Answered step by step
Verified Expert Solution
Question
1 Approved Answer
7 Could you please help me with the Ending Finished Goods Inventory, Selling and Administrative, Cash Budget, Income Statement, and Balance Sheet in excel please



 7
7
Could you please help me with the Ending Finished Goods Inventory, Selling and Administrative, Cash Budget, Income Statement, and Balance Sheet in excel please
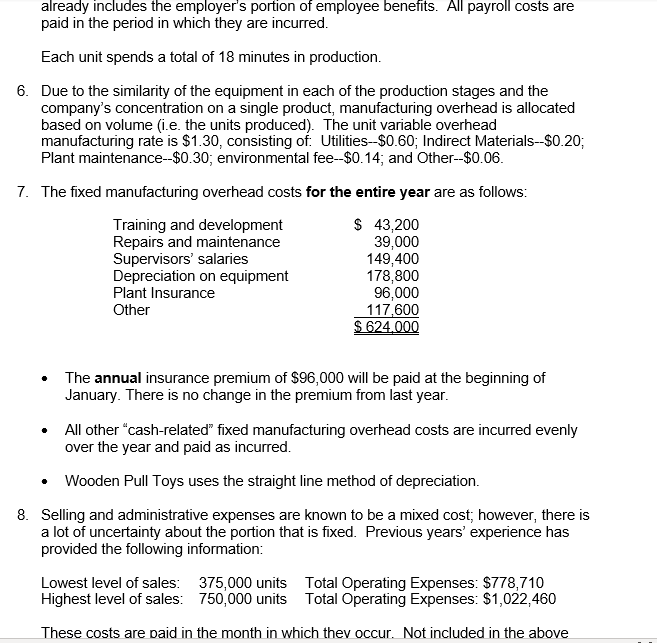
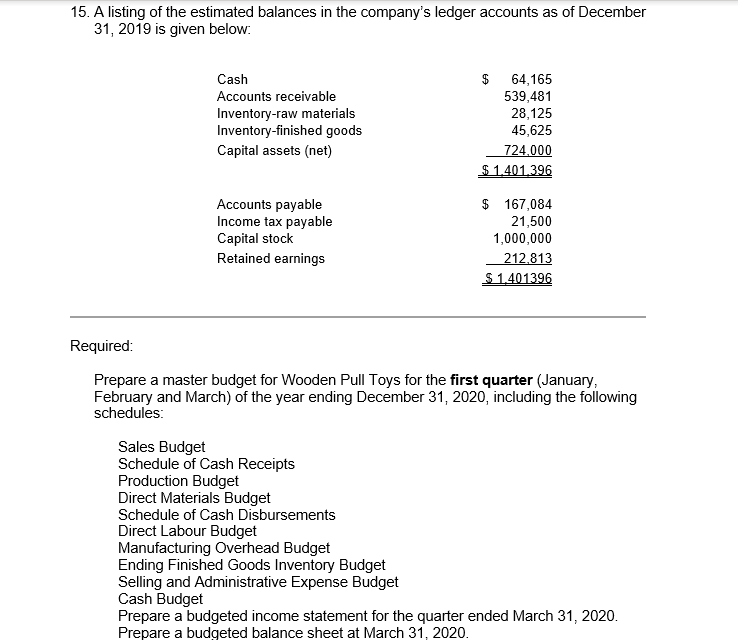
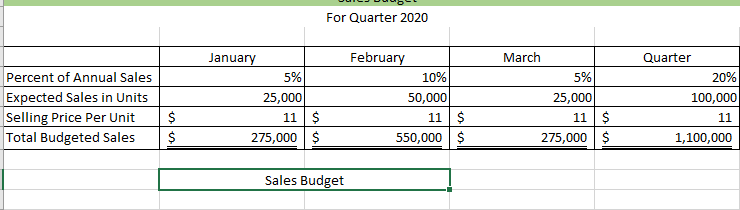
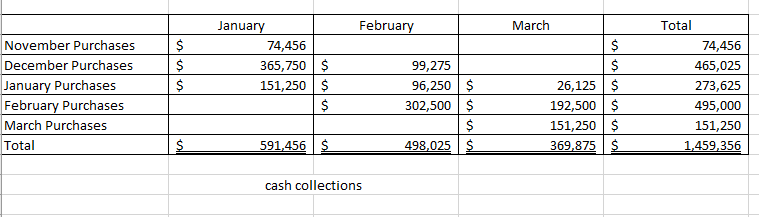
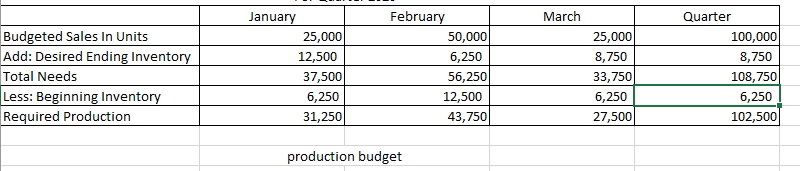
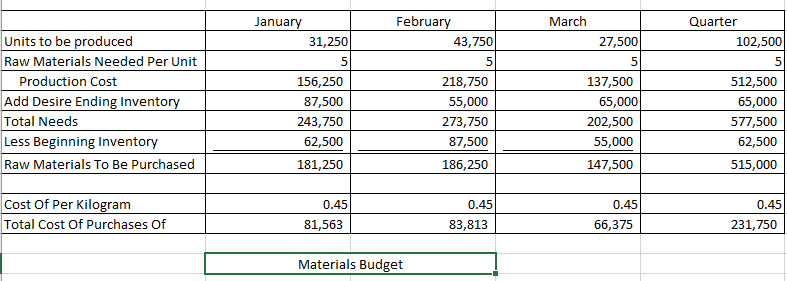
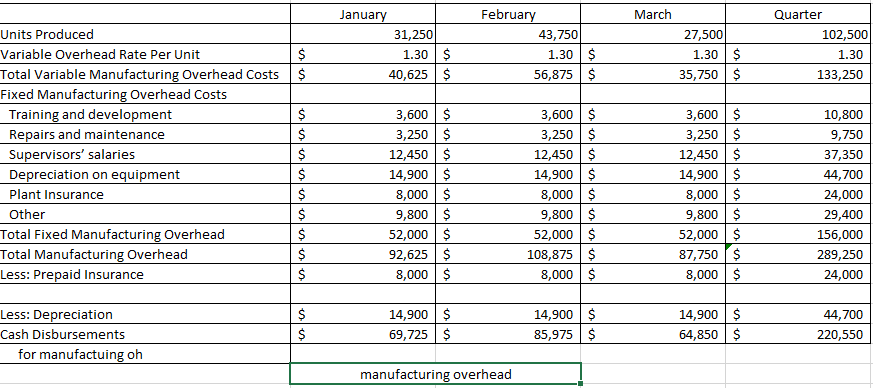
Master Budget Case: Wooden Pull Toys Inc. Wooden Pull Toys Ltd. is a company that manufactures and sells a single product, which they call a Baby Turtle. For planning and control purposes they utilize a quarterly master budget, which is usually developed at least six months in advance of the budget period. Their fiscal year end is December 31. During the summer of 2019, Jimmy C., the Wooden Pull Toys controller, spent considerable time with Fanny L., the Manager of Marketing, putting together a sales forecast for the first quarter of next year (January to March, 2020). Unfortunately, their collaboration worked so well they eloped to Niagara, ON, were married and settled down. Prior to their departure they e-mailed letters of resignation and a cryptic sales forecast to the President of Wooden Pull Toys. Their sales forecast consisted of these few lines: For the year ended December 31, 2019: 475,000 units at $11.00 each* . For the year ended December 31, 2020: 500,000 units at $11.00 each . For the year ended December 31, 2021: 500.000 units at $11.00 each * Expected sales for the year ended December 31, 2019 are based on actual sales to date and budgeted sales for the duration of the year. Wooden Pull Toys' President felt certain that the marriage wouldn't last, and expected Chris would be back any day. But the end of the year is quickly approaching, and there is still no word from the desert. The President, desperately needing the budget completed, has approached you, a management accounting student, for help in preparing the budget for the first quarter. Your conversations with the President and your investigations of the company's records have revealed the following information: 1. Sales of Baby Turtles are seasonal. History shows that January, March, May and June are the slowest months with only 5% of sales for each month. Sales pick up over the summer with July, August and September each contributing 6% to the total Valentines Day in February boosts sales to 10%, and spring break in April accounts for 7%. As Christmas shopping picks up momentum, winter sales start at 10% in October, move to 15% in November and then peak at 20% in December. This pattern of sales is not expected to change in the next two years. 2. From previous experience, management has determined that an ending inventory equal to 25% of the next month's sales is required to fit the buyer's demands. 3. There is only one type of raw material used in the production of Baby Turtles. R700 is a very compact material that is purchased in powder form. Each Baby Turtle requires 5 kilograms of R700, at a cost of $0.45 per kilogram. The supplier of R700 tends to be somewhat erratic so Wooden Pull Toys finds it necessary to maintain an inventory balance equal to 40% of the following month's production needs as a precaution against stock-outs. Wooden Pull Toys pays for 20% of a month's purchases in the month of purchase, 45% in the following month and the remaining 35% two months after the month of purchase. There is no early payment discount. 4. Beginning accounts payable will consist of $167,084 arising from the following estimated direct material purchases for November and December of 2019: R700 purchases in November 2019: R700 purchases in December 2019 $173,953 $132,750 5. Wooden Pull Toys' manufacturing process is highly automated, so their direct labour cost is low. Employees are paid on a per unit basis. Their total pay each month is, therefore, dependent on production volumes and averages $9.00 per hour. This rate already includes the employer's portion of employee benefits. All payroll costs are paid in the period in which they are incurred. Each unit spends a total of 18 minutes in production. 6. Due to the similarity of the equipment in each of the production stages and the company's concentration on a single product, manufacturing overhead is allocated based on volume (i.e. the units produced). The unit variable overhead manufacturing rate is $1.30, consisting of Utilities--$0.60; Indirect Materials--$0.20; Plant maintenance-$0.30, environmental fee--$0.14; and Other--$0.06. 7. The fixed manufacturing overhead costs for the entire year are as follows: Training and development Repairs and maintenance Supervisors' salaries Depreciation on equipment Plant Insurance Other $ 43,200 39.000 149.400 178,800 96.000 117,600 S 624.000 The annual insurance premium of $96,000 will be paid at the beginning of January. There is no change in the premium from last year. All other "cash-related" fixed manufacturing overhead costs are incurred evenly over the year and paid as incurred. Wooden Pull Toys uses the straight line method of depreciation. 8. Selling and administrative expenses are known to be a mixed cost; however, there is a lot of uncertainty about the portion that is fixed. Previous years' experience has provided the following information: Lowest level of sales: 375,000 units Highest level of sales: 750,000 units Total Operating Expenses: $778,710 Total Operating Expenses: $1,022,460 These costs are paid in the month in which they occur. Not included in the above expenses is bad debt expense. 9. Sales are on a cash and credit basis, with 55% collected during the month of the sale, 35% the following month, and 9.5% the month thereafter. 12 of 1% of sales are considered uncollectible (bad debt expense). 10. Sales in November and December 2019 are expected to be $783,750 and $1,045,000 respectively. Based on the above collection pattern this will result in Accounts Receivable of $539,481 at December 31, 2019 which will be collected in January and February, 2020. 11. During the fiscal year ended December 31, 2020, Wooden Pull Toys will be required to make monthly income tax installment payments of $1,500. Outstanding income taxes from the year ended December 31, 2019 must be paid in March 2020. Income tax expense is estimated to be 25% of net income. Income taxes for the year ended December 31, 2020, in excess of installment payments, will be paid in March, 2021. 12. Wooden Pull Toys is planning to acquire additional manufacturing equipment for $304,200 cash. 40% of this amount is to be paid in January 2020, the rest, in February 2020. The manufacturing overhead costs shown above already include the depreciation on this equipment. 13. An arrangement has been made with the local bank that if Wooden Pull Toys maintains a minimum balance of $20,000 in their bank account, they will be given a line of credit at a preferred rate of 6% per annum. All borrowing is considered to happen on the first day of the month, repayments are on the last day of the month. All borrowings and repayments from the bank should be in multiples of $1,000 and interest must be paid at the end of each month. Interest is calculated on the balance at the beginning of the month, which includes any amounts borrowed that month. 14. Wooden Pull Toys Ltd. has a policy of paying dividends at the end of each quarter. The President tells you that the board of directors is planning on continuing their policy of declaring dividends of $50,000 per quarter. 15. A listing of the estimated balances in the company's ledger accounts as of December 31, 2019 is given below. Cash Accounts receivable Inventory-raw materials Inventory-finished goods Capital assets (net) $ 64,165 539,481 28,125 45,625 724,000 $ 1.401.396 Accounts payable Income tax payable Capital stock Retained earnings $ 167,084 21,500 1,000,000 212.813 $ 1.401396 Required: Prepare a master budget for Wooden Pull Toys for the first quarter (January, February and March) of the year ending December 31, 2020, including the following schedules: Sales Budget Schedule of Cash Receipts Production Budget Direct Materials Budget Schedule of Cash Disbursements Direct Labour Budget Manufacturing Overhead Budget Ending Finished Goods Inventory Budget Selling and Administrative Expense Budget Cash Budget Prepare a budgeted income statement for the quarter ended March 31, 2020 Prepare a budgeted balance sheet at March 31, 2020. For Quarter 2020 January March rch 5% 5% Quarter 20% 100,000 Percent of Annual Sales Expected Sales in Units Selling Price Per Unit Total Budgeted Sales February 10% 50,000 11 550,000 25,000 11 275,000 $ $ $ $ 25,000 11 275,000 $ $ $ 1,100,000 Sales Budget February March January 74,456 365,750 151,250 $ $ November Purchases December Purchases January Purchases February Purchases March Purchases Total 99,275 96,250 302,500 $ $ 26,125 192,500 151,250 369,875 Total 74,456 465,025 273,625 495,000 151,250 1,459,356 591.456 $ 498,025 $ $ cash collections March Budgeted Sales In Units Add: Desired Ending Inventory Total Needs Less: Beginning Inventory Required Production January 25,000 12,500 37,500 6,250 31,250 February 50,000 6,250 56,250 12,500 43,750 25,000 8,750 33,750 6,250 27,500 Quarter 100,000 8,750 108,750 6,250 102,500 production budget January March February 43,750 Quarter 102,500 31,250 27,500 Units to be produced Raw Materials Needed Per Unit Production Cost Add Desire Ending Inventory Total Needs Less Beginning Inventory Raw Materials To Be Purchased 156,250 87,500 243,750 62,500 181,250 218,750 55,000 273,750 87,500 186,250 137,500 65,000 202,500 55,000 147,500 512,500 65,000 577,500 62,500 515,000 Cost Of Per Kilogram Total Cost Of Purchases of 0.45 81,563 0.45 83,813 0.45 66,375 0.45 231,750 Materials Budget March January 31,250 1.30 $ 40,625 $ February 43,750 1.30 56,875 Quarter 102,500 1.30 133,250 $ $ $ 27,500 1.30 $ 35,750 $ $ Units Produced Variable Overhead Rate Per Unit Total Variable Manufacturing Overhead Costs Fixed Manufacturing Overhead Costs Training and development Repairs and maintenance Supervisors' salaries Depreciation on equipment Plant Insurance Other Total Fixed Manufacturing Overhead Total Manufacturing Overhead Less: Prepaid Insurance 3,600 3,250 12,450 14,900 8,000 9,800 52,000 92,625 8,000 $ $ $ $ $ $ $ $ $ 3,600 3,250 12,450 14,900 8,000 9,800 52,000 108,875 8,000 $ $ $ $ $ $ $ $ $ 3,600 $ 3,250 $ 12,450 $ 14,900 $ 8,000 $ 9,800 $ 52,000 $ 87,750 $ 8,000 $ 10,800 9,750 37,350 44,700 24,000 29,400 156,000 289,250 24,000 Less: Depreciation Cash Disbursements for manufactuing oh 14,900 69,725 $ $ 14,900 85,975 $ $ 14,900 64,850 $ $ 44,700 220,550 manufacturing overhead headStep by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it
Step: 1

Get Instant Access to Expert-Tailored Solutions
See step-by-step solutions with expert insights and AI powered tools for academic success
Step: 2

Step: 3

Ace Your Homework with AI
Get the answers you need in no time with our AI-driven, step-by-step assistance
Get Started


