Question: Design a voltage divider (see Example 19-3) that would provide one-fifth (0.20) of the battery voltage across R2, Fig. 19-6. What is the ratio

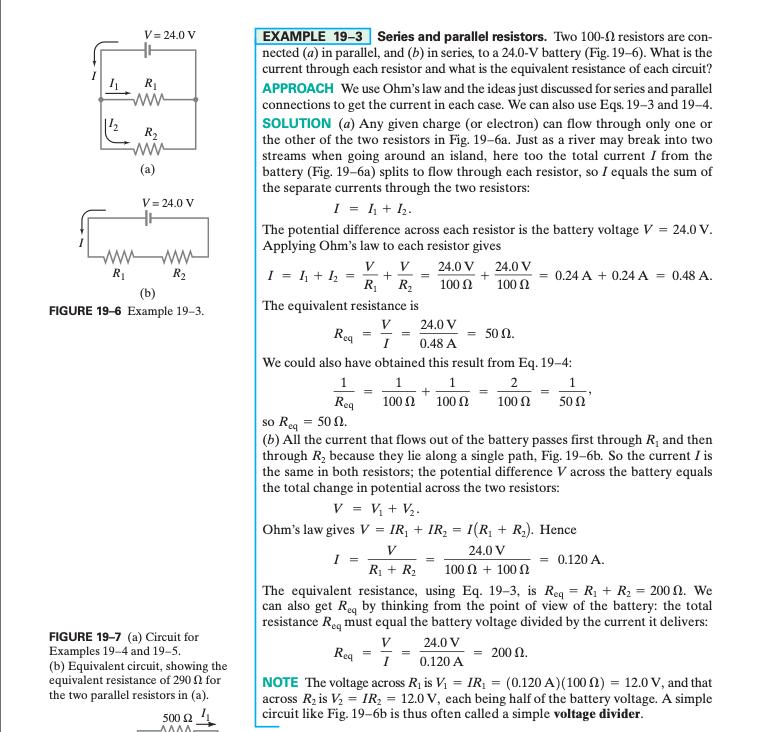
Design a "voltage divider" (see Example 19-3) that would provide one-fifth (0.20) of the battery voltage across R2, Fig. 19-6. What is the ratio R1/R2? 8. EXAMPLE 19-3 Series and parallel resistors. Two 100-N resistors are con- nected (a) in parallel, and (b) in series, to a 24.0-V battery (Fig. 19-6). What is the current through each resistor and what is the equivalent resistance of cach circuit? V = 24.0 V R1 ww APPROACH We use Ohm's law and the ideas just discussed for series and parallel connections to get the current in each case. We can also use Eqs. 19-3 and 19-4. SOLUTION (a) Any given charge (or electron) can flow through only one or the other of the two resistors in Fig. 19-6a. Just as a river may break into two streams when going around an island, here too the total current I from the battery (Fig. 19-6a) splits to flow through each resistor, so I equals the sum of the separate currents through the two resistors: R2 (a) V = 24.0 V I = 1, + . The potential difference across each resistor is the battery voltage V = 24.0 V. Applying Ohm's law to each resistor gives V R,' R, The equivalent resistance is wwwM R1 24.0 V V 24.0 V R2 I = 1 + h = 0.24 A + 0.24 A = 0.48 A. 100 N 100 N () FIGURE 19-6 Example 19-3. V 24.0 V Reg 50 . 0.48 A We could also have obtained this result from Eq. 19-4: 1 2 1 Reg 100 100 100 N 50 so Reg = 50 N. (b) All the current that flows out of the battery passes first through R, and then through R, because they lie along a single path, Fig. 19-6b. So the current I is the same in both resistors; the potential difference V across the battery equals the total change in potential across the two resistors: V = V + V2. Ohm's law gives V = IR, + IR, = 1(R, + R.). Hence V 24.0 V I = R + R2 = 0.120 A. 100 + 100 The equivalent resistance, using Eq. 19-3, is Req = R + R2 = 200 N. We can also get Reg by thinking from the point of view of the battery: the total resistance Reg must equal the battery voltage divided by the current it delivers: FIGURE 19-7 (a) Circuit for Examples 19-4 and 19-5. (b) Equivalent circuit, showing the equivalent resistance of 290 N for the two parallel resistors in (a). V 24.0 V Rea = 200 N. I 0.120 A NOTE The voltage across R, is V = IR; = (0.120 A)(100n) = 12.0 V, and that across R, is V, = IR, = 12.0 V, each being half of the battery voltage. A simple circuit like Fig. 19-6b is thus often called a simple voltage divider. %3D 500 1
Step by Step Solution
3.41 Rating (157 Votes )
There are 3 Steps involved in it
Q8 R1 R2 Vout given thaut Vo... View full answer

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


