Answered step by step
Verified Expert Solution
Question
1 Approved Answer
6. Alternative Methods of Manufacture Sometimes a manufacturer is faced with the problem of the application of alternative methods of manufacture i.e., whether machine work
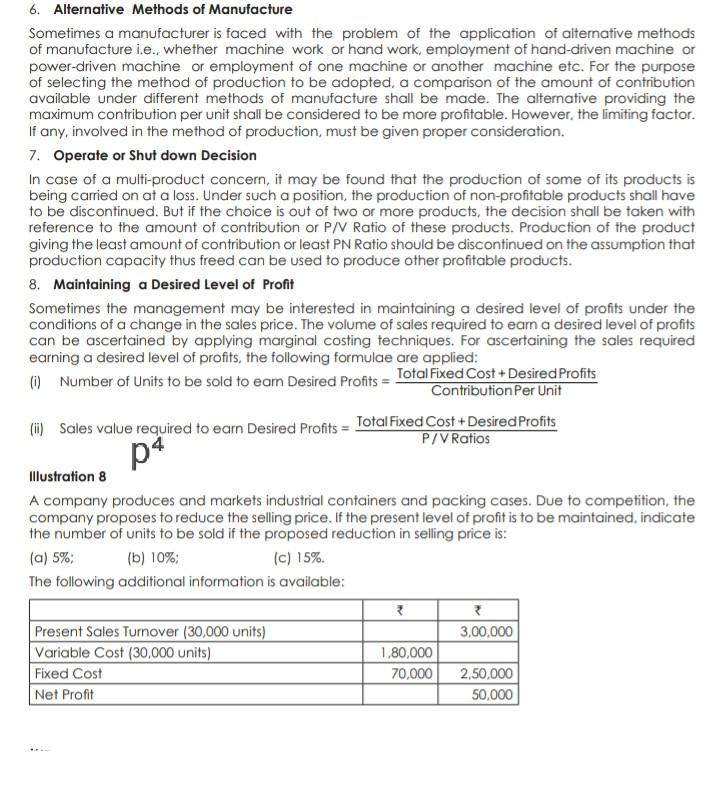
6. Alternative Methods of Manufacture Sometimes a manufacturer is faced with the problem of the application of alternative methods of manufacture i.e., whether machine work or hand work, employment of hand-driven machine or power-driven machine or employment of one machine or another machine etc. For the purpose of selecting the method of production to be adopted, a comparison of the amount of contribution available under different methods of manufacture shall be made. The alternative providing the maximum contribution per unit shall be considered to be more profitable. However, the limiting factor. If any, involved in the method of production, must be given proper consideration. 7. Operate or Shut down Decision In case of a multi-product concern, it may be found that the production of some of its products is being carried on at a loss. Under such a position, the production of non-profitable products shall have to be discontinued. But if the choice is out of two or more products, the decision shall be taken with reference to the amount of contribution or P/N Ratio of these products. Production of the product giving the least amount of contribution or least PN Ratio should be discontinued on the assumption that production capacity thus freed can be used to produce other profitable products. 8. Maintaining a Desired Level of Profit Sometimes the management may be interested in maintaining a desired level of profits under the conditions of a change in the sales price. The volume of sales required to earn a desired level of profits can be ascertained by applying marginal costing techniques. For ascertaining the sales required earning a desired level of profits, the following formulae are applied: (1) Number of Units to be sold to earn Desired Profits = Total Fixed Cost + Desired Profits Contribution Per Unit (i) Sales value required to earn Desired Profits = Total Fixed Cost + Desired Profits P/V Ratios p4 Illustration 8 A company produces and markets industrial containers and packing cases. Due to competition, the company proposes to reduce the selling price. If the present level of profit is to be maintained indicate the number of units to be sold if the proposed reduction in selling price is: (a) 5%; (b) 10%; (c) 15% The following additional information is available: Present Sales Turnover (30,000 units) 3,00,000 Variable Cost (30,000 units) 1.80,000 Fixed Cost 70,000 2,50,000 Net Profit 50,000
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it
Step: 1

Get Instant Access to Expert-Tailored Solutions
See step-by-step solutions with expert insights and AI powered tools for academic success
Step: 2

Step: 3

Ace Your Homework with AI
Get the answers you need in no time with our AI-driven, step-by-step assistance
Get Started


