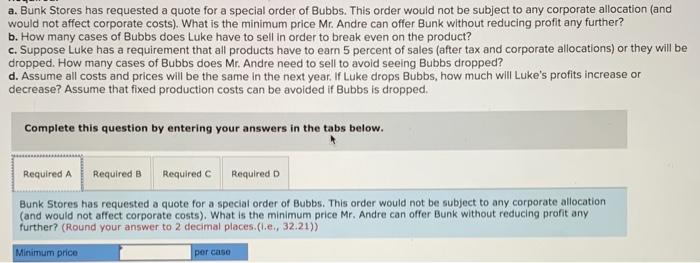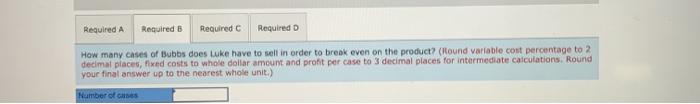

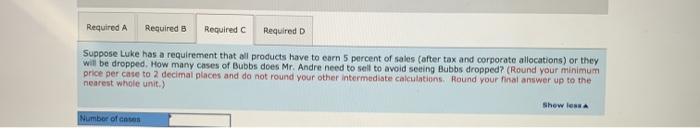
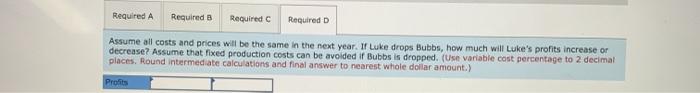
a. Bunk Stores has requested a quote for a special order of Bubbs. This order would not be subject to any corporate allocation (and would not affect corporate costs). What is the minimum price Mr. Andre can offer Bunk without reducing profit any further? b. How many cases of Bubbs does Luke have to sell in order to break even on the product? c. Suppose Luke has a requirement that all products have to earn 5 percent of sales (after tax and corporate allocations) or they will be dropped. How many cases of Bubbs does Mr. Andre need to sell to avoid seeing Bubbs dropped? d. Assume all costs and prices will be the same in the next year. If Luke drops Bubbs, how much will Luke's profits increase or decrease? Assume that fixed production costs can be avoided if Bubbs is dropped. Complete this question by entering your answers in the tabs below. Required A Required B Required C Required D Bunk Stores has requested a quote for a special order of Bubbs. This order would not be subject to any corporate allocation (and would not affect corporate costs). What is the minimum price Mr. Andre can offer Bunk without reducing profit any further? (Round your answer to 2 decimal places.cl.e., 32.21)) Minimum price por case Required A Required B Required C Required How many cases of Bubbs does Luke have to sell in order to break even on the product? (Round variable cost percentage to 2 decimal places, fixed costs to whole dollar amount and profit per case to 3 decimal places for intermediate calculations, Round your final answer up to the nearest whole unit.) Number of cases Required A Required Required c Required D Assume all costs and prices will be the same in the next year. If Luke drops Bubbs, how much will Luke's profits increase or decrease? Assume that fixed production costs can be avoided If Bubbs is dropped. (Use variable cost percentage to 2 decimal places. Round intermediate cakculations and final answer to nearest whole dollar amount.) Puas Required A Required Required c Required D Suppose Luke has a requirement that all products have to earn 5 percent of sales (after tax and corporate allocations) or they will be dropped. How many cases of Bubbs does Mr. Andre need to sell to avoid seeing Bubbs dropped? (Round your minimum price per case to 2 decimal places and do not round your other intermediate calculations. Round your final answer up to the nearest whole unit.) Show less Number of cases Required A Required B Required Required D Assume all costs and prices will be the same in the next year. If Luke drops Bubbs, how much will Luke's profits increase or decrease? Assume that fixed production costs can be avoided if Bubbs is dropped. (Use variable cost percentage to 2 decimal places. Round intermediate calculations and final answer to nearest whole dollar amount.) Profits Luke Corporation produces a variety of products, each within their own division. Last year, the managers at Luke developed and began marketing a new chewing gum, Bubbs, to sell in vending machines. The product, which sells for $5.30 per case, has not had the market success that managers expected and the company is considering dropping Bubbs. The product-line Income statement for the past 12 months follows: $ 14,683, 650 Revenue Costs Manufacturing costs Allocated corporate costo (5) Product-line margin Allowance for tax (208) Product-line profit (loss) $ 14,440,895 734,183 15, 175,078 $ (491,428) 98,285 $ (393,143) All products at Luke receive an allocation of corporate overhead costs, which is computed as 5 percent of product revenue. The 5 percent rate is computed based on the most recent year's corporate cost as a percentage of revenue. Data on corporate costs and revenues for the past two years follow: Most recent year Previous year Corporate Revenue Corporate Overhead Costa $ 107,750,000 $ 5,387,500 76,300,000 4,683,020 Roy O. Andre, the product manager for Bubbs, is concerned about whether the product will be dropped by the company and has employed you as a financial consultant to help with some analysis. In addition to the information given, Mr. Andre provides you with the following data on product costs for Bubbs: Month 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 B 9 10 11 12 Canes 208,000 217.700 215,400 229,000 224,900 238,000 220,700 247, 700 239,300 253,100 250,700 259,700 Production Conta $1,143,328 1,164,828 1,173,481 1,189,023 1,191,32 1,212,173 1,187,199 1,230,274 1,228,726 1,240,825 1,245,260 1,275,951 a. Bunk Stores has requested a quote for a special order of Bubbs. This order would not be subject to any corporate allocation (and would not affect corporate costs). What is the minimum price Mr. Andre can offer Bunk without reducing profit any further? b. How many cases of Bubbs does Luke have to sell in order to break even on the product? c. Suppose Luke has a requirement that all products have to earn 5 percent of sales (after tax and corporate allocations) or they will be dropped. How many cases of Bubbs does Mr. Andre need to sell to avoid seeing Bubbs dropped? d. Assume all costs and prices will be the same in the next year. If Luke drops Bubbs, how much will Luke's profits increase or decrease? Assume that fixed production costs can be avoided if Bubbs is dropped. Complete this question by entering your answers in the tabs below. Required A Required B Required C Required D Bunk Stores has requested a quote for a special order of Bubbs. This order would not be subject to any corporate allocation (and would not affect corporate costs). What is the minimum price Mr. Andre can offer Bunk without reducing profit any further? (Round your answer to 2 decimal places.cl.e., 32.21)) Minimum price por case Required A Required B Required C Required How many cases of Bubbs does Luke have to sell in order to break even on the product? (Round variable cost percentage to 2 decimal places, fixed costs to whole dollar amount and profit per case to 3 decimal places for intermediate calculations, Round your final answer up to the nearest whole unit.) Number of cases Required A Required Required c Required D Assume all costs and prices will be the same in the next year. If Luke drops Bubbs, how much will Luke's profits increase or decrease? Assume that fixed production costs can be avoided If Bubbs is dropped. (Use variable cost percentage to 2 decimal places. Round intermediate cakculations and final answer to nearest whole dollar amount.) Puas Required A Required Required c Required D Suppose Luke has a requirement that all products have to earn 5 percent of sales (after tax and corporate allocations) or they will be dropped. How many cases of Bubbs does Mr. Andre need to sell to avoid seeing Bubbs dropped? (Round your minimum price per case to 2 decimal places and do not round your other intermediate calculations. Round your final answer up to the nearest whole unit.) Show less Number of cases Required A Required B Required Required D Assume all costs and prices will be the same in the next year. If Luke drops Bubbs, how much will Luke's profits increase or decrease? Assume that fixed production costs can be avoided if Bubbs is dropped. (Use variable cost percentage to 2 decimal places. Round intermediate calculations and final answer to nearest whole dollar amount.) Profits Luke Corporation produces a variety of products, each within their own division. Last year, the managers at Luke developed and began marketing a new chewing gum, Bubbs, to sell in vending machines. The product, which sells for $5.30 per case, has not had the market success that managers expected and the company is considering dropping Bubbs. The product-line Income statement for the past 12 months follows: $ 14,683, 650 Revenue Costs Manufacturing costs Allocated corporate costo (5) Product-line margin Allowance for tax (208) Product-line profit (loss) $ 14,440,895 734,183 15, 175,078 $ (491,428) 98,285 $ (393,143) All products at Luke receive an allocation of corporate overhead costs, which is computed as 5 percent of product revenue. The 5 percent rate is computed based on the most recent year's corporate cost as a percentage of revenue. Data on corporate costs and revenues for the past two years follow: Most recent year Previous year Corporate Revenue Corporate Overhead Costa $ 107,750,000 $ 5,387,500 76,300,000 4,683,020 Roy O. Andre, the product manager for Bubbs, is concerned about whether the product will be dropped by the company and has employed you as a financial consultant to help with some analysis. In addition to the information given, Mr. Andre provides you with the following data on product costs for Bubbs: Month 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 B 9 10 11 12 Canes 208,000 217.700 215,400 229,000 224,900 238,000 220,700 247, 700 239,300 253,100 250,700 259,700 Production Conta $1,143,328 1,164,828 1,173,481 1,189,023 1,191,32 1,212,173 1,187,199 1,230,274 1,228,726 1,240,825 1,245,260 1,275,951