Answered step by step
Verified Expert Solution
Question
1 Approved Answer
5:51 Score: 0/14 0/14 answered Progress saved Done o < > 48 Question 1 0/1 pt 4 Details You wish to test the following




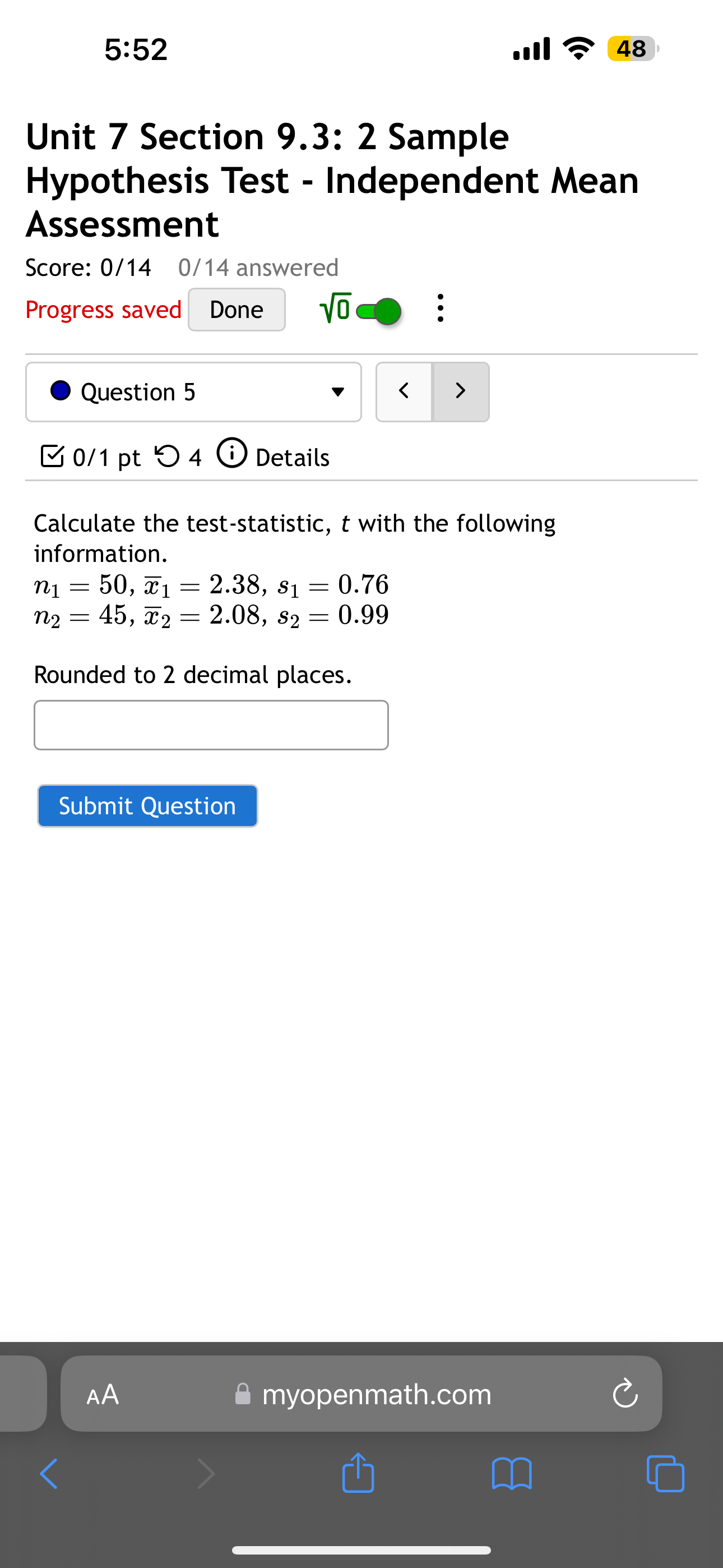
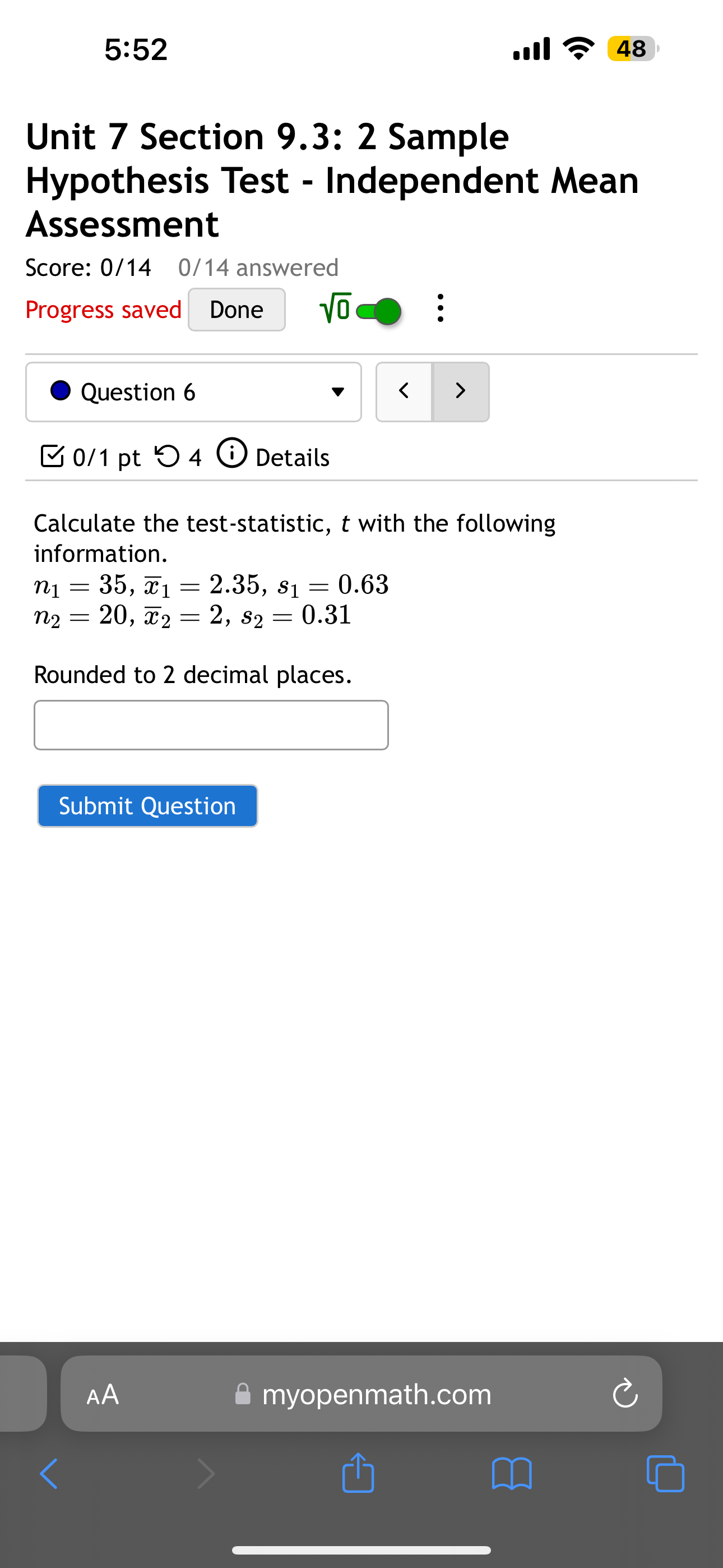

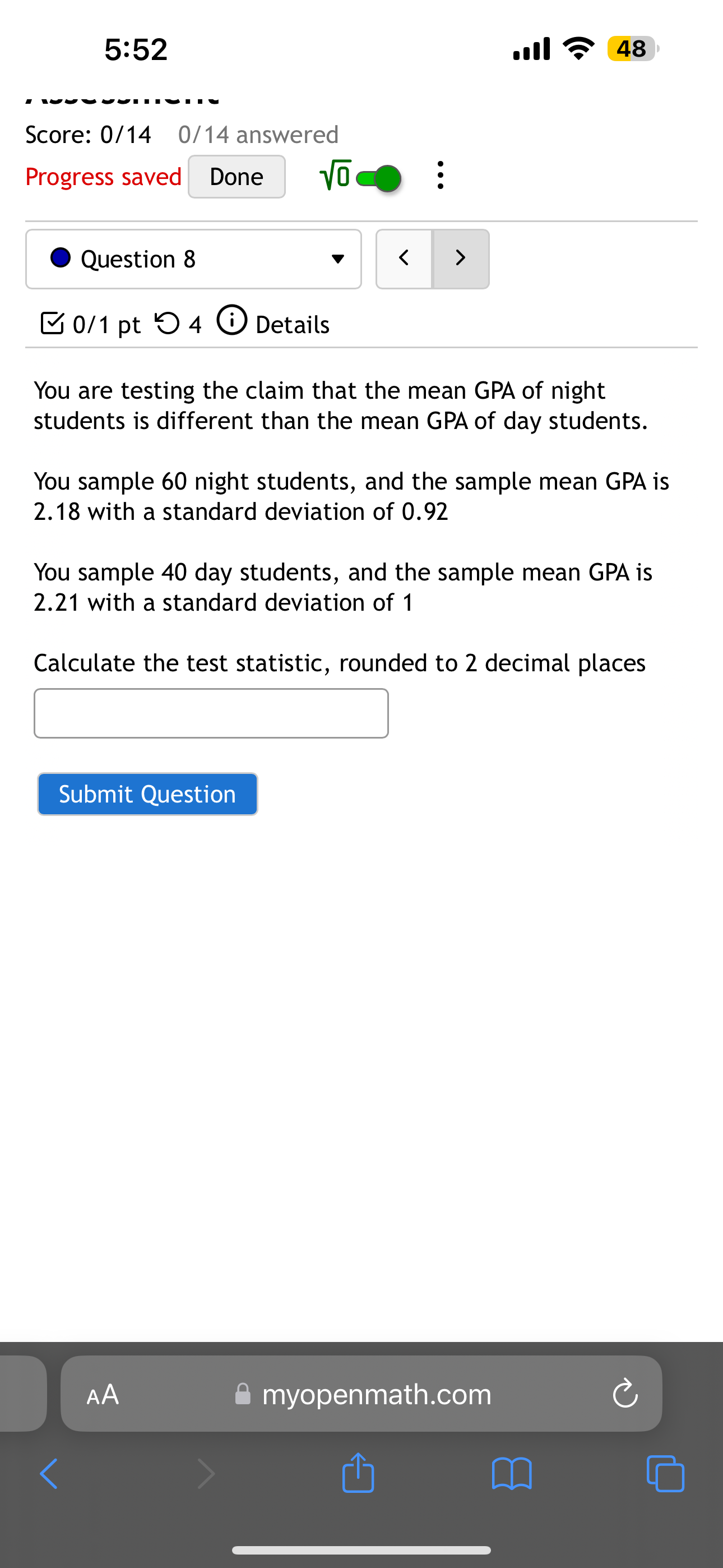

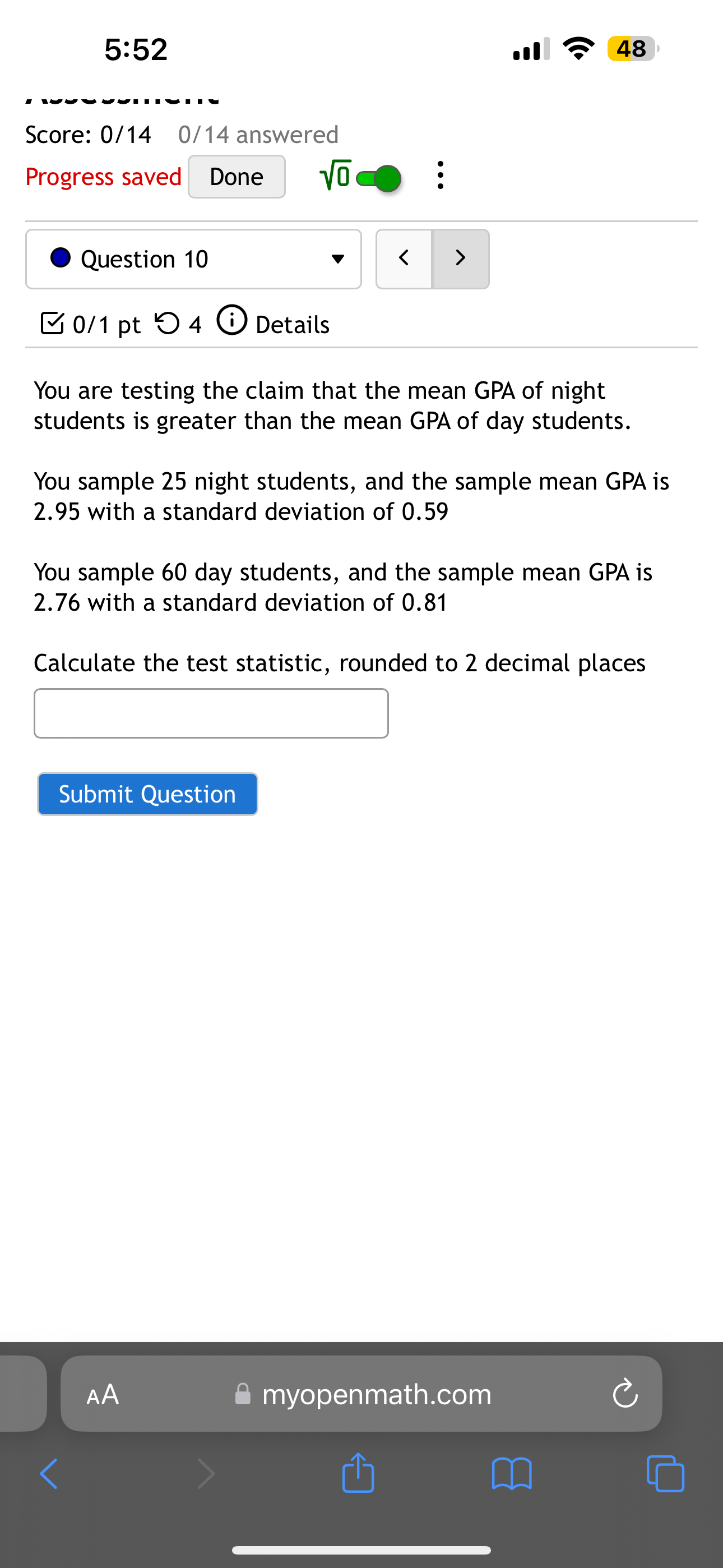




5:51 Score: 0/14 0/14 answered Progress saved Done o < > 48 Question 1 0/1 pt 4 Details You wish to test the following claim (H) at a significance level of a = 0.05. Ho:|1= |2 : < You believe both populations are normally distributed, but you do not know the standard deviations for either. However, you also have no reason to believe the variances of the two populations are not equal. You obtain a sample of size ni = 12 with a mean of M = 60.1 and a standard deviation of SD = 14.5 from the first population. You obtain a sample of size n = 24 with a mean of M = 63.6 and a standard deviation of SD2 population. M2 = 13.9 from the second What is the test statistic for this sample? (Report answer accurate to three decimal places.) test statistic = What is the p-value for this sample? For this calculation, use the conservative under-estimate for the degrees of freedom as mentioned in the textbook. (Report answer accurate to four decimal places.) p-value = The p-value is... less than (or equal to) a greater than a AA myopenmath.com 1 5:51 p-value = The p-value is... less than (or equal to) a greater than a This test statistic leads to a decision to... reject the null accept the null fail to reject the null . 48 As such, the final conclusion is that... There is sufficient evidence to warrant rejection of the claim that the first population mean is less than the second population mean. There is not sufficient evidence to warrant rejection of the claim that the first population mean is less than the second population mean. The sample data support the claim that the first population mean is less than the second population mean. There is not sufficient sample evidence to support the claim that the first population mean is less than the second population mean. Submit Question AA myopenmath.com 5:51 . 48 Test the claim that the mean GPA of night students is significantly different than the mean GPA of day students at the 0.01 significance level. The null and alternative hypothesis would be: : Ho ND Ho = N D Ho: PN PD H NMD H N> D H: PN < PD Ho: pn = pd o: D 0 : PN PD H PNPD H N PD The test is: right-tailed left-tailed two-tailed The sample consisted of 35 night students, with a sample mean GPA of 2.19 and a standard deviation of 0.03, and 35 day students, with a sample mean GPA of 2.24 and a standard deviation of 0.02. The test statistic is: decimals) The p-value is: decimals) Based on this we: Reject the null hypothesis Fail to reject the null hypothesis Submit Question myopenmath.com (to 2 (to 2 5:51 Question 3 < > . 48 0/1 pt 4 Details Test the claim that the mean GPA of night students is smaller than the mean GPA of day students at the .005 significance level. The null and alternative hypothesis would be: Ho PNPD Ho PN = PD H PN > PD H: PN 5:52 . 48 Unit 7 Section 9.3: 2 Sample Hypothesis Test - Independent Mean Assessment Score: 0/14 0/14 answered Progress saved Done Question 5 0/1 pt 4 Details < > Calculate the test-statistic, t with the following information. n = 50, x1 = 2.38, 8 = 0.76 $1 = n2 = 45, x2 = 2.08, s2 = 0.99 Rounded to 2 decimal places. Submit Question AA myopenmath.com 1 5:52 . 48 Unit 7 Section 9.3: 2 Sample Hypothesis Test - Independent Mean Assessment Score: 0/14 0/14 answered Progress saved Done Question 6 0/1 pt 4 Details < > Calculate the test-statistic, t with the following information. n = 35, x1 = 2.35, s = 0.63 n1 $1 n2 = 20, x2 = 2, 82 = 0.31 Rounded to 2 decimal places. Submit Question AA myopenmath.com 1 5:52 0/1 pt 4 Details . 48 Test the claim that the mean GPA of night students is larger than the mean GPA of day students at the 0.005 significance level. The null and alternative hypothesis would be: Ho PNPD Ho H : Pn > PD H N = D Ho: PN PD N D H: PN 5:52 Score: 0/14 0/14 answered Progress saved Done . 48 Question 8 0/1 pt 4 Details < > You are testing the claim that the mean GPA of night students is different than the mean GPA of day students. You sample 60 night students, and the sample mean GPA is 2.18 with a standard deviation of 0.92 You sample 40 day students, and the sample mean GPA is 2.21 with a standard deviation of 1 Calculate the test statistic, rounded to 2 decimal places Submit Question AA myopenmath.com 5:52 Score: 0/14 0/14 answered Progress saved Done Question 9 < > . 48 0/1 pt 4 Details For each scenario listed on the left, determine whether the scenario represents an Independent Samples or Matched pairs situation by placing the appropriate letter in the box provided. Comparing the number of speeding tickets received by men to the number received by women Comparing pre-test scores before training to post-test scores Comparing pain levels of a group receiving a placebo to a group receiving a medicine Comparing pain levels before and after treatment with magnetic therapy a. Independent Samples b. Matched Pairs Submit Question AA myopenmath.com 1 5:52 Score: 0/14 0/14 answered Progress saved Done all 48 Question 10 0/1 pt 4 Details < > You are testing the claim that the mean GPA of night students is greater than the mean GPA of day students. You sample 25 night students, and the sample mean GPA is 2.95 with a standard deviation of 0.59 You sample 60 day students, and the sample mean GPA is 2.76 with a standard deviation of 0.81 Calculate the test statistic, rounded to 2 decimal places Submit Question AA myopenmath.com 1 5:52 Question 12 0/1 pt 4 Details l 48 < Test the claim that the mean GPA of night students is significantly different than the mean GPA of day students at the 0.2 significance level. The null and alternative hypothesis would be: HoND Ho: PN = PD H : < D H: PNPD Ho PN=PD Ho: N = D H : n D Ho: PN = PD H : n > pd Ho: N = D H : N D The test is: right-tailed two-tailed left-tailed The sample consisted of 80 night students, with a sample mean GPA of 2.28 and a standard deviation of 0.07, and 35 day students, with a sample mean GPA of 2.26 and a standard deviation of 0.05. The test statistic is: decimals) The positive critical value is: (to 2 decimals) Based on this we: Fail to reject the null hypothesis Reject the null hypothesis Submit Question myopenmath.com (to 2 5:52 .... 48 0/1 pt 4 Details You wish to test the following claim (Ha) at a significance level of a = 0.001. : = Ha : 1 # You believe both populations are normally distributed, but you do not know the standard deviations for either. However, you also have no reason to believe the variances of the two populations are not equal. You obtain a sample of size n = 22 with a mean of M = 67.6 and a standard deviation of SD1 = 12.8 from the first population. You obtain a sample of size n 18 with a mean of M2 = 55.8 and a standard deviation of SD2 = 11.8 from the second population. = What is the test statistic for this sample? (Report answer accurate to three decimal places.) test statistic = What is the p-value for this sample? For this calculation, use the conservative under-estimate for the degrees of freedom...that is to say, instead of using use df = = N1 + n2 2, df min (n1, n2) 1. - (Report answer accurate to four decimal places.) p-value = The p-value is... less than (or equal to) a greater than a AA myopenmath.com 5:52 freedom...that is to say, instead of using df = N1 + n2 - 2. use .... 48 df =min (n, n2) - 1. (Report answer accurate to four decimal places.) p-value = The p-value is... less than (or equal to) a greater than a This test statistic leads to a decision to... reject the null accept the null fail to reject the null As such, the final conclusion is that... There is sufficient evidence to warrant rejection of the claim that the first population mean is not equal to the second population mean. There is not sufficient evidence to warrant rejection of the claim that the first population mean is not equal to the second population mean. The sample data support the claim that the first population mean is not equal to the second population mean. There is not sufficient sample evidence to support the claim that the first population mean is not equal to the second population mean. Submit Question myopenmath.com 5:52 Ill 48 Hypothesis Test - Independent Mean Assessment Score: 0/14 0/14 answered Progress saved Done Question 14 0/1 pt 4 Details < > For each scenario listed on the left, determine whether the scenario represents an Independent Samples or Matched pairs situation by placing the appropriate letter in the box provided. Comparing pain levels of a group receiving a placebo to a group receiving a medicine Comparing pre-test scores before training to post-test scores Comparing pain levels before and after treatment with magnetic therapy - Comparing the number of speeding tickets received by men to the number received by women a. Independent Samples b. Matched Pairs Submit Question myopenmath.com
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it
Step: 1

Get Instant Access to Expert-Tailored Solutions
See step-by-step solutions with expert insights and AI powered tools for academic success
Step: 2

Step: 3

Ace Your Homework with AI
Get the answers you need in no time with our AI-driven, step-by-step assistance
Get Started


