Answered step by step
Verified Expert Solution
Question
1 Approved Answer
6.CRPO Case Study Noon Company The following information refers to Noon Company Assets Non-current assets, total 101 000 000 Current assets Inventory 11 000 000
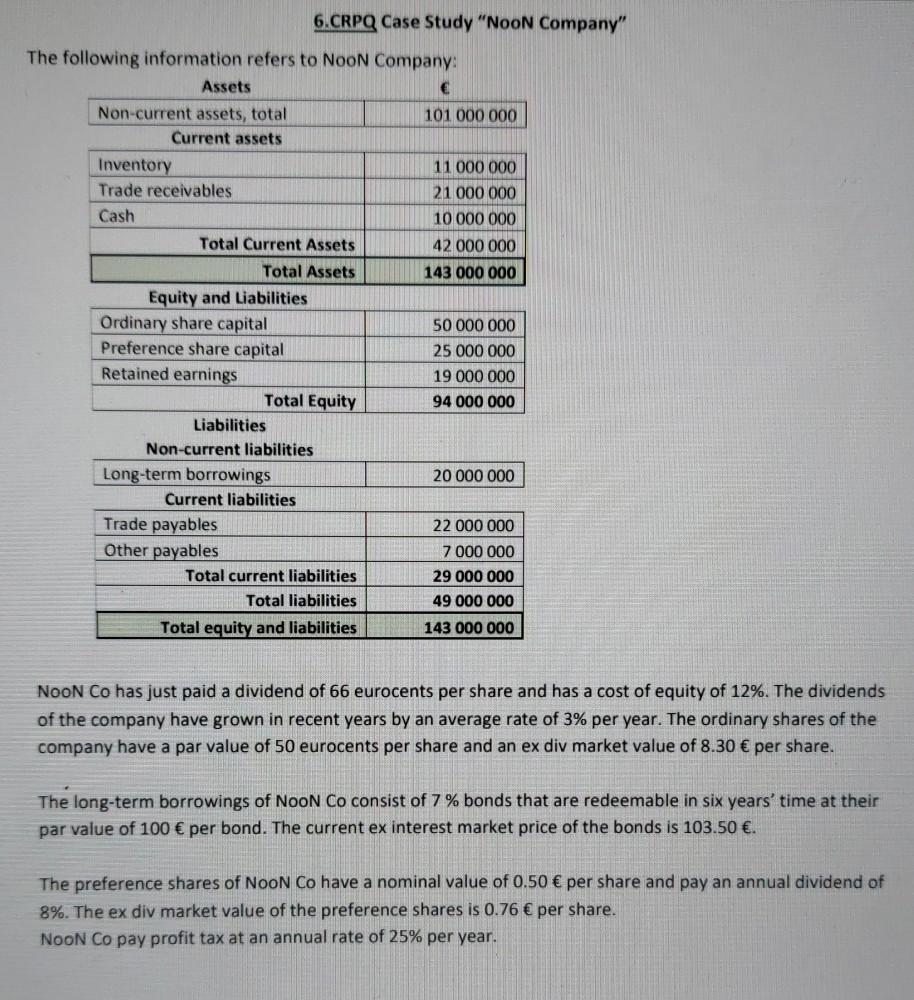

6.CRPO Case Study "Noon Company" The following information refers to Noon Company Assets Non-current assets, total 101 000 000 Current assets Inventory 11 000 000 Trade receivables 21 000 000 Cash 10 000 000 Total Current Assets 42 000 000 Total Assets 143 000 000 Equity and Liabilities Ordinary share capital 50 000 000 Preference share capital 25 000 000 Retained earnings 19 000 000 Total Equity 94 000 000 Liabilities Non-current liabilities Long-term borrowings 20 000 000 Current liabilities Trade payables 22 000 000 Other payables 7 000 000 Total current liabilities 29 000 000 Total liabilities 49 000 000 Total equity and liabilities 143 000 000 NOON Co has just paid a dividend of 66 eurocents per share and has a cost of equity of 12%. The dividends of the company have grown in recent years by an average rate of 3% per year. The ordinary shares of the company have a par value of 50 eurocents per share and an ex div market value of 8.30 per share. The long-term borrowings of Noon Co consist of 7% bonds that are redeemable in six years' time at their par value of 100 per bond. The current ex interest market price of the bonds is 103.50 . The preference shares of Noon Co have a nominal value of 0.50 per share and pay an annual dividend of 8%. The ex div market value of the preference shares is 0.76 per share. NOON Co pay profit tax at an annual rate of 25% per year. 3. Calculate the after-tax cost of debt of NooN Co. Comment. The after-tax cost of debt of NooN Co can be found by linear interpolation! You need to calculate present value for all cash flows which relates to these bonds (investment in bonds at TO, interest payments T1-T6 and principal repayment at T6. Using two different discount rotes (you sholl use 5% and 4%), you shall find PV for these two cash flows (PV@5% and PV @4%) and calculate NPV for both discount rates. For PV, NPV calculations you must use Excel functions (spreadsheet formulas) - not discount factors from table! Then with linear interpolation you can find what shall be after-tax cost of debt. 3.1. Annual after-tax interest payment per year ............ 3.2. After-tax cost of debt %
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it
Step: 1

Get Instant Access to Expert-Tailored Solutions
See step-by-step solutions with expert insights and AI powered tools for academic success
Step: 2

Step: 3

Ace Your Homework with AI
Get the answers you need in no time with our AI-driven, step-by-step assistance
Get Started


