Question
A flat steel plate is sprayed with 1.0 mm thick film of paint. The steel plate is 2.5 m by 1 m. The paint consists
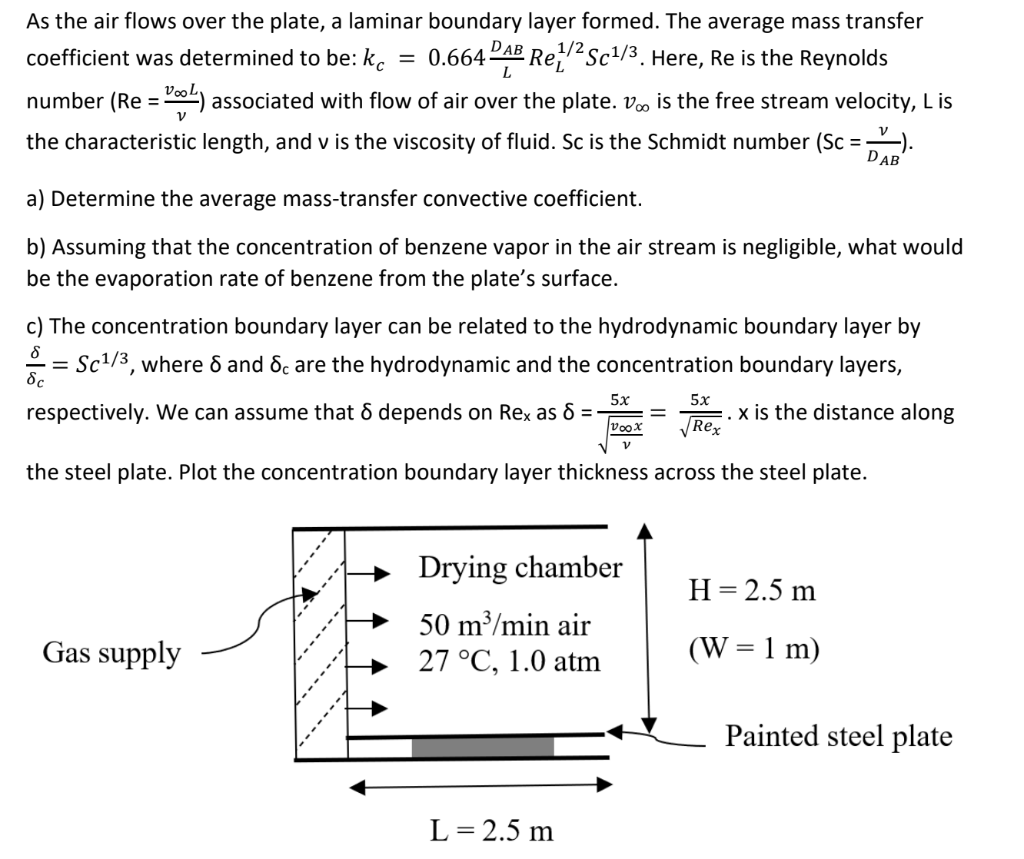
A flat steel plate is sprayed with 1.0 mm thick film of paint. The steel plate is 2.5 m by 1 m. The paint consists of benzene as the solvent. Fifty cubic meters per minute of air are blown into the drying chamber as shown in the Figure below. The chamber is 2.5 m in length, 2.5 m in height, and 1 m in width. The temperature of the air and the plate is 27 C and the system is maintained at a pressure of 1 atm. The paint surface exerts a partial pressure of 0.137atm. Under these conditions, the DAB equals 0.0972 cm2 s-1 and the viscosity of the benzene vapor is 1.569*10-5 m2 s-1.
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it
Step: 1

Get Instant Access to Expert-Tailored Solutions
See step-by-step solutions with expert insights and AI powered tools for academic success
Step: 2

Step: 3

Ace Your Homework with AI
Get the answers you need in no time with our AI-driven, step-by-step assistance
Get Started


