Answered step by step
Verified Expert Solution
Question
1 Approved Answer
7) 0.5 kg of Nitrogen is compressed in a polytropic process with n = 1.3 from 150 kPa and 20C to 900 kPa in

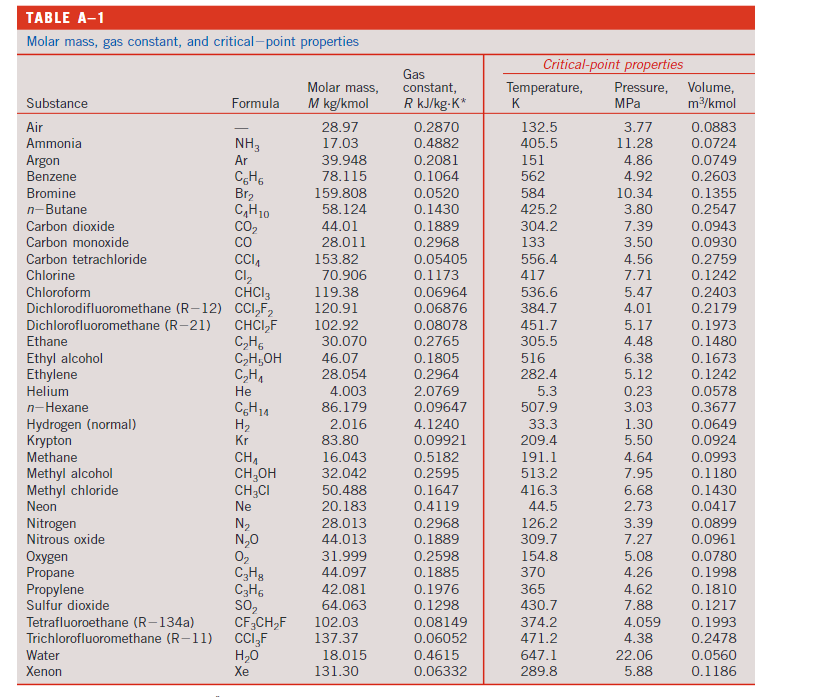
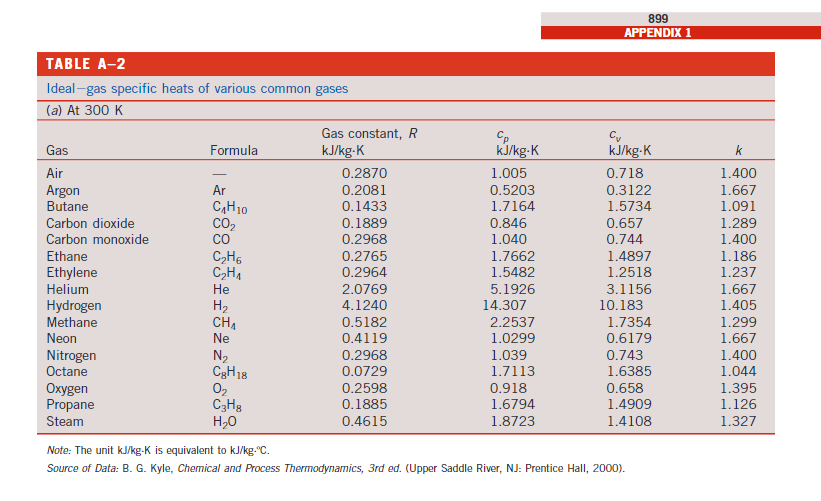
7) 0.5 kg of Nitrogen is compressed in a polytropic process with n = 1.3 from 150 kPa and 20C to 900 kPa in a piston-cylinder device. Determine the work done on the gas and heat transferred during this process. TABLE A-1 Molar mass, gas constant, and critical-point properties Gas Critical-point properties Molar mass, constant, Temperature, Pressure, Volume, Substance Air Ammonia Argon Formula M kg/kmol R kJ/kg.K* K MPa m/kmol 28.97 0.2870 132.5 3.77 0.0883 NH3 17.03 0.4882 405.5 11.28 0.0724 Ar 39.948 0.2081 151 4.86 0.0749 Benzene Bromine n-Butane Carbon dioxide C6H6 78.115 0.1064 562 4.92 0.2603 Br 159.808 0.0520 584 10.34 0.1355 CH 10 58.124 0.1430 425.2 3.80 0.2547 CO 44.01 0.1889 304.2 7.39 0.0943 Carbon monoxide CO 28.011 0.2968 133 3.50 0.0930 Carbon tetrachloride CCI 153.82 0.05405 556.4 4.56 0.2759 Chlorine Cl 70.906 0.1173 417 7.71 0.1242 Chloroform CHCI3 119.38 0.06964 536.6 5.47 0.2403 Dichlorodifluoromethane (R-12) CC12F2 120.91 0.06876 384.7 4.01 0.2179 Dichlorofluoromethane (R-21) CHCIF 102.92 0.08078 451.7 5.17 0.1973 Ethane C2H6 30.070 0.2765 305.5 4.48 0.1480 Ethyl alcohol CHOH 46.07 0.1805 516 6.38 0.1673 Ethylene CH 28.054 0.2964 282.4 5.12 0.1242 Helium He 4.003 2.0769 5.3 0.23 0.0578 n-Hexane 614 86.179 0.09647 507.9 3.03 0.3677 Hydrogen (normal) H 2.016 4.1240 33.3 1.30 0.0649 Krypton Kr 83.80 0.09921 209.4 5.50 0.0924 Methane CH1 16.043 0.5182 191.1 4.64 0.0993 Methyl alcohol CH3OH 32.042 0.2595 513.2 7.95 0.1180 Methyl chloride CH3Cl 50.488 0.1647 416.3 6.68 0.1430 Neon Ne 20.183 0.4119 44.5 2.73 0.0417 Nitrogen N 28.013 0.2968 126.2 3.39 0.0899 Nitrous oxide NO 44.013 0.1889 309.7 7.27 0.0961 Oxygen 02 31.999 0.2598 154.8 5.08 0.0780 Propane C3H8 44.097 0.1885 370 4.26 0.1998 Propylene C3H6 42.081 0.1976 365 4.62 0.1810 Sulfur dioxide SO2 64.063 0.1298 430.7 7.88 0.1217 Tetrafluoroethane (R-134a) CF3CH2F 102.03 0.08149 374.2 4.059 0.1993 Trichlorofluoromethane (R-11) CCI 3F 137.37 0.06052 471.2 4.38 0.2478 Water HO 18.015 0.4615 647.1 22.06 0.0560 Xenon Xe 131.30 0.06332 289.8 5.88 0.1186 TABLE A-2 Ideal-gas specific heats of various common gases (a) At 300 K 899 APPENDIX 1 Gas Air Formula Gas constant, R kJ/kg-K Cv kJ/kg-K kJ/kg-K k 0.2870 1.005 0.718 1.400 Argon Ar 0.2081 0.5203 0.3122 1.667 Butane CH 10 0.1433 1.7164 1.5734 1.091 Carbon dioxide CO 0.1889 0.846 0.657 1.289 Carbon monoxide CO 0.2968 1.040 0.744 1.400 Ethane C2H6 0.2765 1.7662 1.4897 1.186 Ethylene CH1 0.2964 1.5482 1.2518 1.237 Helium He 2.0769 5.1926 3.1156 1.667 Hydrogen H 4.1240 14.307 10.183 1.405 Methane CH1 0.5182 2.2537 1.7354 1.299 Neon Ne 0.4119 1.0299 0.6179 1.667 Nitrogen N 0.2968 1.039 0.743 1.400 Octane C8H18 0.0729 1.7113 1.6385 1.044 Oxygen 02 0.2598 0.918 0.658 1.395 Propane C3H8 0.1885 1.6794 1.4909 1.126 Steam HO 0.4615 1.8723 1.4108 1.327 Note: The unit kJ/kg-K is equivalent to kJ/kg-C. Source of Data: B. G. Kyle, Chemical and Process Thermodynamics, 3rd ed. (Upper Saddle River, NJ: Prentice Hall, 2000).
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it
Step: 1
Solutions Step 1 Work done during polytopic ...
Get Instant Access to Expert-Tailored Solutions
See step-by-step solutions with expert insights and AI powered tools for academic success
Step: 2

Step: 3

Ace Your Homework with AI
Get the answers you need in no time with our AI-driven, step-by-step assistance
Get Started


