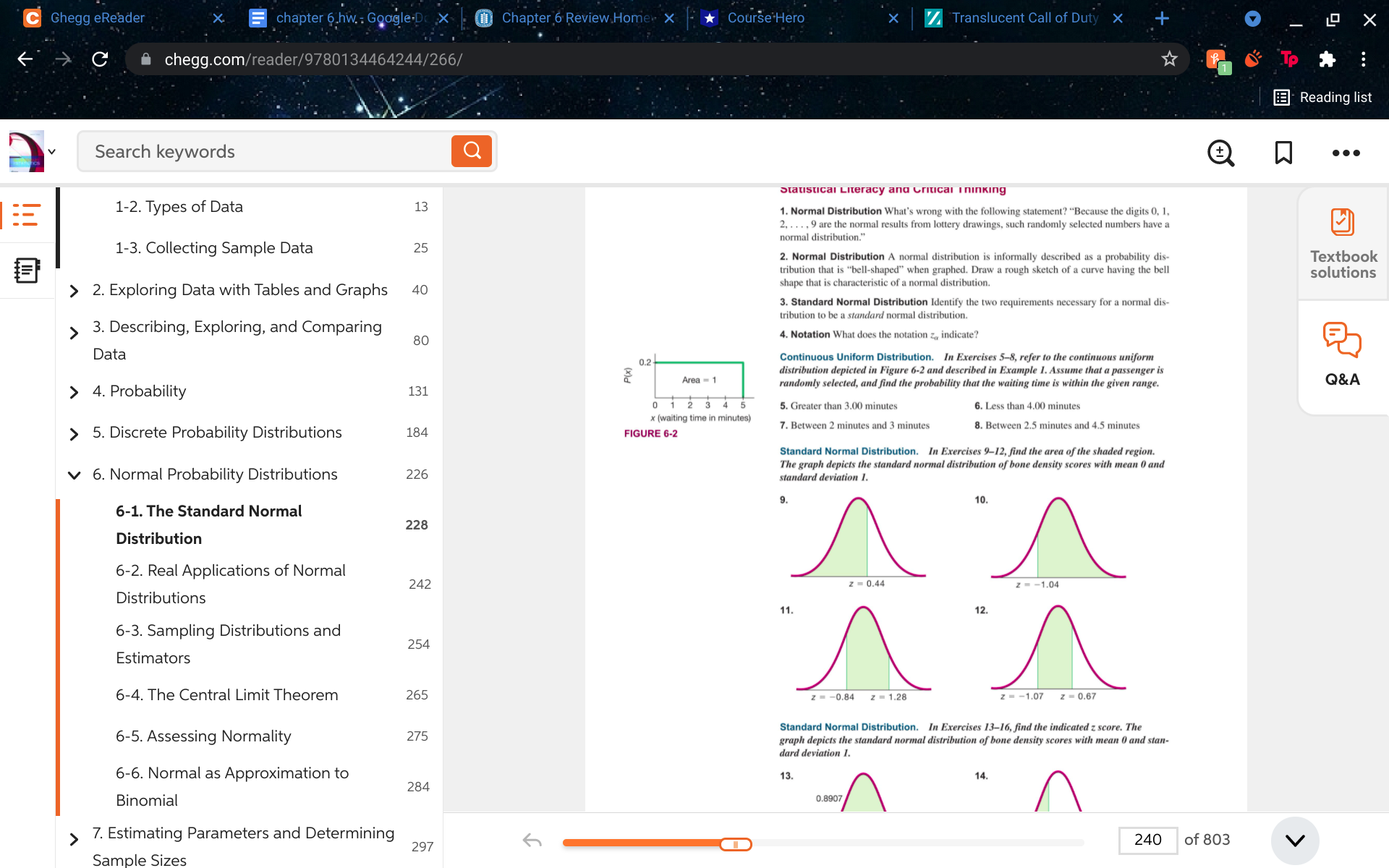
9, 10, 11, 12
C Chegg eReader chapter 6 hw. : Google.Dc X Chapter 6 Review Home X Course Hero X Translucent Call of Duty X 4 X C A chegg.com/reader/9780134464244/266/ To . .. Reading list 2 Search keywords Q . . . Statistical Literacy and critical I ninking 1-2. Types of Data 13 1. Normal Distribution What's wrong with the following statement? "Because the digits 0, 1, 2, . . . . 9 are the normal results from lottery drawings, such randomly selected numbers have a normal distribution." 1-3. Collecting Sample Data 25 2. Normal Distribution A normal distribution is informally described as a probability dis- Textbook tribution that is "bell-shaped" when graphed. Draw a rough sketch of a curve having the bell solutions > 2. Exploring Data with Tables and Graphs 40 shape that is characteristic of a normal distribution. 3. Standard Normal Distribution Identify the two requirements necessary for a normal dis- tribution to be a standard normal distribution. 3. Describing, Exploring, and Comparing 80 4. Notation What does the notation z, indicate? Data 0.2 Continuous Uniform Distribution. In Exercises 5-8, refer to the continuous uniform distribution depicted in Figure 6-2 and described in Example 1. Assume that a passenger is Area = 1 Q&A > 4. Probability randomly selected, and find the probability that the waiting time is within the given range. 131 0 1 2 3 4 5 5. Greater than 3.00 minutes 6. Less than 4.00 minutes x (waiting time in minutes) > 5. Discrete Probability Distributions 184 7. Between 2 minutes and 3 minutes 8. Between 2.5 minutes and 4.5 minutes FIGURE 6-2 Standard Normal Distribution. In Exercises 9-12, find the area of the shaded region. The graph depicts the standard normal distribution of bone density scores with mean 0 and 6. Normal Probability Distributions 226 standard deviation 1. 10. 6-1. The Standard Normal 228 Distribution 6-2. Real Applications of Normal 242 z = 0.44 Z = -1.04 Distributions 11. 12. 6-3. Sampling Distributions and 254 Estimators 6-4. The Central Limit Theorem 265 z = -0.84 z = 1.28 z = -1.07 z = 0.67 6-5. Assessing Normality Standard Normal Distribution. In Exercises 13-16, find the indicated z score. The 275 graph depicts the standard normal distribution of bone density scores with mean 0 and stan- dard deviation 1. 6-6. Normal as Approximation to 13 14. 284 Binomial 0.8907 > 7. Estimating Parameters and Determining 297 240 of 803 V Sample Sizes