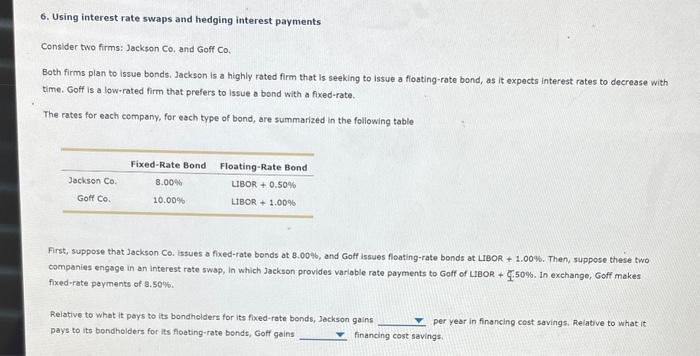
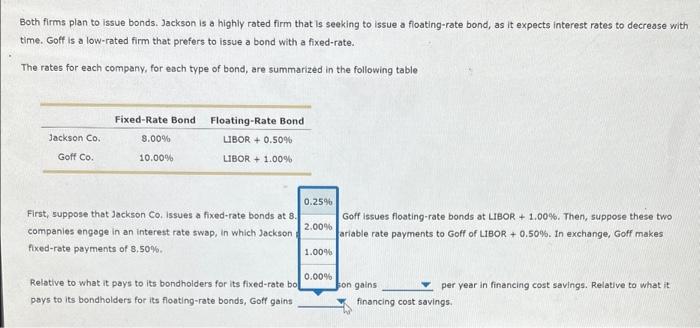
6. Using interest rate swaps and hedging interest payments Consider two firms: Jaekson Co, and Goff Co. Both firms plan to issue bonds. Jackson is a highly rated firm that is seeking to issue a floating-rate bond, as it expects interest rates to decrease with time. Goff is a low-rated firm that prefers to issue a bond with a fixed-rate. The rates for each company, for eech type of bond, are summarized in the following table First, suppose that Jackson Co. Issues a fixed-rate bonds at 8.0096, and Gotf issues floating-rate bonds at LrBoR +1.00%. Then, suppose these two companies engage in an interest rate swap, in which Jackson provides varlable rate payments to Goff of LIBOR + G.50\%. In exchange, Goff makes. fixed-rate peyments of 8.50%. Relative to whet it pays to its bondhelders for its fixed-rate bonds, Jackson gains per year in financing cost savings. Relative to what it pays to its bondholders for its floeting-rate bonds, Goff gains financing cost savings: Consider two firms: Jackson Co. and Goff Co. Both firms plan to issue bonds. Jackson is a highly rated firm that is seeking to issue a floating-rate bond, as it expects interest rates to decrease v time. Goff is a low-rated firm that prefers to issue a bond with a fixed-rate. The rates for each company, for each type of bond, are summarized in the following table First, suppose that Jackson Co. issues a fixed-rate bonds at 8.00%, and Goff issuc 1.50%-rate bonds at LIBOR + 1.00\%, Then, suppose these two companies engage in an interest rate swap, in which Jackson provides variable rat 1.00% ts to Goff of LIBOR +0.50%. In exchange, Goff makes fixed-rate payments of 8.50%. Relative to what it pays to lts bondholders for its fixed-rate bonds, Jackson gains: per year in financing cost savings. Relative to what it pays to its bondholders for its floating-rate bonds, Goff gains financing cost savings. Both firms plan to issue bonds. Jackson is a highly rated firm that is seeking to issue a floating-rate bond, as it expects interest rates to decrease with time. Goff is a low-rated firm that prefers to issue a bond with a fixed-rate. The rates for each company, for each type of bond, are summarized in the following table First, suppose that Jackson Co, Issues a fixed-rate bonds at 8. companies engage in an interest rate swap, in which Jackson fuxed-rate payments of 8,50%. pays to its bondholders for its floating-rate bonds, Goff gains financing cost savings