Answered step by step
Verified Expert Solution
Question
1 Approved Answer
A horizontal cylinder 0.457 m long is divided into two parts, A and B (see Figure P 3.5) by a latched piston. As illustrated,
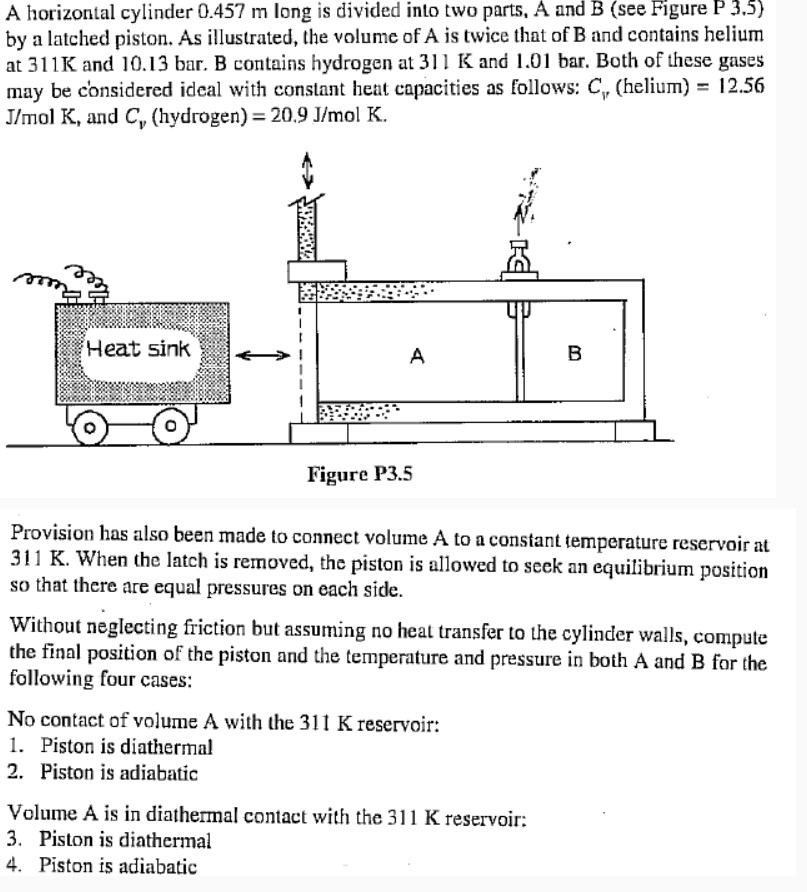
A horizontal cylinder 0.457 m long is divided into two parts, A and B (see Figure P 3.5) by a latched piston. As illustrated, the volume of A is twice that of B and contains helium at 311K and 10.13 bar. B contains hydrogen at 311 K and 1.01 bar. Both of these gases may be considered ideal with constant heat capacities as follows: C, (helium) = 12.56 J/mol K, and C,, (hydrogen) = 20.9 J/mol K. Heat sink A B Figure P3.5 Provision has also been made to connect volume A to a constant temperature reservoir at 311 K. When the latch is removed, the piston is allowed to seek an equilibrium position so that there are equal pressures on each side. Without neglecting friction but assuming no heat transfer to the cylinder walls, compute the final position of the piston and the temperature and pressure in both A and B for the following four cases: No contact of volume A with the 311 K reservoir: 1. Piston is diathermal 2. Piston is adiabatic Volume A is in diathermal contact with the 311 K reservoir: 3. Piston is diathermal 4. Piston is adiabatic
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it
Step: 1

Get Instant Access to Expert-Tailored Solutions
See step-by-step solutions with expert insights and AI powered tools for academic success
Step: 2

Step: 3

Ace Your Homework with AI
Get the answers you need in no time with our AI-driven, step-by-step assistance
Get Started


