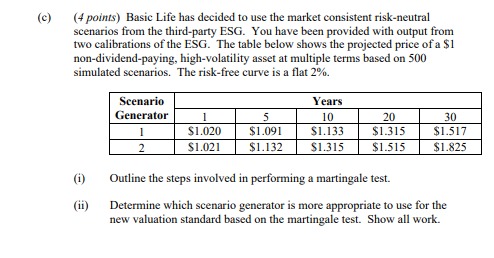
(8 points) Energetic's GUI companies all use the same model for evaluating external risks. The model was developed by Energetic and is run independently by each GUI in its Risk Management Department. Refer to section 0.11 of the Case Study. You are provided an overview of the External Risk Model (ExRM): The scenarios used in the model are evaluated and updated every two years . The model engine is evaluated and updated every four years by the department within Energetic that built the model . Model inputs (interest rates, market share, commodity prices, etc.) are updated quarterly . Model output is compared to the prior quarter's output to ensure reasonableness The following scenarios are used in the ExRM: Scenario # Scenario Description The temperature drops five degrees below the lowest recorded temperature for a period of ten days within a given year 2 State regulatory change in Colorado that increases GUI expenses by 10% but does not allow for an increase in rates charged 3 Supply of natural gas drops by 20% for a period of one year (a) (2 points) ExRM must include the following types of scenarios in the model: Global Scenario . . Multi-Event Scenario Synthetic Scenario Identify the type of scenario for each of the Scenarios 1, 2 and 3. Justify your response.(b) (2 points) You are asked to evaluate the ExRM using Model Validation Principles Applied to Risk and Capital Models as identified by the North American CRO Council. (i) Identify two Principles that Energetic follows. Justify your response. (ii) Identify two Principles that Energetic is clearly not following. Justify your response. (c) (2 points) Energetic plans to look at the external risks in aggregate for its three main operating businesses. Energetic instructed its other businesses to begin using the same ExRM and to include Scenario 2 and Scenario 3 in each of their models. Evaluate Scenario 2 and Scenario 3 for use in CR and EUI. (d) (2 points) Energetic's CRO has proposed that in order to determine the total exposure across the three main operating businesses, each business would identify its own top five risks, and Energetic would simply sum the resultant exposures. (i) Evaluate the CRO's proposed aggregation process. (1i) Propose an alternative aggregation approach.(1/ points) Basic Life sells life insurance and variable annuity products with guaranteed minimum benefits. A new insurance contract valuation standard, which requires market consistent valuation, is being released. (a) (1.5 points) You have been asked to apply the new standard to the company's variable annuity products. (i) Explain why stochastic scenarios would be appropriate to value the variable annuity liabilities. (ii) Assess whether risk-neutral scenarios are the appropriate type to use. (b) (1.5 points) Basic Life is considering purchasing a third-party economic scenario generator (ESG) for calculating its insurance contract liability under the new standard. The ESG is fully calibrated and parameterized for both real-world and market consistent risk-neutral scenarios. The following information is provided on the calibration and parameterization. . Risk-neutral scenarios o The model's calibration process is designed to reproduce the prices of traded derivatives o The underlying yield curve is as of the date of the derivative prices used to calibrate the model . Real-world scenarios o The model is calibrated to incorporate dynamics that are representative of the possible future paths of economic variables o The model is parameterized only using current market inputs Evaluate the calibration and parameterization of the ESG.(c) (4 points) Basic Life has decided to use the market consistent risk-neutral scenarios from the third-party ESG. You have been provided with output from two calibrations of the ESG. The table below shows the projected price of a $1 non-dividend-paying, high-volatility asset at multiple terms based on 500 simulated scenarios. The risk-free curve is a flat 2% Scenario Years Generator 5 10 20 30 $1.020 $1.091 $1.133 $1.315 $1.517 2 $1.021 $1.132 $1.315 $1.515 $1.825 (i) Outline the steps involved in performing a martingale test. (1i) Determine which scenario generator is more appropriate to use for the new valuation standard based on the martingale test. Show all work.(d) (2 points) Basic Life's current economic capital (EC) calculation uses deterministic scenarios. The CFO is concerned that the EC does not appropriately quantify the impact of a market downturn on guaranteed payouts associated with the variable annuity products. He tells you the company is considering using the new ESG to calculate EC to address this concern. (i) Explain whether the new risk-neutral ESG is appropriate to use for calculating EC for variable annuities. In addition, the CFO proposes that the following risk metrics be considered for quantifying the market risk: Value at Risk Standard Deviation . Tail Value at Risk (CTE) . Maximum Loss Recommend which of the proposed metrics is the most appropriate to quantify EC for market risk. Justify your choice. (e) (2 points) Basic Life is considering launching a single premium immediate annuity (SPIA) product. (i) Describe how launching a SPIA product could result in a diversification benefit for Basic Life. (1i) Compare and contrast the use of a correlation matrix versus a copula to reflect this diversification benefit in the EC calculation