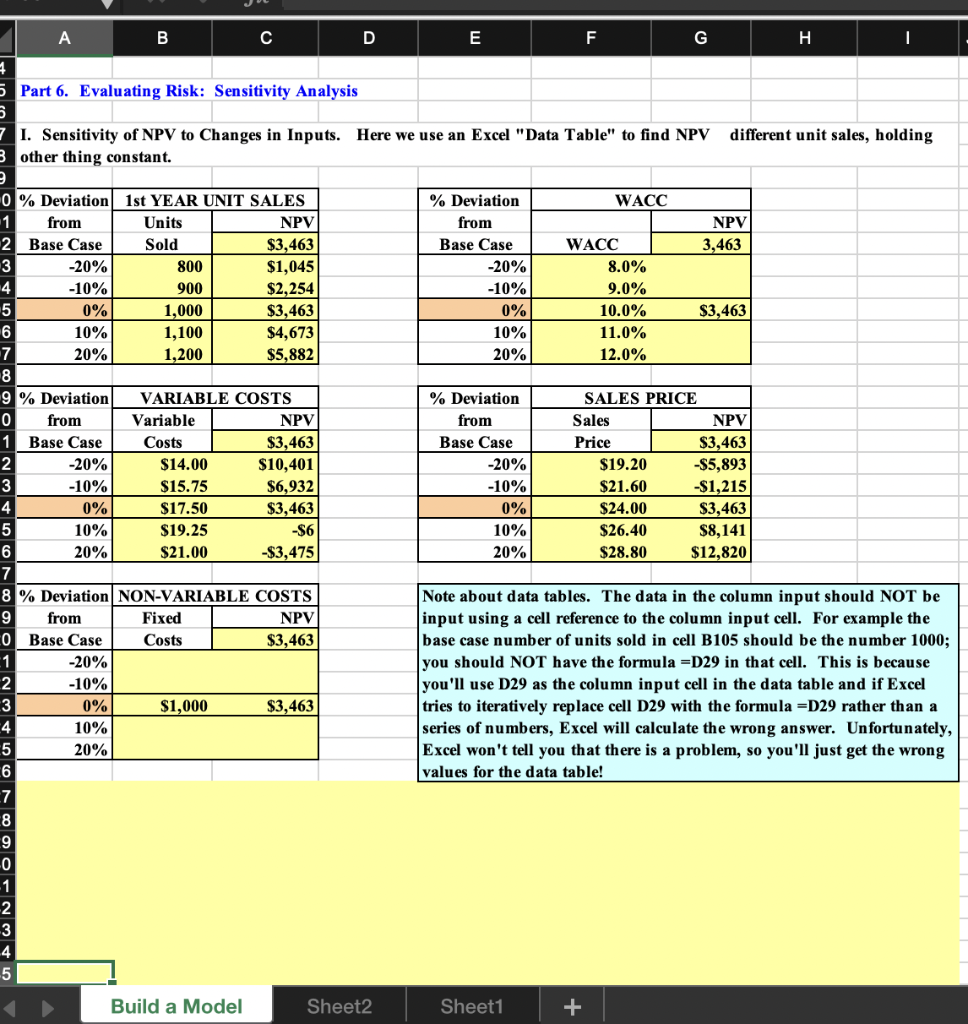
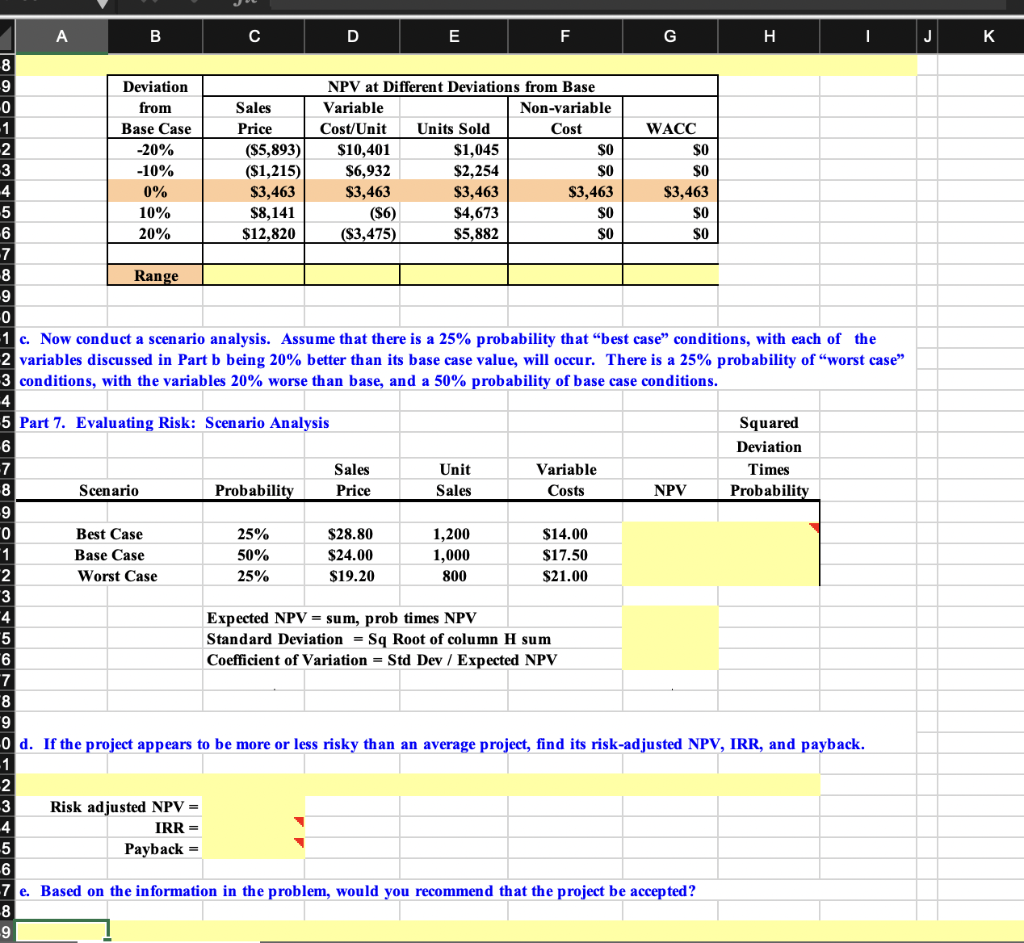
A B C D E F G H I 24 5 Part 6. Evaluating Risk: Sensitivity Analysis different unit sales, holding 7 I. Sensitivity of NPV to Changes in Inputs. Here we use an Excel "Data Table" to find NPV 3 other thing constant. WACC NPV 3,463 % Deviation from Base Case -20% -10% 0% 10% 20% WACC 8.0% 9.0% 10.0% 11.0% 12.0% $3,463 $3,463 % Deviation from Base Case -20% -10% SALES PRICE Sales NPV Price $3,463 $19.20 -S5,893 $21.60 -$1,215 $24.00 $3,463 $26.40 $8,141 $28.80 $12,820 0% 10% 20% 0% Deviation 1st YEAR UNIT SALES 1 from Units NPV 2 Base Case Sold $3,463 3 -20% 800 $1,045 4 -10% 900 $2,254 5 0% 1,000 $3,463 6 10% 1,100 $4,673 7 20% 1,200 $5,882 8 9 % Deviation VARIABLE COSTS 0 from Variable NPV 1 Base Case Costs 2 -20% $14.00 $10,401 3 -10% $15.75 $6,932 4 0% $17.50 $3,463 5 10% $19.25 -$6 6 20% $21.00 -$3,475 7 8 % Deviation NON-VARIABLE COSTS 9 from Fixed NPV O Base Case Costs $3,463 1 -20% 2 3 0% $1,000 $3,463 4 10% 5 20% 6 7 8 9 -0 -1 2 3 4 5 -10% Note about data tables. The data in the column input should NOT be input using a cell reference to the column input cell. For example the base case number of units sold in cell B105 should be the number 1000; you should NOT have the formula =D29 in that cell. This is because you'll use D29 as the column input cell in the data table and if Excel tries to iteratively replace cell D29 with the formula =D29 rather than a series of numbers, Excel will calculate the wrong answer. Unfortunately, Excel won't tell you that there is a problem, so you'll just get the wrong values for the data table! Build a Model Sheet2 Sheet1 + J K Price A B D E G H 8 9 Deviation NPV at Different Deviations from Base -0 from Sales Variable Non-variable -1 Base Case Cost/Unit Units Sold Cost WACC 2 -20% ($5,893) $10,401 $1,045 SO $0 3 -10% ($1,215) $6,932 $2,254 SO $0 4 0% $3,463 $3,463 $3,463 $3,463 $3,463 5 10% $8,141 (56) $4,673 $0 $0 -6 20% $12,820 ($3,475) $5,882 SO $0 7 8 Range 9 0 1 c. Now conduct a scenario analysis. Assume that there is a 25% probability that "best case" conditions, with each of the 2 variables discussed in Part b being 20% better than its base case value, will occur. There is a 25% probability of worst case 3 conditions, with the variables 20% worse than base, and a 50% probability of base case conditions. 4 5 Part 7. Evaluating Risk: Scenario Analysis Squared 6 Deviation -7 Sales Unit Variable Times 8 Scenario Probability Price Sales Costs NPV Probability 9 0 Best Case 25% $28.80 1,200 $14.00 1 Base Case 50% $24.00 1,000 $17.50 2 Worst Case 25% $19.20 800 $21.00 3 4 Expected NPV = sum, prob times NPV 5 Standard Deviation = Sq Root of column H sum "6 Coefficient of Variation = Std Dev / Expected NPV 7 8 "9 0 d. If the project appears to be more or less risky than an average project, find its risk-adjusted NPV, IRR, and payback. 1 2 3 Risk adjusted NPV = 4 IRR - 5 Payback - -6 7 e. Based on the information in the problem, would you recommend that the project be accepted? 8 9 A B C D E F G H I 24 5 Part 6. Evaluating Risk: Sensitivity Analysis different unit sales, holding 7 I. Sensitivity of NPV to Changes in Inputs. Here we use an Excel "Data Table" to find NPV 3 other thing constant. WACC NPV 3,463 % Deviation from Base Case -20% -10% 0% 10% 20% WACC 8.0% 9.0% 10.0% 11.0% 12.0% $3,463 $3,463 % Deviation from Base Case -20% -10% SALES PRICE Sales NPV Price $3,463 $19.20 -S5,893 $21.60 -$1,215 $24.00 $3,463 $26.40 $8,141 $28.80 $12,820 0% 10% 20% 0% Deviation 1st YEAR UNIT SALES 1 from Units NPV 2 Base Case Sold $3,463 3 -20% 800 $1,045 4 -10% 900 $2,254 5 0% 1,000 $3,463 6 10% 1,100 $4,673 7 20% 1,200 $5,882 8 9 % Deviation VARIABLE COSTS 0 from Variable NPV 1 Base Case Costs 2 -20% $14.00 $10,401 3 -10% $15.75 $6,932 4 0% $17.50 $3,463 5 10% $19.25 -$6 6 20% $21.00 -$3,475 7 8 % Deviation NON-VARIABLE COSTS 9 from Fixed NPV O Base Case Costs $3,463 1 -20% 2 3 0% $1,000 $3,463 4 10% 5 20% 6 7 8 9 -0 -1 2 3 4 5 -10% Note about data tables. The data in the column input should NOT be input using a cell reference to the column input cell. For example the base case number of units sold in cell B105 should be the number 1000; you should NOT have the formula =D29 in that cell. This is because you'll use D29 as the column input cell in the data table and if Excel tries to iteratively replace cell D29 with the formula =D29 rather than a series of numbers, Excel will calculate the wrong answer. Unfortunately, Excel won't tell you that there is a problem, so you'll just get the wrong values for the data table! Build a Model Sheet2 Sheet1 + J K Price A B D E G H 8 9 Deviation NPV at Different Deviations from Base -0 from Sales Variable Non-variable -1 Base Case Cost/Unit Units Sold Cost WACC 2 -20% ($5,893) $10,401 $1,045 SO $0 3 -10% ($1,215) $6,932 $2,254 SO $0 4 0% $3,463 $3,463 $3,463 $3,463 $3,463 5 10% $8,141 (56) $4,673 $0 $0 -6 20% $12,820 ($3,475) $5,882 SO $0 7 8 Range 9 0 1 c. Now conduct a scenario analysis. Assume that there is a 25% probability that "best case" conditions, with each of the 2 variables discussed in Part b being 20% better than its base case value, will occur. There is a 25% probability of worst case 3 conditions, with the variables 20% worse than base, and a 50% probability of base case conditions. 4 5 Part 7. Evaluating Risk: Scenario Analysis Squared 6 Deviation -7 Sales Unit Variable Times 8 Scenario Probability Price Sales Costs NPV Probability 9 0 Best Case 25% $28.80 1,200 $14.00 1 Base Case 50% $24.00 1,000 $17.50 2 Worst Case 25% $19.20 800 $21.00 3 4 Expected NPV = sum, prob times NPV 5 Standard Deviation = Sq Root of column H sum "6 Coefficient of Variation = Std Dev / Expected NPV 7 8 "9 0 d. If the project appears to be more or less risky than an average project, find its risk-adjusted NPV, IRR, and payback. 1 2 3 Risk adjusted NPV = 4 IRR - 5 Payback - -6 7 e. Based on the information in the problem, would you recommend that the project be accepted? 8 9








