Answered step by step
Verified Expert Solution
Question
1 Approved Answer
A B D E F G H 1 Click on the NPV and IRR tab and enter your name in Cell C1. If Cell

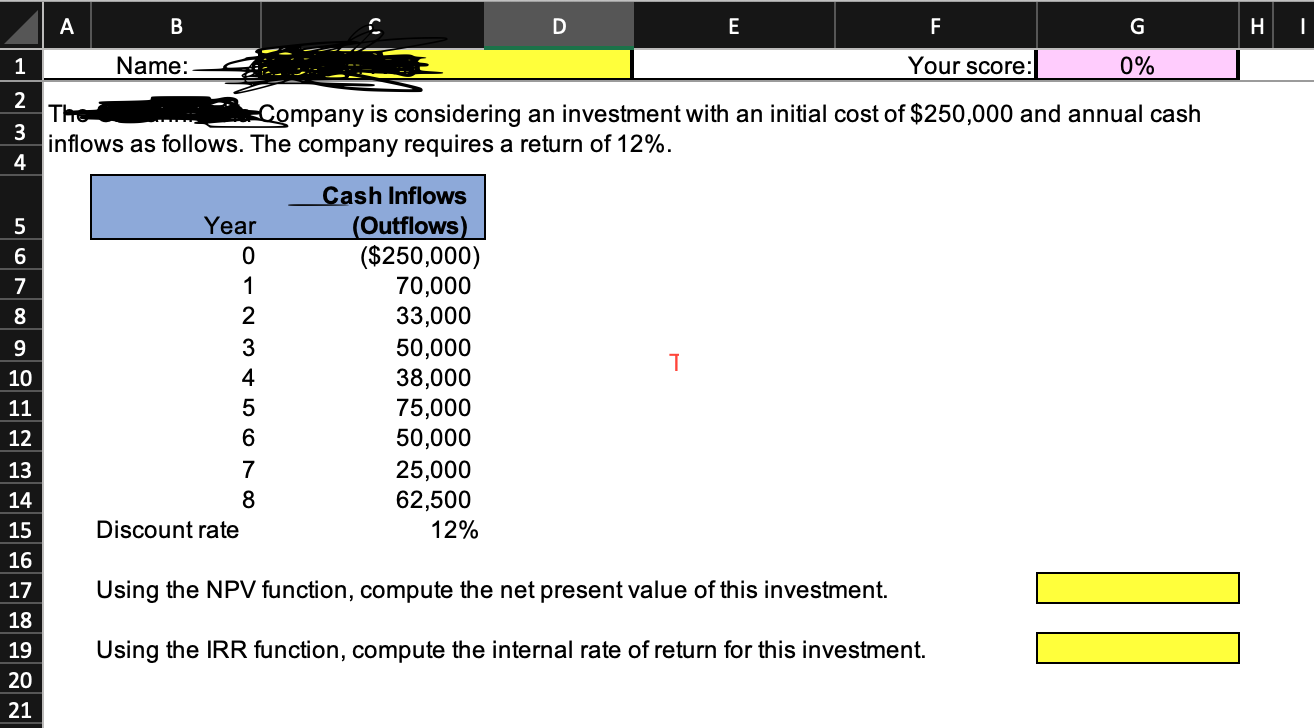
A B D E F G H 1 Click on the "NPV and IRR" tab and enter your name in Cell C1. If Cell C1 is left blank, you will not be able to see your score. 2 Each yellow cell requires a formula. 3 The formula must only contain cell addresses. 4 Each correct formula will begin with =, +, or -. 5 The basic mathematical operators are +, -, * and / 6 Addition: To add the values in cells A1 and B4, the formula is =A1+B4 7 Subtraction: To subtract the value in cell B4 from the value in cell A1, the formula is =A1-B4 8 Multiplication: To multiply the values in cells A1 and B4, the formula is =A1*B4 9 Division: To divide the value in cell A1 by the value in cell B4, the formula is =A1/B4 10 11 Using the NPV function. The NPV function returns the net present value of an investment based on a discount rate and a series of future 12 cash outflows (negative values) and cash inflows (positive values). 13 The NPV function has the following syntax: =NPV(Rate, Value1, [Value2]...) 14 Value 1 must be the amount of cashflow at the END of the first period. 15 The initial cash flow must be added in separately, and is NOT part of the NPV formula. 16 17 Using the IRR function. The IRR function returns rate of return of a given series of cash flows. 18 The IRR function has the following syntax: 19 20 Using absolute addresses 22 =IRR(Values, [Guess]) 21 Once a formula is created, you will often want to copy the formula to other columns and rows. It's important to understand that excel always uses "relative addresses" unless you indicate otherwise by creating an "absolute address". For example, if you are calculating the cost of purchasing 2 boxes of cereal at a cost of $3.95 per box, the formula in cell B28 is =B26*B27. Although we read cell B28 as "Multiply 2 boxes by $3.95", Excel is actually calculating the value in cell B28 as "Multiply the value in the cell in the same column (column B) 2 rows above (row 26) by the value in the cell in the same column 1 row above (row 27). 23 24 25 26 Boxes of cereal 2 6 11 15 27 Price per box 28 Total cost $3.95 $7.90 $23.70 $43.45 $59.25 29 30 This works just fine to calculate the cost of 2 boxes, but if we copy the formula in cell B28 to C28, Excel will assume relative references. The formula in 31 cell C28 will become =C26*C27. Since Cell C27 is blank, the formula will return a value of $0 (which is an excellent deal for 6 boxes of cereal, but it isn't 32 accurate!) Adding a $ sign before the column or row reference locks the formula to a specific location. 33 34 35 If we modify the formula in cell B28 to =B26*$B$27 before we copy the formula, Excel will not change the row or the column of the second variable. 36 When the formula is copied to columns C through E, the formulas become: 37 38 39 Cell C28 =C26*$B$27 Cell D28 =D26*$B$27 40 41 Cell E28 =E26*$B$27 42 Sometimes, you will want the column to stay fixed, but allow the row to remain relative when it's copied. If so, add a dollar sign before the column, but 43 not the row (i.e.$B27) If you want the row to stay fixed, but allow the column to remain relative when it's copied, add a dollar sign before the row, but 44 not the column (i.e. B$27). Tapping the F4 button while entering the formula (or in the formula bar) toggles among the 3 absolute options (Absolute 45 Column and Absolute Row $B$28, Absolute Column and Relative Row $B28, Relative Column and Absolute Row B$28) 46 47 48 49 50 51 A B 1 Name: 2 The 3 4 D E F G H | Your score: 0% Company is considering an investment with an initial cost of $250,000 and annual cash inflows as follows. The company requires a return of 12%. Cash Inflows 5698 Year 0 (Outflows) ($250,000) 7 1 70,000 2 33,000 9 3 50,000 T 10 4 38,000 11 5 75,000 12 6 50,000 13 7 25,000 14 8 62,500 15 Discount rate 12% 16 17 Using the NPV function, compute the net present value of this investment. 18 19 Using the IRR function, compute the internal rate of return for this investment. 20 21
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it
Step: 1

Get Instant Access to Expert-Tailored Solutions
See step-by-step solutions with expert insights and AI powered tools for academic success
Step: 2

Step: 3

Ace Your Homework with AI
Get the answers you need in no time with our AI-driven, step-by-step assistance
Get Started


