Answered step by step
Verified Expert Solution
Question
1 Approved Answer
6.4 Harmonic forcing of a mass-spring-damper system. (Section 13.2). Homework 5.4 shows a Scotch-yoke moving P with yp(t) = A sin(t). The equation of
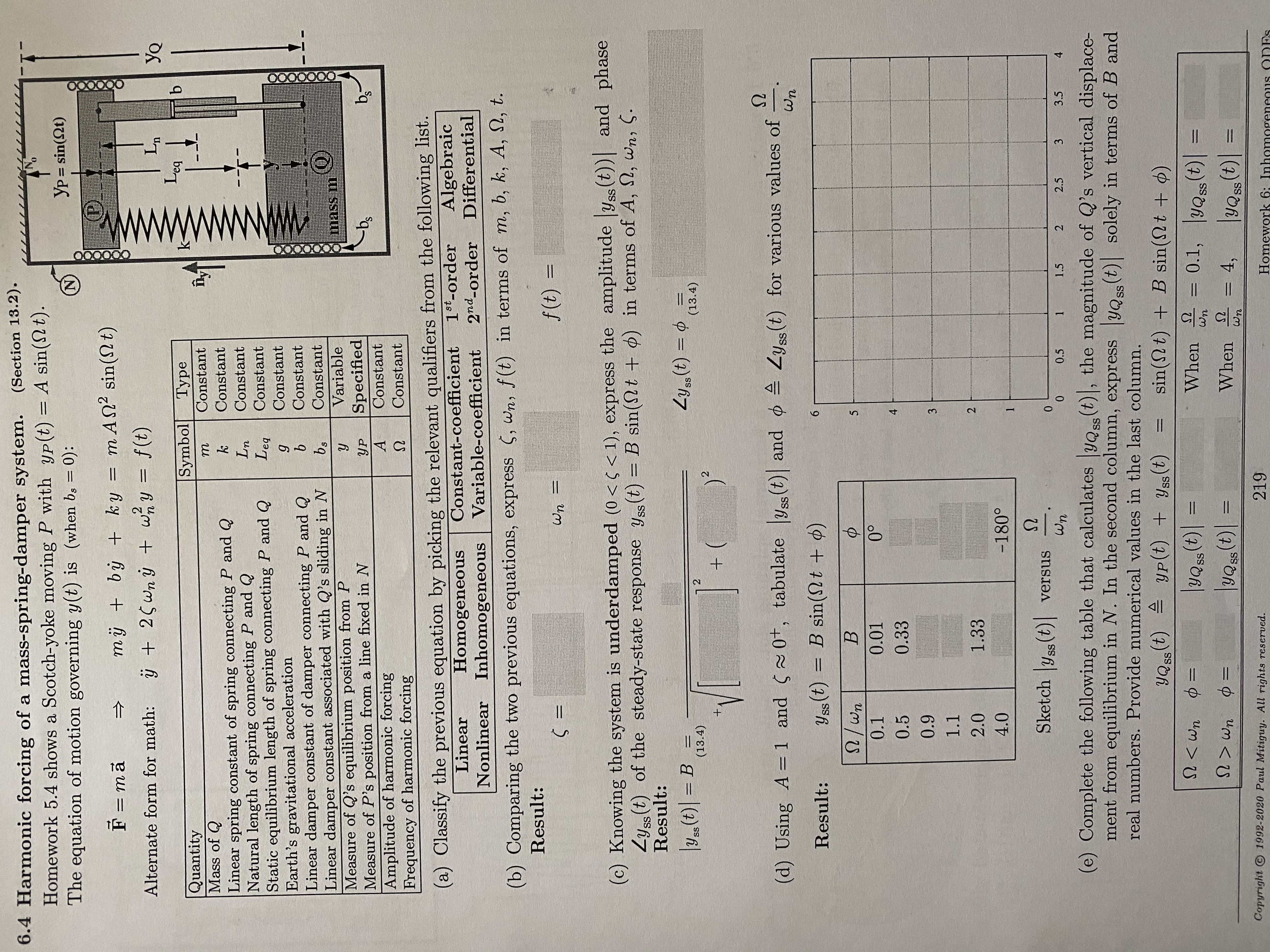

6.4 Harmonic forcing of a mass-spring-damper system. (Section 13.2). Homework 5.4 shows a Scotch-yoke moving P with yp(t) = A sin(t). The equation of motion governing y(t) is (when bs = 0): Yp=sin(t) Lea F = m == Alternate form for math: m + by + ky = m An sin(t) + 25 wn + w/y = f(t) 000000 Symbol Type Quantity m Constant Mass of Q Linear spring constant of spring connecting P and Q Natural length of spring connecting P and Q k Constant Ln Constant Static equilibrium length of spring connecting P and Q Earth's gravitational acceleration Lea Constant Constant g Linear damper constant of damper connecting P and Q Linear damper constant associated with Q's sliding in N Measure of Q's equilibrium position from P Measure of P's position from a line fixed in N b Constant bs Constant Y Variable mas m Specified Amplitude of harmonic forcing A Constant Constant b Frequency of harmonic forcing -bs (a) Classify the previous equation by picking the relevant qualifiers from the following list. Linear Homogeneous Nonlinear Inhomogeneous Constant-coefficient 1st-order Algebraic 2nd-order Differential Variable-coefficient (b) Comparing the two previous equations, express (, wn, f(t) in terms of m, b, k, A, , t. Result: 5 = wn = f(t) = YQ (c) Knowing the system is underdamped (0 < < < 1), express the amplitude |yss (t))| and phase Lyss(t) of the steady-state response yss (t) = B sin(t + ) in terms of A, 2, wn, S. Result: SS |yss (t)| = B = SS Zyss (t) = 6 = (13.4) 72 (13.4) + + ) 2 (d) Using A = 1 and (0+, tabulate | ss (t) and |ys(t) Zyss (t) for various values of Zys(t) Wn Result: Yss (t) = B sin(t + ) 6 / wn B 5 0.1 0.01 0 4 0.5 0.33 0.9 3 1.1 2.0 1.33 2 4.0 -180 1 Sketch |yss (t)| versus Wn 0 0 0.5 1 1.5 2 2.5 3 3.5 4 (e) Complete the following table that calculates |yQ (t)|, the magnitude of Q's vertical displace- ment from equilibrium in N. In the second column, express yQss (t) solely in terms of B and real numbers. Provide numerical values in the last column. < YQss (t) Ef = = YP (t) + Yss (t) |YQss (t)| = |YQss (t)| = = sin(t) + B sin(t + ) When When Wn = 0.1, = 4, Wn s(t)| |YQss (t)| = Copyright 1992-2020 Paul Mitiguy. All rights reserved. 219 Homework 6: (f) The previous results show that particle Q appears to be rigidly connected to P at low/high frequency, whereas Q moves very little in N at low/high frequency. The most energetic motion of Q in N occurs when 6.5 Steady-state response to harmonic forcing. (Section 13.2). sin(Ot)
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it
Step: 1

Get Instant Access to Expert-Tailored Solutions
See step-by-step solutions with expert insights and AI powered tools for academic success
Step: 2

Step: 3

Ace Your Homework with AI
Get the answers you need in no time with our AI-driven, step-by-step assistance
Get Started


