Question
A combined gas turbine-vapor power plant has a net power output of 45 MW. Air enters the compressor of the gas turbine at 100 kPa,
A combined gas turbine-vapor power plant has a net power output of 45 MW. Air enters the compressor of the gas turbine at 100 kPa, 300 K, and is compressed to 1200 kPa. The isentropic efficiency of the compressor is 84%. The condition at the inlet to the turbine is 1200 kPa, 1400 K. Air expands through the turbine, which has an isentropic efficiency of 88%, to a pressure of 100 kPa. The air then passes through the interconnecting heat exchanger and is finally discharged at 400 K. Steam enters the turbine of the vapor power cycle at 8 MPa, 400C, and expands to the condenser pressure of 8 kPa. Water enters the pump as saturated liquid at 8 kPa. The turbine and pump of the vapor cycle have isentropic efficiencies of 90 and 80%, respectively. Thermodynamics calculation should be conducted for the known condition illustrated in Figure 1.
a. Determine the mass flow rates of the air and the steam, each in kg/s, and the net power developed by the gas turbine and vapor power cycle, each in MW.
b. Develop a full accounting of the net rate of exergy increase as the air passes through the gas turbine combustor. Discuss. Let T0=300~K, p0=100kPa.
c. Calculate the cooling water's mass flow rate.
d. Calculate the fuel required for the combined gas turbine-vapor system illustrated in figure 1.
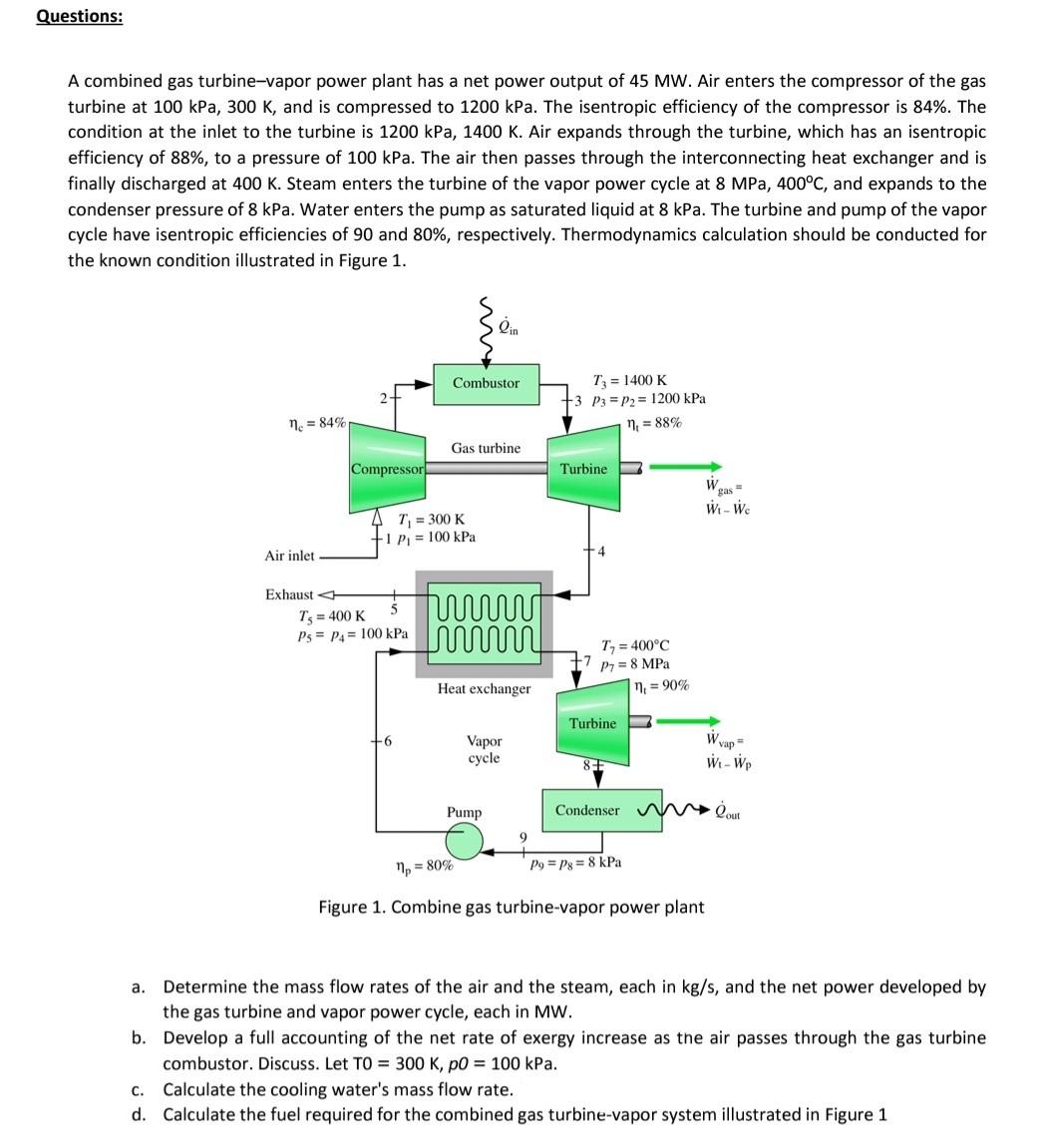
A combined gas turbine-vapor power plant has a net power output of 45MW. Air enters the compressor of the gas turbine at 100kPa,300K, and is compressed to 1200kPa. The isentropic efficiency of the compressor is 84%. The condition at the inlet to the turbine is 1200kPa,1400K. Air expands through the turbine, which has an isentropic efficiency of 88%, to a pressure of 100kPa. The air then passes through the interconnecting heat exchanger and is finally discharged at 400K. Steam enters the turbine of the vapor power cycle at 8MPa,400C, and expands to the condenser pressure of 8kPa. Water enters the pump as saturated liquid at 8kPa. The turbine and pump of the vapor cycle have isentropic efficiencies of 90 and 80%, respectively. Thermodynamics calculation should be conducted for the known condition illustrated in Figure 1. Figure 1. Combine gas turbine-vapor power plant a. Determine the mass flow rates of the air and the steam, each in kg/s, and the net power developed by the gas turbine and vapor power cycle, each in MW. b. Develop a full accounting of the net rate of exergy increase as the air passes through the gas turbine combustor. Discuss. Let TO =300K,pO=100kPa. c. Calculate the cooling water's mass flow rate. d. Calculate the fuel required for the combined gas turbine-vapor system illustrated in Figure 1 A combined gas turbine-vapor power plant has a net power output of 45MW. Air enters the compressor of the gas turbine at 100kPa,300K, and is compressed to 1200kPa. The isentropic efficiency of the compressor is 84%. The condition at the inlet to the turbine is 1200kPa,1400K. Air expands through the turbine, which has an isentropic efficiency of 88%, to a pressure of 100kPa. The air then passes through the interconnecting heat exchanger and is finally discharged at 400K. Steam enters the turbine of the vapor power cycle at 8MPa,400C, and expands to the condenser pressure of 8kPa. Water enters the pump as saturated liquid at 8kPa. The turbine and pump of the vapor cycle have isentropic efficiencies of 90 and 80%, respectively. Thermodynamics calculation should be conducted for the known condition illustrated in Figure 1. Figure 1. Combine gas turbine-vapor power plant a. Determine the mass flow rates of the air and the steam, each in kg/s, and the net power developed by the gas turbine and vapor power cycle, each in MW. b. Develop a full accounting of the net rate of exergy increase as the air passes through the gas turbine combustor. Discuss. Let TO =300K,pO=100kPa. c. Calculate the cooling water's mass flow rate. d. Calculate the fuel required for the combined gas turbine-vapor system illustrated in Figure 1
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it
Step: 1

Get Instant Access to Expert-Tailored Solutions
See step-by-step solutions with expert insights and AI powered tools for academic success
Step: 2

Step: 3

Ace Your Homework with AI
Get the answers you need in no time with our AI-driven, step-by-step assistance
Get Started


