AI
Get the answers you need in no time with our AI-driven, step-by-step assistance
Get Started


