Answered step by step
Verified Expert Solution
Question
1 Approved Answer
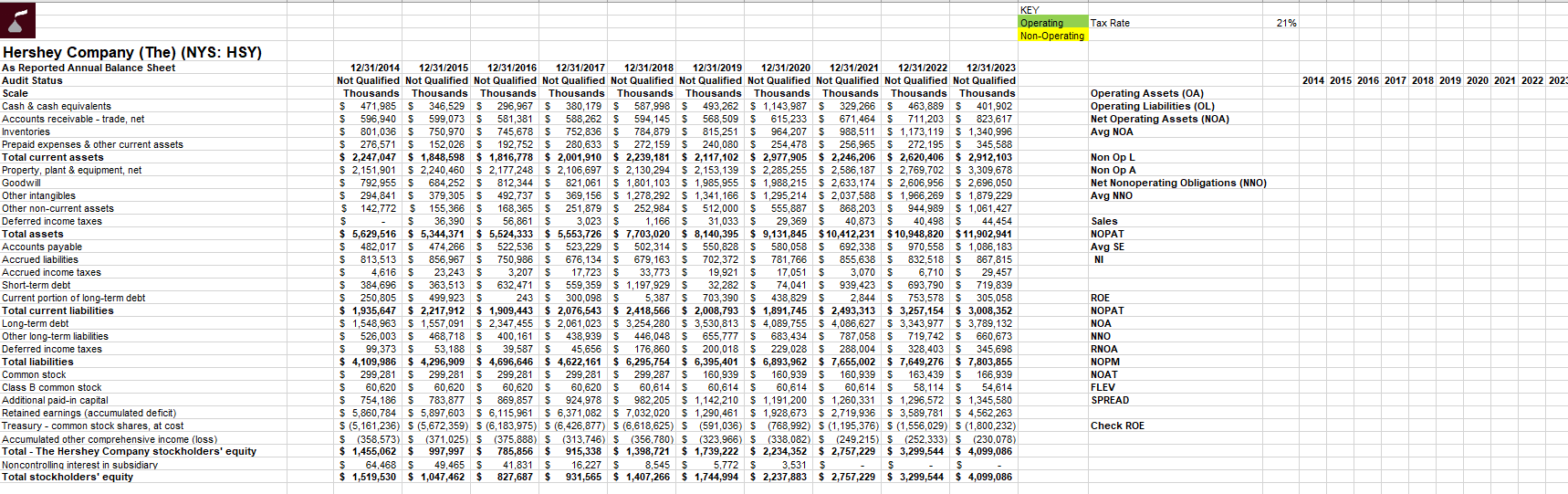
a . Classify all income statement and balance sheet items as either operating or non - operating. Highlight all operating items in green and all
a Classify all income statement and balance sheet items as either operating or nonoperating. Highlight all operating items in green and all nonoperating items in yellow. For classifications that are subject to debate ie nontraditional accounts that were not covered in the textbook or videos provide arguments to support your classification. You can use a cell comment or a textbox to provide your arguments.
b Perform a complete disaggregation of ROE for each of the years in the tables. Please show Excel Calculations. Include the results of your analysis on the Summary tab of the Excel file. Use formulas in Excel to compute the components of ROE so that I can replicate your work. You should assume that the statutory tax rate including both federal and state taxes is for the last few years
Ratios Summary Sheet Not Comprehensive, but Pretty Close for ACCT
Profitability Ratios:
Return on Equity ROE: Net Income NI Average Stockholders Equity
Return on Assets ROA: Net Income NI Average Total Assets ATA
Adj ROA: Net income AfterTax Interest Expense Minority Interest ATA
Profit Margin PM: Net Income NI Net Sales Revenue
Asset Turnover AT: Net Sales Revenue Average Total Assets
We sometimes Adjust the NI number above for onetime items and other AQ Issues.
Gross Profit Ratio GPR: Net Sales Revenue Cost of Goods Sold Net Sales Revenue
Dividend Yield DY: Dividends Per Share DPS Stock Price
Earnings Per Share EPS: NI Divs on Preferred Stock Weighted Avg. # of Common Shares Outstanding
PriceEarnings Ratios PE: Stock Price SP Earnings Per Share EPS
Cash Return on Assets CROA: Operating Cash Flows CFO Average Total Assets ATA
Cash Flows to Sale CFS: Operating Cash Flows CFO Sales
Operating Profitability Ratios:
Net Operating Profit Before Tax NOPBT: Op Revenue Op Expenses ie before Interest and Tax
Net Operating Profit After Tax NOPAT: NOPBT Tax on Operating Profit
Tax on Operating Profit Tax Expense Pretax NonOp Expense Income x Statutory Tax Rate
If firms have Income net of Expenses from Interest then you subtract not add the Tax Shield
Tax Shield Pretax Nonoperating Expense x Statutory Tax Rate
Net Operating Assets NOA Operating Assets Operating Liabilities
Return on Net Operating Assets RNOA NOPAT Average NOA
Net Nonoperating Obligations NNO Nonoperating Liabilities Nonoperating Assets
If firms have more Nonoperating Assets than Liabilities this would be a negative number
Return on Equity ROE: RNOA Nonoperating Return
Financial Leverage FLEV: Average NNO Average Total Stockholders Equity
Nonoperating Return Financial Leverage FLEV x Spread
Net Nonoperating Expense Percentage NNEP: NOPAT Consolidated Net Income
Alt NNEP: Nonoperating Expenses x Statutory Tax Rate
Spread RNOA Net Nonoperating Expense Percentage NNEP
NNEP NNE Average NNO
Efficiency Ratios Somewhat Profitability, Somewhat Liquidity:
Accounts Receivable Turnover ART: Net Credit Sales or Sales Average AR
Average Collection Period: Accounts Receivable Turnover
Inventory Turnover Ratio INVTR: Cost of Goods Sold Average Inventory
Average Inventory Days Outstanding: Inventory Turnover Ratio
Accounts Payable Turnover APT: Cost of Goods Sold Delta in Inventory Average Accounts Payable
Average Payment Period: Accounts Payable Turnover
Liquidity Ratios:
Net Working Capital NWC: Current Assets Current Liabilities
Current Ratio CR: Current Assets Current Liabilities
AcidTest Ratio ATR: Cash Current Investments Accounts Receivable Current Liabilities
ATR is also known as the Quick Ratio
Cash Flow from Operations CFO to Current Liabilities: CFO Average Current Liabilities
Days of Working Capital Financing Needed Average Inventory Days Average Collection Period Average Payment Period also known as the Cash Conversion Cycle
Revenues to Cash Ratio: Revenues Average Cash Balance
Solvency Ratios:
DebttoEquity Ratio DER: Total Liabilities Total Stockholders Equity
Times Interest Earned TIER: Net Income Interest Expense Tax Expense Interest Expense
If firm has Minority Interest in Earnings MIE add MIE to Numerator for TIER also
Liabilities to Assets Ratio: Total Liabilities Total Assets
LongTerm Debt LTD to LongTerm Capital Ratio: LTD LTD Shareholders Equity
LongTerm Debt LTD to Shareholders Equity Ratio: LTD Shareholders Equity
Cash Flow from Operations CFO to Total Liabilities: CFO Average Total Liabilities
EBITDA Coverage: Earnings Before Taxes Interest Expense, net Depreciation Amortization Interest Expense
Free Cash Flow from Operations FCFO to Total Debt: CFO CAPEX Average ShortTerm Debt Average LongTerm Debt
Total DebttoEquity: LongTerm Debt including Current Portion
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it
Step: 1

Get Instant Access to Expert-Tailored Solutions
See step-by-step solutions with expert insights and AI powered tools for academic success
Step: 2

Step: 3

Ace Your Homework with AI
Get the answers you need in no time with our AI-driven, step-by-step assistance
Get Started


