Answered step by step
Verified Expert Solution
Question
1 Approved Answer
A decision tree is similar to a 1-decision list, except now we allow the single literal decision conditions to be placed in a binary tree,
A decision tree is similar to a 1-decision list, except now we allow the single literal decision conditions to be placed in a binary tree, with the decisin bits placed only at the leaves. To evaluate such a tree T on a input
of a eplision {0,1)^n, we follow the path through T defined by starting at the root T and evaluating the literal at each node on input a, going left if the evaluation yields 0 and right if ti yields 1. The value T(a) is the bit value stored at the leaf reached by this path.

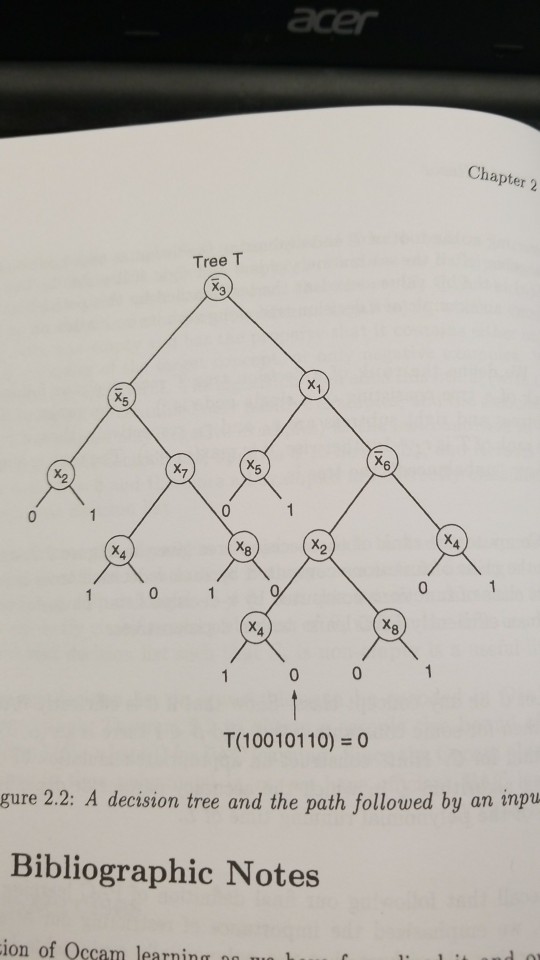
Occam's Razor 45 starting at the root of T and evaluating the literal at each node on input a, going left if the evaluation yields 0 and right if it yields 1. The value T(a) is the bit value stored at the leaf reached by this path. Figure 2.2 shows an example of a decision tree along with its evaluation on an input. We define the rank of a decision tree T recursively as follows: rank of a tree consisting of a single node is 0. If the ranks of T's left subtrees and right subtrees are ri and rR respectively, then if TR the rank of T is TL +1; otherwise, it is max(rL, TR). The rank is a measure the of how "unbalanced" the tree is. Compute the rank of the decision tree given in Figure 2.2, and shovw that the class of functions computed by rank r decision trees is included in the class of functions computed by r-decision lists. Thus, for any fixed r we can efficiently PAC learn rank r decision trees
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it
Step: 1

Get Instant Access to Expert-Tailored Solutions
See step-by-step solutions with expert insights and AI powered tools for academic success
Step: 2

Step: 3

Ace Your Homework with AI
Get the answers you need in no time with our AI-driven, step-by-step assistance
Get Started


