Answered step by step
Verified Expert Solution
Question
1 Approved Answer
7.40. A random walk on a graph goes from vertex to adjacent vertex by walking along the connecting edge. It chooses the edge at
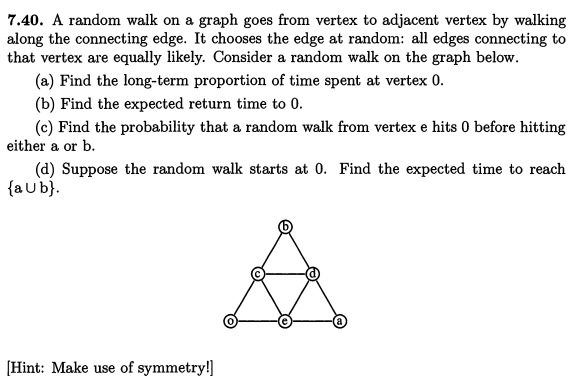
7.40. A random walk on a graph goes from vertex to adjacent vertex by walking along the connecting edge. It chooses the edge at random: all edges connecting to that vertex are equally likely. Consider a random walk on the graph below. (a) Find the long-term proportion of time spent at vertex 0. (b) Find the expected return time to 0. (c) Find the probability that a random walk from vertex e hits 0 before hitting either a or b. (d) Suppose the random walk starts at 0. Find the expected time to reach {a Ub}. [Hint: Make use of symmetry!] A
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it
Step: 1

Get Instant Access to Expert-Tailored Solutions
See step-by-step solutions with expert insights and AI powered tools for academic success
Step: 2

Step: 3

Ace Your Homework with AI
Get the answers you need in no time with our AI-driven, step-by-step assistance
Get Started


