Question
A conservatively financed firm would A. use long-term financing for all fixed assets and short-term financing for all other assets. B. finance a portion of
A conservatively financed firm would
A. use long-term financing for all fixed assets and short-term financing for all other assets.
B. finance a portion of permanent assets and short-term assets with short-term debt.
C. use equity to finance fixed assets, use long-term debt to finance permanent assets, and use short-term debt to finance fluctuating current assets
D. use long-term financing for three items: permanent current assets, fixed assets, and a portion of the short-term fluctuating assets. Then use short-term financing for all other short-term assets.
Royal Enterprises suffers from poor cash management. Which type of cash balance should Royal Enterprises focus on in order to ensure its suppliers are paid in a timely manner?
A. Transactions balance
B. Speculative balance
C. Precautionary balance
D. Compensating balance
Royal Enterprises is considering changing its banking relationship. One of the banks under consideration charges very low service fees, but requires that the firm maintain a minimum balance in their account. What type of account is this?
A. Maintenance balance
B. Compensating balance
C. Speculative balance
D. Transactions balance
Twinco received a $10,000 check from one of its clients on the fifth day of the month, deposited it in its bank account, and recorded it on its accounting records. It will take two days for Twincos bank to process the check and send it to the customers bank, and another two days for the customers bank to process and release the funds. This would describe:
A. Aggressive working capital policy
B. Lockbox collection process
C. Remote disbursement
D. Collection float
Campus Books holds the bare amount of inventory possible. New supplies are delivered just as previous supplies run out. While this minimizes carrying costs, it increases the risk of stock outs. Which inventory method is Campus Books using?
A. Red-line method
B. EOQ model
C. Just-in-time
D. Safety Stock
Using the table below, identify the cash management motives companies have for holding cash by placing an X in the box opposite the description
|
| Compensating Balance | Precautionary Balance | Speculative Balance | Transactions Balance |
| Enables firm to take advantage of bargain purchases |
|
|
|
|
| Protects firm from unforeseeen fluctuations in cash flow |
|
|
|
|
| Balance maintained to offset cost of bank services |
|
|
|
|
| Required to make payment for day-to-day operations and expenses |
|
|
|
|
Identify each of the working capital management terms in the table below by placing an X in the box opposite its description.
|
| Cash Budget | Current Ratio | Net Working Capital | Spontaneous Liabilities | Working Capital |
| Forecasts a firms cash inflows and outflows |
|
|
|
|
|
| Firms current assets |
|
|
|
|
|
| Difference between a firms current assets and current liabilities |
|
|
|
|
|
| The firms current assets divided by its current liabilities |
|
|
|
|
|
| Current liabilities that grow as the firm grows |
|
|
|
|
|
Consider the graph below and answer the questions which follow.
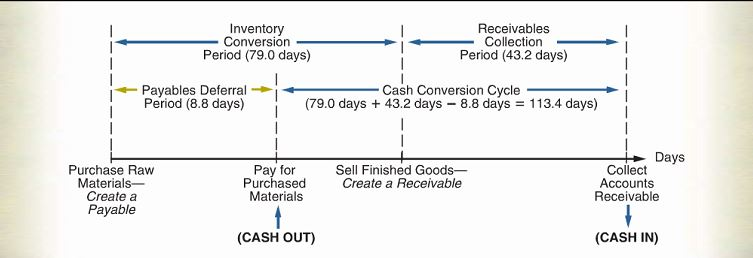
- Describe the Cash Conversion Cycle; include references to the graph.
- Define four actions a firm could take to reduce its cash conversion cycle
c. Why is the cash conversion cycle important to the financial manager?
Thunder Corporation has annual credit sales of $2,000,000. Current expenses for the Collection Department are $30,000; bad debt losses are 2%. Current DSO is 30 days. Thunder Corp. is considering loosening its credit policy such that collection expenses will fall to $22,000 annually. The change is expected to increase bad debt losses to 3% and to increase DSO to 45 days. Due to the looser policy, sales are expected to increase to $2,200,000. The companys cost of capital is 12%, variable costs are 75%, and marginal tax rate is 40%.
Refer to the table below and answer the questions which follow.
|
| Current Policy | Proposed Policy | Change |
| Sales | $2,000,000 | $2,200,000 | $200,000 |
| Production costs | (1,500,000) |
|
|
| Profit before credit costs and taxes | 500,000 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| Credit Related Costs |
|
|
|
| Carrying costs | (15,000) | (24,750) |
|
| Collection expense | (30,000) |
|
|
| Bad Debt losses | (40,000) |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| Profit before taxes | 415,000 |
|
|
| Taxes | (166,000) |
|
|
| Net Income | $249,000 |
|
|
- Compute the change in Net Income under the proposed policy by completing the table.
b. Explain which policy you consider to be the best. Justify your answer.
- Which assumptions are most sensitive to change? Explain why you think so.
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it
Step: 1

Get Instant Access to Expert-Tailored Solutions
See step-by-step solutions with expert insights and AI powered tools for academic success
Step: 2

Step: 3

Ace Your Homework with AI
Get the answers you need in no time with our AI-driven, step-by-step assistance
Get Started


