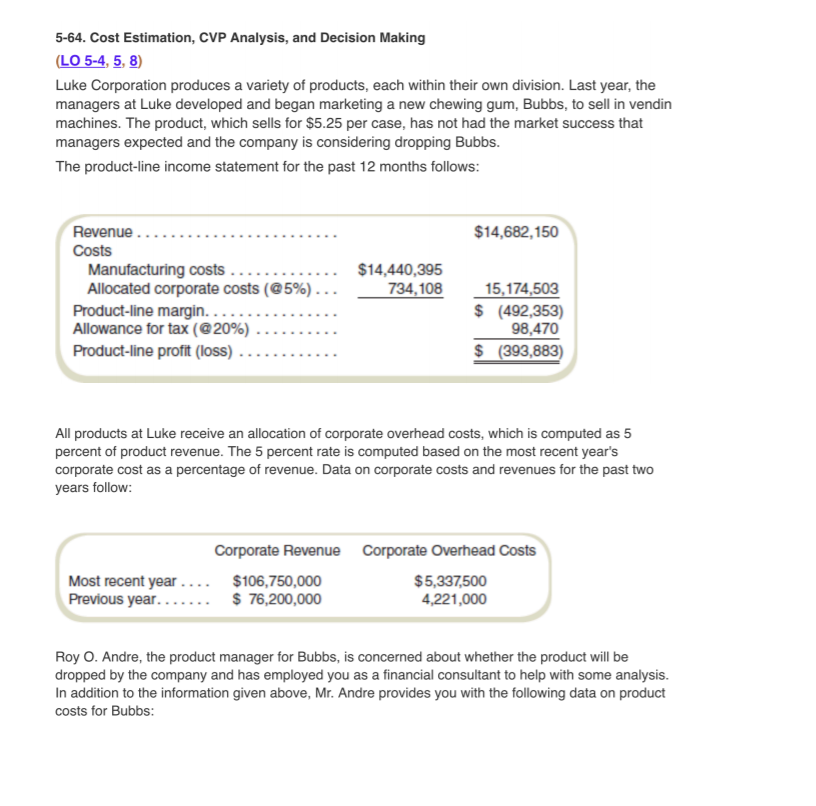


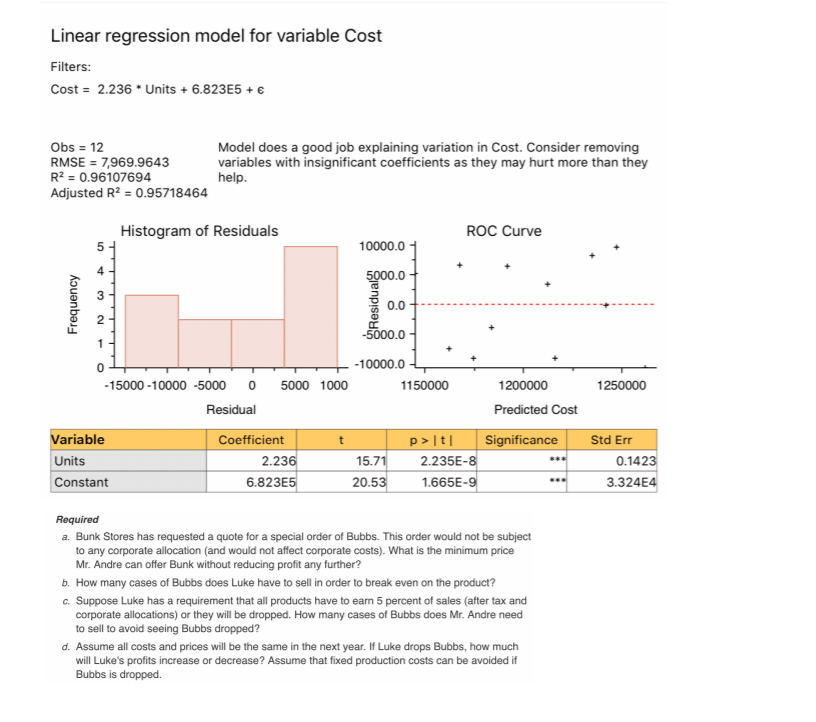
5-64. Cost Estimation, CVP Analysis, and Decision Making LO 5-4, 5, 8) Luke Corporation produces a variety of products, each within their own division. Last year, the managers at Luke developed and began marketing a new chewing gum, Bubbs, to sell in vendin machines. The product, which sells for $5.25 per case, has not had the market success that managers expected and the company is considering dropping Bubbs The product-line income statement for the past 12 months follows $14,682,150 Costs Allocated corporate costs (@5%).. 734,108 15,174,503 $ (492,353) 98,470 $ (393,883) Allowance for tax (@20%) .. All products at Luke receive an allocation of corporate overhead costs, which is computed as 5 percent of product revenue. The 5 percent rate is computed based on the most recent year's corporate cost as a percentage of revenue. Data on corporate costs and revenues for the past two years follow: Corporate Revenue Corporate Overhead Costs Most recent year... $106,750,000 $5,337,500 4,221,000 Roy O. Andre, the product manager for Bubbs, is concerned about whether the product will be dropped by the company and has employed you as a financial consultant to help with some analysis. In addition to the information given above, Mr. Andre provides you with the following data on product costs for Bubbs All products at Luke receive an allocation of corporate overhead costs, which is computed as 5 percent of product revenue. The 5 percent rate is computed based on the most recent year's corporate cost as a percentage of revenue. Data on corporate costs and revenues for the past two years follow Corporate Revenue Corporate Overhead Costs $5,337500 4,221,000 Most recent year.... $106,750,000 Roy O. Andre, the product manager for Bubbs, is concerned about whether the product will be dropped by the company and has employed you as a financial consultant to help with some analysis. In addition to the information given above, Mr. Andre provides you with the following data on product costs for Bubbs Month Cases Production Costs $1,139,828 1,161,328 1,169,981 1,185,523 1,187827 1,208,673 1,183,699 1,226,774 1,225,226 1,237,325 1,241,760 ,272,451 2.._ _.. _.... 217,200 6 237,000 9 0. ___.__... 252,600 Please answer the following questions. A regression analysis of the Bubbs p cost data is shown below. You may need the results to answer some of the questions. 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. How many cases of Bubbs did Lukes sell (based on sales revenue)? Using the high low method determine the variable corporate overhead cost per sales dollar. Round your answer to five significant digits. Based on the above what is the variable corporate overhead cost per case. Round your answer to five significant digits. Based on the above what is the fixed corporate overhead cost per month. Round your answer to the nearest dollar. Using the regression given below what is the variable production cost per case of Bubbs? Round your answer to three decimals. Using the regression given below what is the fixed production cost per month of Bubbs? Round your answer to the nearest 100 dollars. What is the total variable cost per case? Round your answer to four decimals. What is the contribution margin per case of Bubbs? Round your answer to four decimals 8. 9. What is the monthly average number of cases of Bubbs that Lukes sold last year? Round to the nearest 10. What is the monthly break-even number of cases of Bubbs? Consider whether or not to include some 11. What is the fixed production cost per case based on the current sales volume per month? Round to four 12. The following questions are based on Luke's current accounting practices. Recalculate the CM per case whole number portion of the fixed allocated costs. Round to the nearest whole number decimals. of Bubbs based on production costs and the treatment of allocated overhead as a variable cost based orn revenues. Round to four decimals. 13. Calculate the break-even for Bubbs in cases per month based on production fixed costs and the CM calculated above. 14. Write out a profit formula for Bubbs using Q, CM, and FC as in the prior question. For the desired profit note the after tax profit is.05 P Q/(1-TX), where P is the selling price per case and TX is the tax rate. Now solve for Q to determine the number of case Bubbs must produce and sell per month to earn a 5% return on revenues Linear regression model for variable Cost Filters: Cost 2.236 Units+6.823E5 + e Obs 12 RMSE 7,969.9643 R2 0.96107694 Adjusted R2 0.95718464 Model does a good job explaining variation in Cost. Consider removing variables with insignificant coefficients as they may hurt more than they help Histogram of Residuals ROC Curve 10000.0 4 3 2 5000.0 -5000.0 -10000.0 15000-10000 -5000 05000 1000 1150000 1200000 1250000 Residual Predicted Cost Variable Units Constant Coefficient p>lt Significance Std Err 2.236 15.7 2.235E 0.1423 3.324E4 6.823E5 20.53 1.665E a. Bunk Stores has requested a quote for a special order of Bubbs. This order would not be subject to any corporate allocation (and would not affect corporate costs). What is the minimum price Mr. Andre can offer Bunk without reducing profit any further? b. How many cases of Bubbs does Luke have to sell in order to break even on the product? c. Suppose Luke has a requirement that all products have to ean 5 percent of sales (after tax and corporate allocations) or they will be dropped. How many cases of Bubbs does Mr. Andre need to sell to avoid seeing Bubbs dropped? d. Assume all costs and prices will be the same in the next year. If Luke drops Bubbs, how much will Luke's profits increase or decrease? Assume that fixed production costs can be avoided if Bubbs is dropped. 5-64. Cost Estimation, CVP Analysis, and Decision Making LO 5-4, 5, 8) Luke Corporation produces a variety of products, each within their own division. Last year, the managers at Luke developed and began marketing a new chewing gum, Bubbs, to sell in vendin machines. The product, which sells for $5.25 per case, has not had the market success that managers expected and the company is considering dropping Bubbs The product-line income statement for the past 12 months follows $14,682,150 Costs Allocated corporate costs (@5%).. 734,108 15,174,503 $ (492,353) 98,470 $ (393,883) Allowance for tax (@20%) .. All products at Luke receive an allocation of corporate overhead costs, which is computed as 5 percent of product revenue. The 5 percent rate is computed based on the most recent year's corporate cost as a percentage of revenue. Data on corporate costs and revenues for the past two years follow: Corporate Revenue Corporate Overhead Costs Most recent year... $106,750,000 $5,337,500 4,221,000 Roy O. Andre, the product manager for Bubbs, is concerned about whether the product will be dropped by the company and has employed you as a financial consultant to help with some analysis. In addition to the information given above, Mr. Andre provides you with the following data on product costs for Bubbs All products at Luke receive an allocation of corporate overhead costs, which is computed as 5 percent of product revenue. The 5 percent rate is computed based on the most recent year's corporate cost as a percentage of revenue. Data on corporate costs and revenues for the past two years follow Corporate Revenue Corporate Overhead Costs $5,337500 4,221,000 Most recent year.... $106,750,000 Roy O. Andre, the product manager for Bubbs, is concerned about whether the product will be dropped by the company and has employed you as a financial consultant to help with some analysis. In addition to the information given above, Mr. Andre provides you with the following data on product costs for Bubbs Month Cases Production Costs $1,139,828 1,161,328 1,169,981 1,185,523 1,187827 1,208,673 1,183,699 1,226,774 1,225,226 1,237,325 1,241,760 ,272,451 2.._ _.. _.... 217,200 6 237,000 9 0. ___.__... 252,600 Please answer the following questions. A regression analysis of the Bubbs p cost data is shown below. You may need the results to answer some of the questions. 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. How many cases of Bubbs did Lukes sell (based on sales revenue)? Using the high low method determine the variable corporate overhead cost per sales dollar. Round your answer to five significant digits. Based on the above what is the variable corporate overhead cost per case. Round your answer to five significant digits. Based on the above what is the fixed corporate overhead cost per month. Round your answer to the nearest dollar. Using the regression given below what is the variable production cost per case of Bubbs? Round your answer to three decimals. Using the regression given below what is the fixed production cost per month of Bubbs? Round your answer to the nearest 100 dollars. What is the total variable cost per case? Round your answer to four decimals. What is the contribution margin per case of Bubbs? Round your answer to four decimals 8. 9. What is the monthly average number of cases of Bubbs that Lukes sold last year? Round to the nearest 10. What is the monthly break-even number of cases of Bubbs? Consider whether or not to include some 11. What is the fixed production cost per case based on the current sales volume per month? Round to four 12. The following questions are based on Luke's current accounting practices. Recalculate the CM per case whole number portion of the fixed allocated costs. Round to the nearest whole number decimals. of Bubbs based on production costs and the treatment of allocated overhead as a variable cost based orn revenues. Round to four decimals. 13. Calculate the break-even for Bubbs in cases per month based on production fixed costs and the CM calculated above. 14. Write out a profit formula for Bubbs using Q, CM, and FC as in the prior question. For the desired profit note the after tax profit is.05 P Q/(1-TX), where P is the selling price per case and TX is the tax rate. Now solve for Q to determine the number of case Bubbs must produce and sell per month to earn a 5% return on revenues Linear regression model for variable Cost Filters: Cost 2.236 Units+6.823E5 + e Obs 12 RMSE 7,969.9643 R2 0.96107694 Adjusted R2 0.95718464 Model does a good job explaining variation in Cost. Consider removing variables with insignificant coefficients as they may hurt more than they help Histogram of Residuals ROC Curve 10000.0 4 3 2 5000.0 -5000.0 -10000.0 15000-10000 -5000 05000 1000 1150000 1200000 1250000 Residual Predicted Cost Variable Units Constant Coefficient p>lt Significance Std Err 2.236 15.7 2.235E 0.1423 3.324E4 6.823E5 20.53 1.665E a. Bunk Stores has requested a quote for a special order of Bubbs. This order would not be subject to any corporate allocation (and would not affect corporate costs). What is the minimum price Mr. Andre can offer Bunk without reducing profit any further? b. How many cases of Bubbs does Luke have to sell in order to break even on the product? c. Suppose Luke has a requirement that all products have to ean 5 percent of sales (after tax and corporate allocations) or they will be dropped. How many cases of Bubbs does Mr. Andre need to sell to avoid seeing Bubbs dropped? d. Assume all costs and prices will be the same in the next year. If Luke drops Bubbs, how much will Luke's profits increase or decrease? Assume that fixed production costs can be avoided if Bubbs is dropped










