Question
(a) Explain why the variances for fixed costs are generally different from the variances for variable costs. Use an example to support your explanation. In
(a) Explain why the variances for fixed costs are generally different from the variances for variable costs. Use an example to support your explanation. In particular, for control purposes, why is an efficiency (i.e., quantity or volume) variance not calculated for fixed manufacturing overhead?
(b)Construct the master and flexible budgets to compare them with the actual performance: The actual income statement in the first six months was as follows at the volume of 78,000 units.

Calculate a series of variances to reconcile the budgeted and actual profits (i.e., total, sales, materials, labour, and fixed overhead variances). Ensure that you show both the price and quantity variances for sales, materials, and labour. The companys budgeted and actual profits should be reconciled at the end of your answer to confirm that your analyses were correct.
(c) Suggest who is potentially responsible for the sales, materials, and labour variances calculated in (b) and explain why.
(d) Explain whether and why some responsibility centres are responsible only for costs, some only for revenue, and some for both. Provide an example for each case.
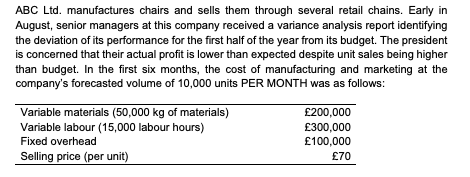
ABC Ltd. manufactures chairs and sells them through several retail chains. Early in August, senior managers at this company received a variance analysis report identifying the deviation of its performance for the first half of the year from its budget. The president is concerned that their actual profit is lower than expected despite unit sales being higher than budget. In the first six months, the cost of manufacturing and marketing at the company's forecasted volume of 10,000 units PER MONTH was as follows: Variable materials (50,000 kg of materials) Variable labour (15,000 labour hours) Fixed overhead Selling price (per unit) 200,000 300,000 100,000 70 Sales revenue 4,680,000 Costs: Variable materials (429,000 kg of materials) 1,930,500 Variable labour (124,800 labour hours) 1,996,800 Fixed overhead 600,000 4,527,300 Profit 152,700 ABC Ltd. manufactures chairs and sells them through several retail chains. Early in August, senior managers at this company received a variance analysis report identifying the deviation of its performance for the first half of the year from its budget. The president is concerned that their actual profit is lower than expected despite unit sales being higher than budget. In the first six months, the cost of manufacturing and marketing at the company's forecasted volume of 10,000 units PER MONTH was as follows: Variable materials (50,000 kg of materials) Variable labour (15,000 labour hours) Fixed overhead Selling price (per unit) 200,000 300,000 100,000 70 Sales revenue 4,680,000 Costs: Variable materials (429,000 kg of materials) 1,930,500 Variable labour (124,800 labour hours) 1,996,800 Fixed overhead 600,000 4,527,300 Profit 152,700Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it
Step: 1

Get Instant Access to Expert-Tailored Solutions
See step-by-step solutions with expert insights and AI powered tools for academic success
Step: 2

Step: 3

Ace Your Homework with AI
Get the answers you need in no time with our AI-driven, step-by-step assistance
Get Started


