A periodic square wave m(t) (Fig. P5.4-2a) frequency-modulates a carrier of frequency fe = 10 kHz with Af = 1 kHz. The carrier amplitude
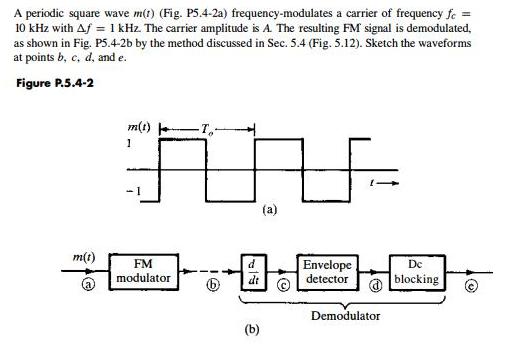
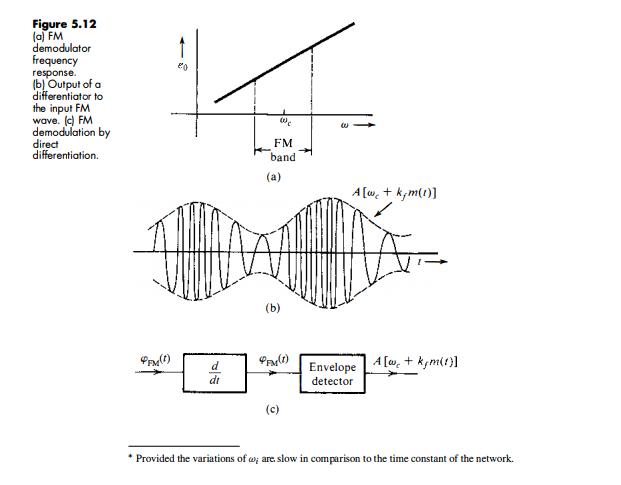
A periodic square wave m(t) (Fig. P5.4-2a) frequency-modulates a carrier of frequency fe = 10 kHz with Af = 1 kHz. The carrier amplitude is A. The resulting FM signal is demodulated, as shown in Fig. P5.4-2b by the method discussed in Sec. 5.4 (Fig. 5.12). Sketch the waveforms at points b, c, d, and e. Figure P.5.4-2 m(t) 1 (a) m(t) FM Envelope detector Dc blocking modulator dt Demodulator (b) Figure 5.12 (a) FM demodulator frequency response. (b) Output of a differentiator to the input FM wave. (c) FM demodulation by direct differentiation. FM band (a) A [w, + k,m(1)] (b) d Envelope A [w, + kym(1}] di detector * Provided the variations of w; are. slow in comparison to the time constant of the network.
Step by Step Solution
3.50 Rating (150 Votes )
There are 3 Steps involved in it
Step: 1

See step-by-step solutions with expert insights and AI powered tools for academic success
Step: 2

Step: 3

Ace Your Homework with AI
Get the answers you need in no time with our AI-driven, step-by-step assistance
Get Started


