Question
6.18c. Flash calculations: the Rachford-Rice method for ideal mixtures (a) Show that the problem of flash vaporization of a multicomponent ideal mixture can be reformulated
6.18c. Flash calculations: the Rachford-Rice method for ideal mixtures\ (a) Show that the problem of flash vaporization of a multicomponent ideal mixture can be reformulated as suggested by Rachford and Rice (Doherty and Malone, 2001):\
f(\\\\phi )=\\\\sum_(i=1)^C (z_(i)(m_(i)-1))/(1+\\\\phi (m_(i)-1))=0 where m_(i)=(P_(i))/(P)\ x_(i)=(z_(i))/(1+\\\\phi (m_(i)-1)),i=1,2,cdots,C\ y_(i)=m_(i)x_(i),i=1,2,cdots,C\ D=\\\\phi F,W=(1-\\\\phi )F\ Equation (6-109) is solved iteratively for
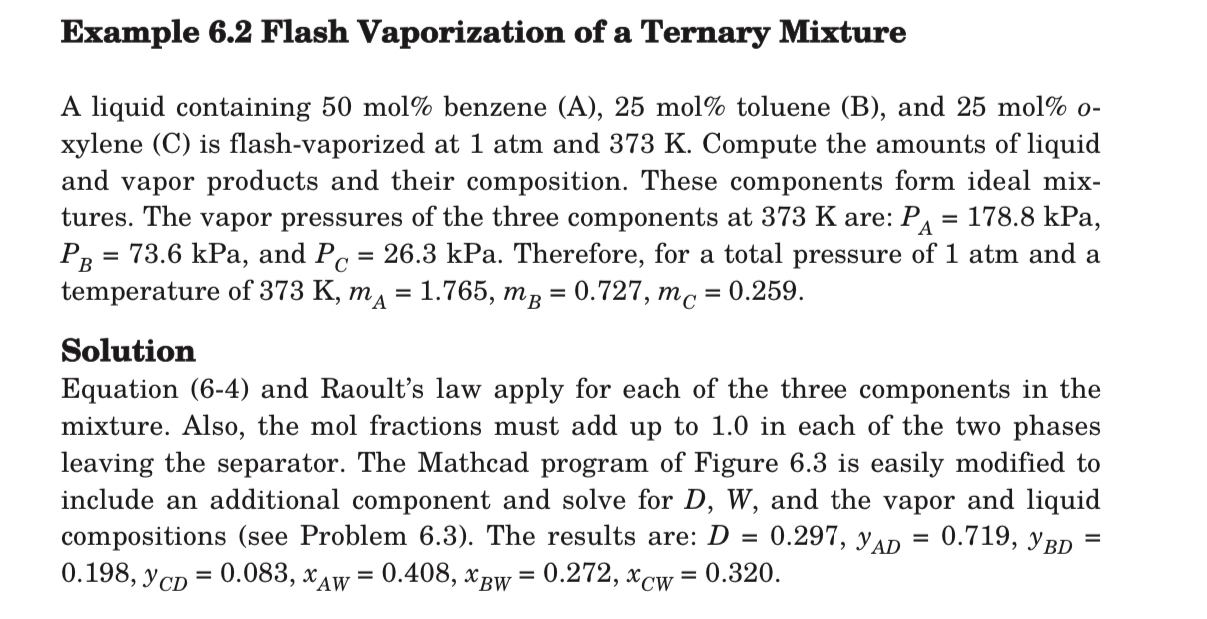
\\\\phi ; all other variables are calculated explicitly from equations (6-110) to (6-112).\ (b) Solve Example 6.2 using the Rachford-Rice method.\ \ Example 6.2 Flash Vaporization of a Ternary Mixture\ A liquid containing
50mol%benzene (A),
25mol%toluene (B), and
25mol%oxylene
(C)is flash-vaporized at
1atmand
373K. Compute the amounts of liquid and vapor products and their composition. These components form ideal mixtures. The vapor pressures of the three components at
373Kare:
P_(A)=178.8kPa,
P_(B)=73.6kPa, and
P_(C)=26.3kPa. Therefore, for a total pressure of
1atmand a temperature of
373K,m_(A)=1.765,m_(B)=0.727,m_(C)=0.259.\ Solution\ Equation (6-4) and Raoult's law apply for each of the three components in the mixture. Also, the mol fractions must add up to 1.0 in each of the two phases leaving the separator. The Mathcad program of Figure 6.3 is easily modified to include an additional component and solve for
D,W, and the vapor and liquid compositions (see Problem 6.3). The results are:
D=0.297,y_(AD)=0.719,y_(BD)=
0.198,y_(CD)=0.083,x_(AW)=0.408,x_(BW)=0.272,x_(CW)=0.320.
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it
Step: 1

Get Instant Access to Expert-Tailored Solutions
See step-by-step solutions with expert insights and AI powered tools for academic success
Step: 2

Step: 3

Ace Your Homework with AI
Get the answers you need in no time with our AI-driven, step-by-step assistance
Get Started


