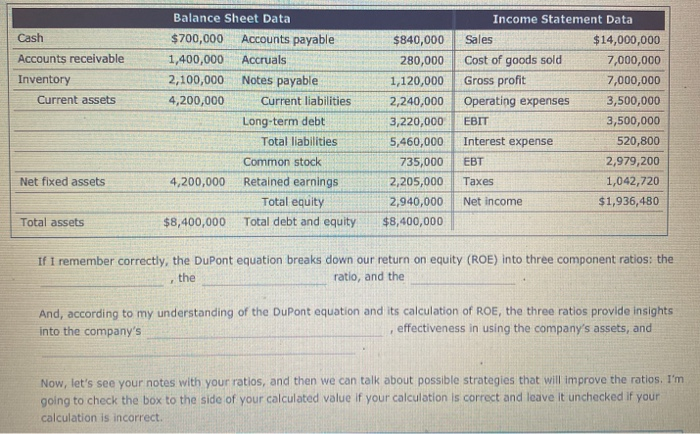
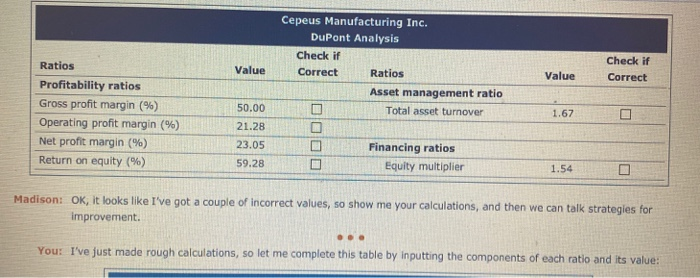
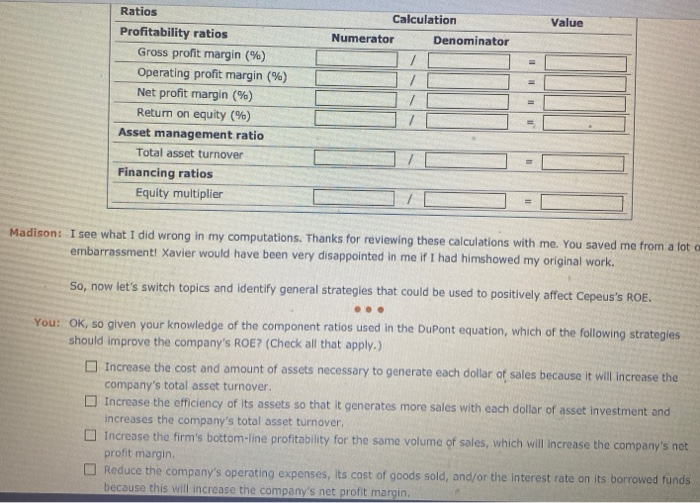
9. An analysis of company performance using DuPont analysis Walking down the hall of your office building with a sheaf of papers in her hand, your friend and colleague, Madison, stepped into your office and asked the following. Madison: Do you have 10 or 15 minutes that you can spare? You: Sure, I've got a meeting in an hour, but I don't want to start something new and then be interrupted by the meeting, so how can I help? Madison: I've been reviewing the company's financial statements and looking for general ways to improve our performance, in general, and the company's return on equity, or ROE, in particular. Xavier, my new team leader, suggested that I start by using a DuPont analysis, and I'd like to run my numbers and conclusions by you, to see if I've missed anything. Here are the balance sheet and income statement data that Xavier gave me, and here are my notes with my calculations. Could you start by making sure that my numbers are correct? You Give me a minute to look at these financial statements and to remember what I know about the DuPont analysis. Cash Accounts receivable Inventory Current assets Balance Sheet Data $700,000 Accounts payable 1,400,000 Accruals 2,100,000 Notes payable 4,200,000 Current liabilities Long-term debt Total liabilities Common stock 4,200,000 Retained earnings Total equity $8,400,000 Total debt and equity $840,000 280,000 1,120,000 2,240,000 3,220,000 5,460,000 735,000 2,205,000 2,940,000 $8,400,000 Income Statement Data Sales $ 14,000,000 Cost of goods sold 7 ,000,000 Gross profit 7,000,000 Operating expenses 3,500,000 EBIT 3,500,000 Interest expense 520,800 EBT 2,979,200 Taxes 1,042,720 Net income $1,936,480 Net fixed assets Total assets If I remember correctly, the DuPont equation breaks down our return on equity (ROE) into three component ratios: the ratio, and the And, according to my understanding of the DuPont equation and its calculation of ROE, the three ratios provide insights into the company's effectiveness in using the company's assets, and Now, let's see your notes with your ratios, and then we can talk about possible strategies that will improve the ratios. I'm going to check the box to the side of your calculated value if your calculation is correct and leave it unchecked if your calculation is incorrect. Cepeus Manufacturing Inc. DuPont Analysis Check if Correct Ratios Asset management ratio Total asset turnover Check if Correct Ratios Value Value Profitability ratios Gross profit margin (%) Operating profit margin (%) Net profit margin (%) Return on equity (%) 50.00 21.28 23.05 Financing ratios Equity multiplier 59.28 Madison: OK, it looks like I've got a couple of incorrect values, so show me your calculations, and then we can talk strategies for Improvement. You: I've just made rough calculations, so let me complete this table by inputting the components of each ratio and its value: Value Calculation Numerator Denominator Ratios Profitability ratios Gross profit margin (%) Operating profit margin (%) Net profit margin (%) Return on equity (%) Asset management ratio Total asset turnover Financing ratios Equity multiplier Madison: I see what I did wrong in my computations. Thanks for reviewing these calculations with me. You saved me from a lot embarrassment Xavier would have been very disappointed in me if I had himshowed my original work. So, now let's switch topics and identify general strategies that could be used to positively affect Cepeus's ROE You: OK, so given your knowledge of the component ratios used in the DuPont equation, which of the following strategies should improve the company's ROE? (Check all that apply.) Increase the cost and amount of assets necessary to generate each dollar of sales because it will increase the company's total asset turnover. Increase the efficiency of its assets so that it generates more sales with each dollar of asset investment and increases the company's total asset turnover. Increase the firm's bottom-line profitability for the same volume of sales, which will increase the company's net profit margin. Reduce the company's operating expenses, its cost of goods sold, and/or the interest rate on its borrowed funds because this will increase the company's net profit margin