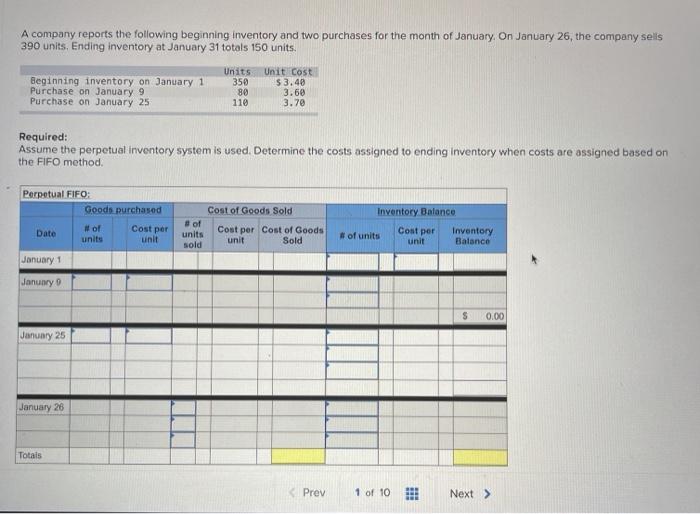
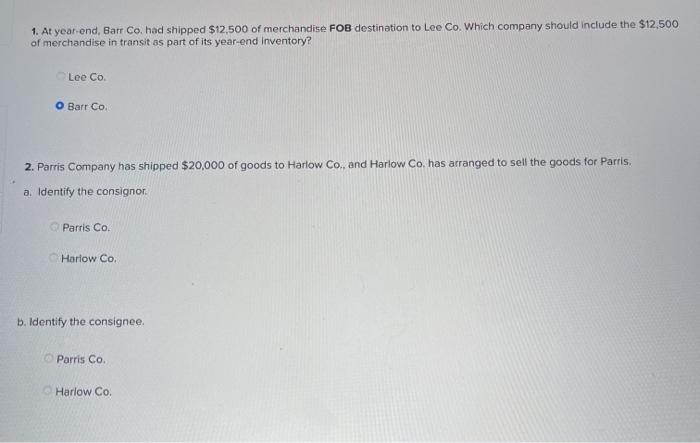
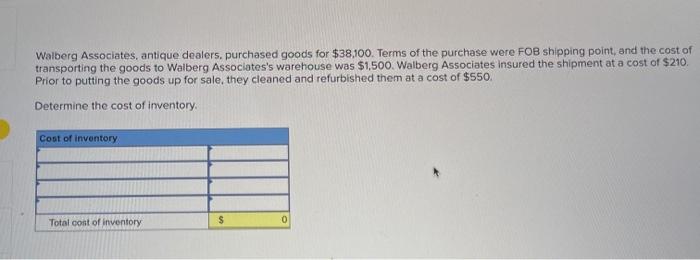
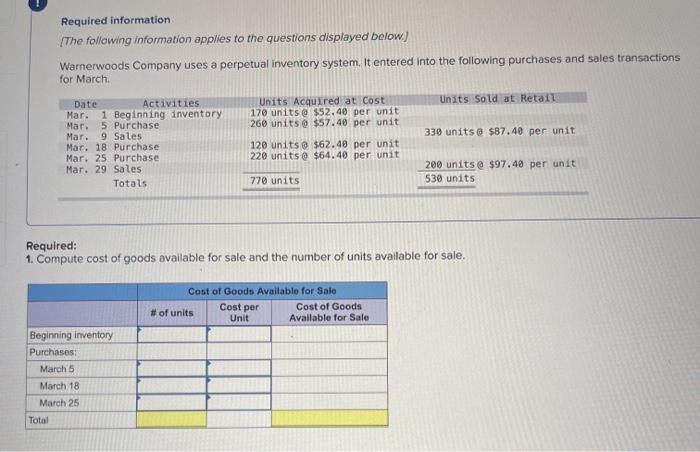
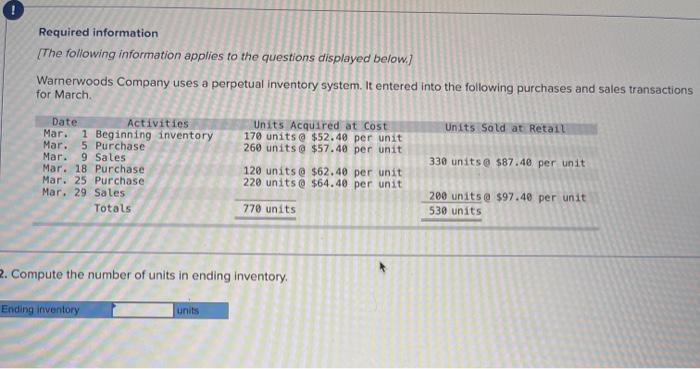
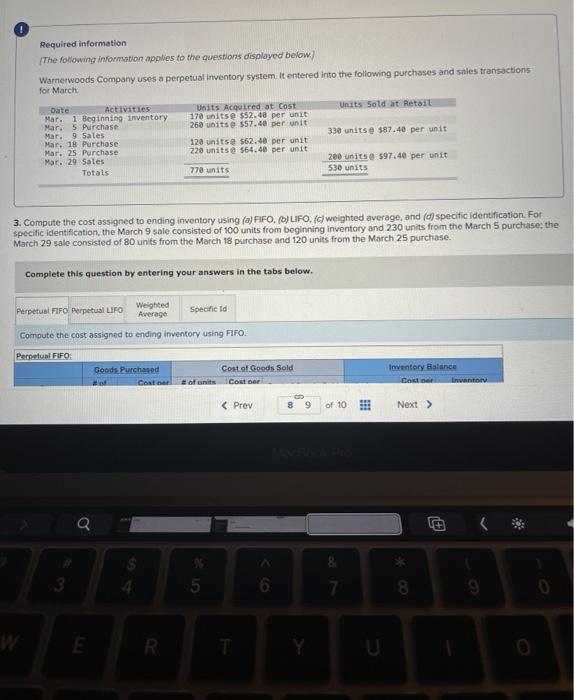
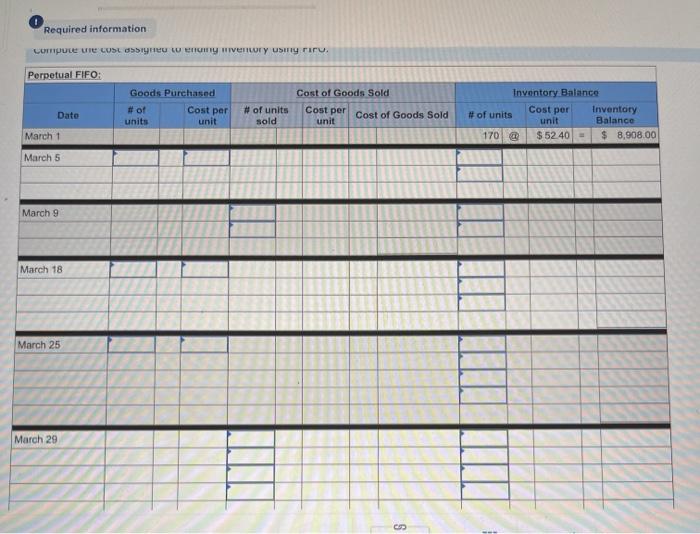
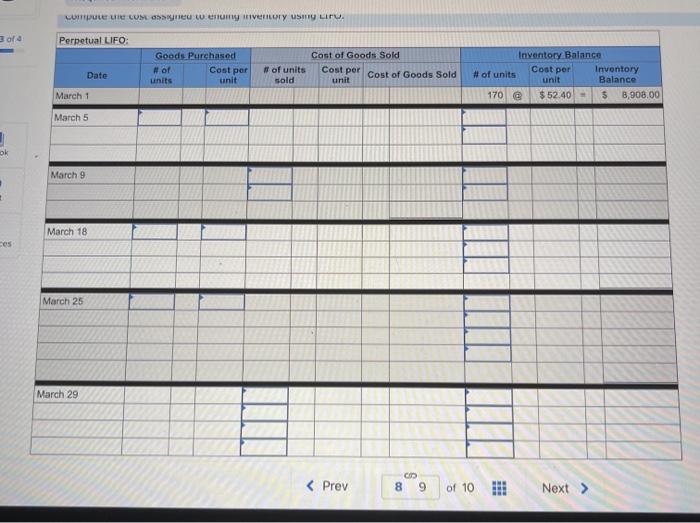
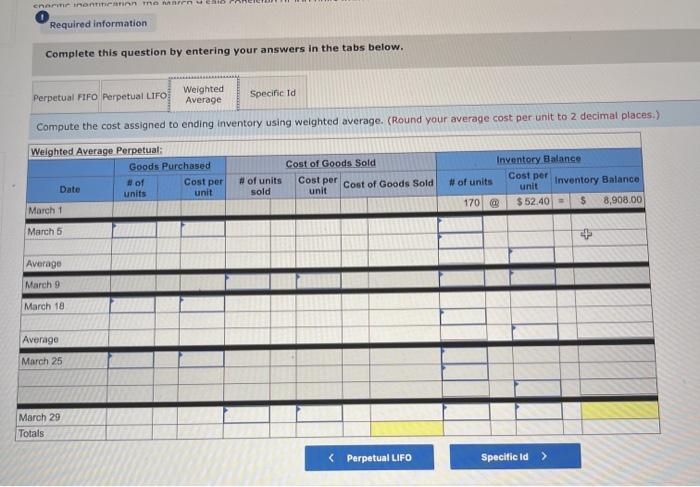
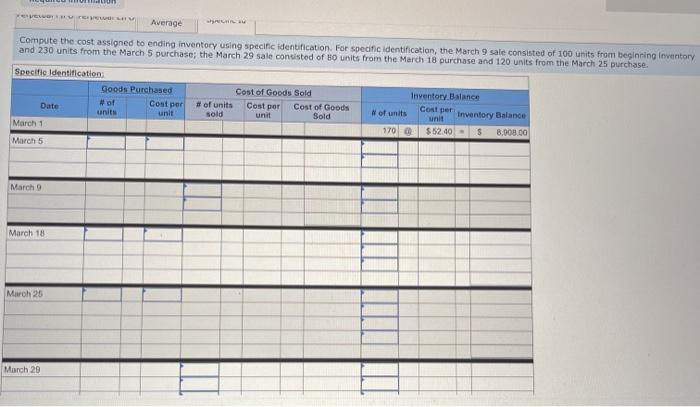
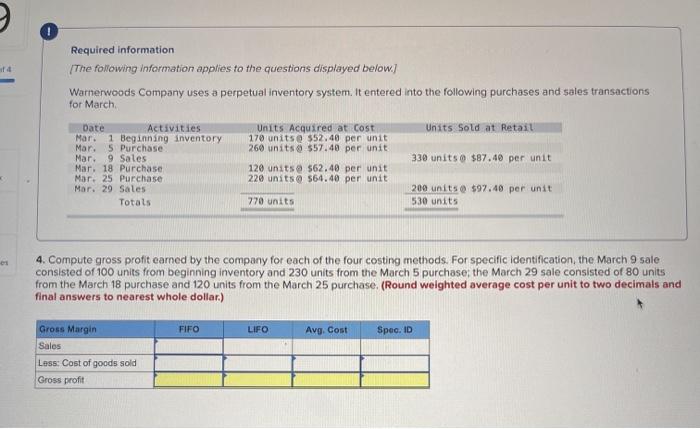
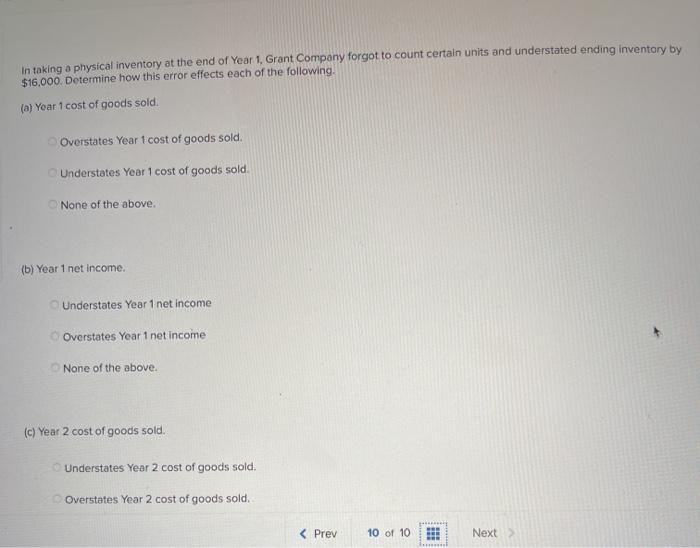
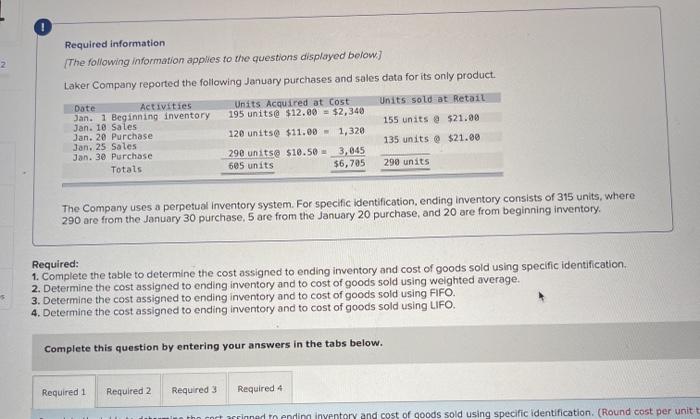
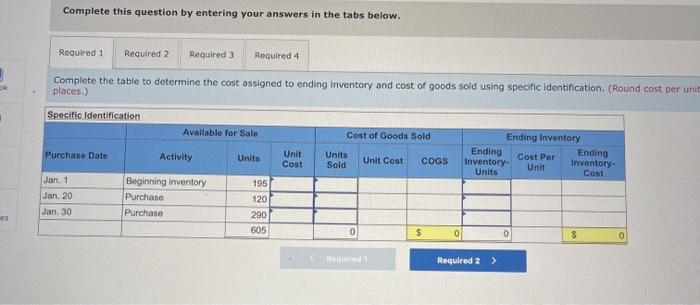
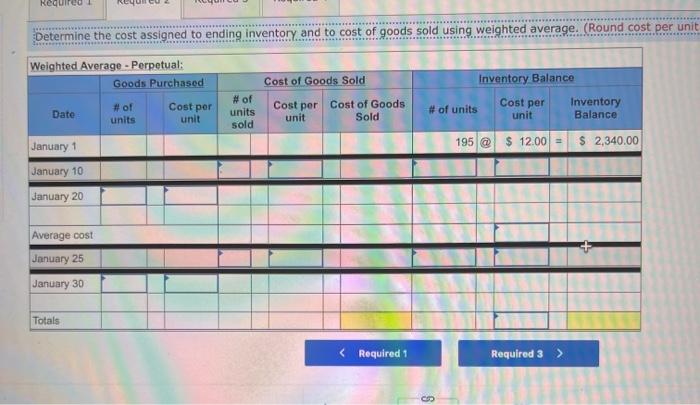
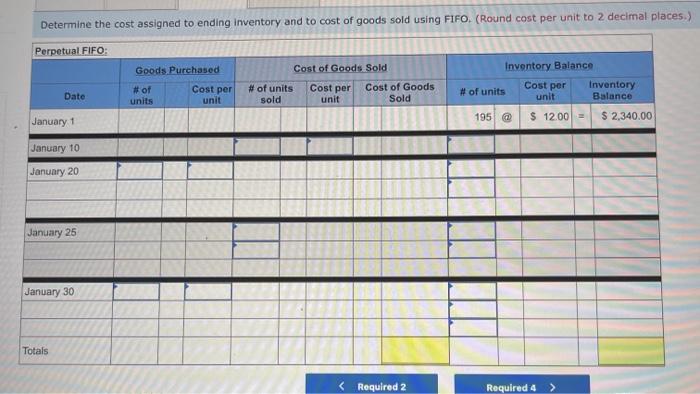
A company reports the following beginning inventory and two purchases for the month of January. On January 26, the company sells 390 units Ending inventory at January 31 totals 150 units. Beginning inventory on January 1 Purchase on January 9 Purchase on January 25 Units 350 80 110 Unit Cost $ 3.40 3.60 3.70 Required: Assume the perpetual inventory system is used. Determine the costs assigned to ending inventory when costs are assigned based on the FIFO method Cost of Goods Sold Perpetual FIFO: Goods purchased Date # of Cost per units unit Inventory Balance of units sold Cost per Cost of Goods unit Sold Cost per # of units unit Inventory Balance January 1 January S 0.00 January 25 January 26 Totais Prev 1 of 10 Next > 1. At year end, Barr Co. had shipped $12.500 of merchandise FOB destination to Lee Co. Which company should include the $12,500 of merchandise in transit as part of its year-end Inventory? Lee Co O Barr Co. 2. Parris Company has shipped $20,000 of goods to Harlow Co., and Harlow Co, has arranged to sell the goods for Parris. a. Identify the consignor Parris Co. Harlow Co. b. Identify the consignee. Parris Co. Harlow Co. c. Which company should include any unsold goods as part of its inventory? Harlow Co. Parris Co. Walberg Associates, antique dealers. purchased goods for $38,100. Terms of the purchase were FOB shipping point, and the cost of transporting the goods to Wolberg Associates's warehouse was $1,500. Walberg Associates insured the shipment at a cost of $210. Prior to putting the goods up for sale, they cleaned and refurbished them at a cost of $550. Determine the cost of inventory Cost of inventory Total cost of inventory $ 0 Required information The following information applies to the questions displayed below.) Warnerwoods Company uses a perpetual inventory system. It entered into the following purchases and sales transactions for March Units Sold at Retail Units Acquired at Cost 170 units @ $52.40 per unit 260 units @ $57.40 per unit 330 units @ $87.40 per unit Date Activities Mar. 1 Beginning inventory Mar. 5 Purchase Mar. 9 Sales Mar. 18 Purchase Mar. 25 Purchase Mar. 29 Sales Totals 120 units @ $62.40 per unit 220 units @ $64.40 per unit 200 units @ $97.40 per unit 530 units 770 units Required: 1. Compute cost of goods available for sale and the number of units available for sale. Cost of Goods Available for Sale Cost per Cost of Goods # of units Unit Available for Sale Beginning inventory Purchases March 5 March 18 March 25 Total Required information [The following information applies to the questions displayed below.) Warnerwoods Company uses a perpetual inventory system. It entered into the following purchases and sales transactions for March Units Sold at Retail Date Activities Mar. 1 Beginning inventory Mar. 5 Purchase Mar. 9 Sales Mar. 18 Purchase Mar. 25 Purchase Mar. 29 Sales Totals Units Acquired at Cost 170 units@ $52.40 per unit 260 units@ $57.40 per unit 120 units @ $62.40 per unit 220 units@ $64.40 per unit 330 units@ $87.40 per unit 770 units 200 units@ $97.40 per unit 530 units 2. Compute the number of units in ending inventory Ending inventory units Required information The following information applies to the questions displayed below) Warnerwoods Company uses a perpetual inventory system. It entered into the following purchases and sales transactions for March Units Sold at Retail Date Activities Mar. 1 Beginning inventory Mar. 5 Purchase Mar. 9 Sales Mar. 18 Purchase Mar. 25 Purchase Mar. 29 Sales Totals Units Acquired at Cost 170 units@ $52.40 per unit 250 units @ $57.40 per unit 120 units@ $62.40 per unit 220 units 564.40 per unit 330 units @ $87.40 per unit 200 units 597.40 per unit 530 units 778 units 3. Compute the cost assigned to ending inventory using (a) FIFO, () LIFO. Ic/ weighted average, and (d) specific identification. For specific identification, the March 9 sale consisted of 100 units from beginning inventory and 230 units from the March 5 purchase the March 29 sale consisted of 80 units from the March 18 purchase and 120 units from the March 25 purchase. Complete this question by entering your answers in the tabs below. Weighted Perpetual FIFO perpetual LIFO Average Specific id Compute the cost assigned to ending inventory Using FIFO. Perpetual Fifo Goods Purchased Costner of units Cost of Goods Sold Costa Inventory Balance Canto Q 5 6. 8 E R. Required information Lumpule WE LOST THU LU vencry Usiny riru. Perpetual FIFO: Goods Purchased # of Cost per units unit Cost of Goods Sold Cost per unit Cost of Goods Sold # of units sold Date Inventory Balance Cost per # of units Inventory unit Balance 170 $ 52.40 - $ 8,908.00 March 1 March 5 March 9 March 18 March 25 March 29 LULE ULUM tenung verLUTY USI LITU. 3o Perpetual LIFO Goods Purchased # of Cost per units unit Cost of Goods Sold #of units Cost per Cost of Goods Sold sold unit Date Inventory Balance Cost per # of units Inventory unit Balance 170 @ $52.40 - $ 8,908.00 March 1 March 5 ok March 9 March 18 March 25 March 29 enari non hann Required information Complete this question by entering your answers in the tabs below. Weighted Perpetual Fifo Perpetual LIFO Specific Id Average Compute the cost assigned to ending inventory using weighted average. (Round your average cost per unit to 2 decimal places.) Weighted Average Perpetual: Goods Purchased # of Cost per Date units unit March 1 Cost of Goods Sold # of units Cost per cost of Goods Sold sold unit Inventory Balance Cost per # of units unit Inventory Balance 170 @ $ 52.40 $ 8,908.00 March 5 Average March 9 March 18 Average March 25 March 29 Totals Perpetual LIFO Specific id > VEEL Average Compute the cost assigned to ending inventory using specific identification. For specific identification, the March 9 sale consisted of 100 units from beginning inventory and 230 units from the March 5 purchase; the March 29 sale consisted of Ounits from the March 18 purchase and 120 units from the March 25 purchase. Specific Identification: Goods Purchased Date #of Cost per units unit March 1 March 5 Cost of Goods Sold # of units Cost per Cost of Goods sold unit Sold Inventory Balance of units Cost per inventory Balance 170 $52.40 $ 8.000.00 March March 18 March 25 March 20 Required information The following information applies to the questions displayed below.] Warnerwoods Company uses a perpetual inventory system. It entered into the following purchases and sales transactions for March Date Activities Units Acquired at cost Units Sold at Retail Mar. 1 Beginning inventory 170 units@ $52.48 per unit Mar. 5 Purchase 260 units@ $57.40 per unit Mar. 9 Sales 330 units @ $87.40 per unit Mar. 18 Purchase 120 units@ $62.40 per unit Mar. 25 Purchase 220 units@ $64.40 per unit Mar. 29 Sales 200 units @ $97.40 per unit Totals 770 units 530 units 4. Compute gross profit earned by the company for each of the four costing methods. For specific identification, the March 9 sale consisted of 100 units from beginning inventory and 230 units from the March 5 purchase the March 29 sale consisted of 80 units from the March 18 purchase and 120 units from the March 25 purchase. (Round weighted average cost per unit to two decimals and final answers to nearest whole dollar) FIFO LIFO Avg. Cost Spec.ID Gross Margin Sales Less: Cost of goods sold Gross profit In taking a physical inventory at the end of Year 1, Grant Company forgot to count certain units and understated ending inventory by $16,000. Determine how this error effects each of the following. (a) Year 1 cost of goods sold. Overstates Year 1 cost of goods sold. Understates Year 1 cost of goods sold. None of the above. (b) Year 1 net income Understates Year 1 net income Overstates Year 1 net income None of the above. (c) Year 2 cost of goods sold. Understates Year 2 cost of goods sold. Overstates Year 2 cost of goods sold. Required Determine the cost assigned to ending inventory and to cost of goods sold using weighted average. (Round cost per unit Weighted Average - Perpetual: Goods Purchased Cost of Goods Sold Cost per Cost of Goods unit Sold Cost per Inventory Balance Cost per Inventory # of units unit Balance # of units sold Date #of units unit 195 @ $ 12.00 = $ 2,340.00 January 1 January 10 January 20 Average cost January 25 January 30 Totals S Determine the cost assigned to ending Inventory and to cost of goods sold using FIFO. (Round cost per unit to 2 decimal places.) Perpetual FIFO: Goods Purchased Cost of Goods Sold # of units Cost per Date #of units Cost per unit Cost of Goods Sold Inventory Balance Cost per # of units Inventory unit Balance 195 @ $ 12.00 = $ 2,340.00 sold unit January 1 January 10 January 20 January 25 January 30 Totals Required 2 Required 4 Required 1 Required 2 Required 3 Required 4 2 Determine the cost assigned to ending inventory and to cost of goods sold using LIFO. (Round cost per unit to 2 decimal places Perpetual LIFO: Goods Purchased # of Cost per units unit Cost of Goods Sold of units Cost per Cost of Goods sold unit Sold Date Inventory Balance Cost per Inventory # of units unit Balance 195 @ $ 12.00 = $ 2,340.00 January 1 January 10 January 20 January 25 January 30 Totals