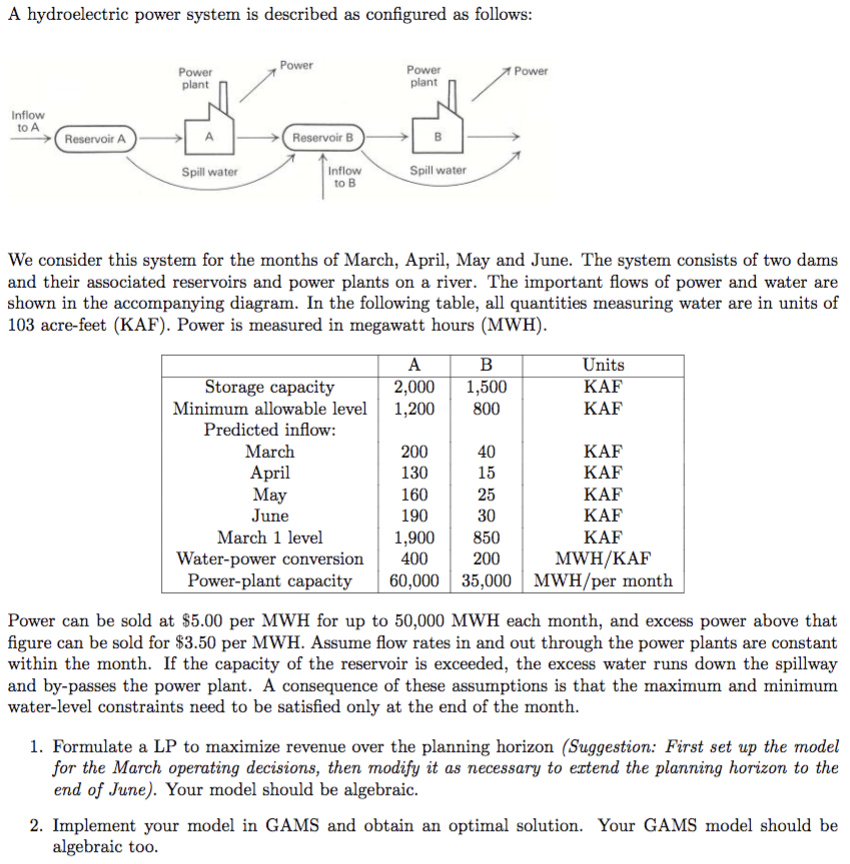
A hydroelectric power system is described as configured as follows: Power Power Power Power plant plant Inflow to A Reservoir B Reservoir A Inflow to B Spill water Spill water We consider this system for the months of March, April, May and June. The system consists of two dams and their associated reservoirs and power plants on a river. The important flows of power and water are shown in the accompanying diagram. In the following table, all quantities measuring water are in units of 103 acre-feet (KAF). Power is measured in megawatt hours (MWH) 2,000 1,200 1,500 Units AF Storage capacity Minimum allowable level AF 800 Predicted inflow March AF AF 200 40 pril ay June 130 15 F 160 25 F F 190 30 March 1 level 1,900 850 MWH/KAF 60,000 35,000 MWH/per month Water-power conversion Power-plant capacity 400 200 Power can be sold at $5.00 per MWH for up to 50,000 MWH each month, and excess power above that figure can be sold for $3.50 per MWH. Assume flow rates in and out through the power plants are constant within the month. If the capacity of the reservoir is exceeded, the excess water runs down the spillway and by-passes the power plant. A consequence of these assumptions is that the maximum and minimum water-level constraints need to be satisfied only at the end of the month 1. Formulate a LP to maximize revenue over the planning horizon (Suggestion: First set up the model for the March operating decisions, then modify it as necessary to extend the planning horizon to the end of June). Your model should be algebraic 2. Implement your model in GAMS and obtain an optimal solution. Your GAMS model should be algebraic too. A hydroelectric power system is described as configured as follows: Power Power Power Power plant plant Inflow to A Reservoir B Reservoir A Inflow to B Spill water Spill water We consider this system for the months of March, April, May and June. The system consists of two dams and their associated reservoirs and power plants on a river. The important flows of power and water are shown in the accompanying diagram. In the following table, all quantities measuring water are in units of 103 acre-feet (KAF). Power is measured in megawatt hours (MWH) 2,000 1,200 1,500 Units AF Storage capacity Minimum allowable level AF 800 Predicted inflow March AF AF 200 40 pril ay June 130 15 F 160 25 F F 190 30 March 1 level 1,900 850 MWH/KAF 60,000 35,000 MWH/per month Water-power conversion Power-plant capacity 400 200 Power can be sold at $5.00 per MWH for up to 50,000 MWH each month, and excess power above that figure can be sold for $3.50 per MWH. Assume flow rates in and out through the power plants are constant within the month. If the capacity of the reservoir is exceeded, the excess water runs down the spillway and by-passes the power plant. A consequence of these assumptions is that the maximum and minimum water-level constraints need to be satisfied only at the end of the month 1. Formulate a LP to maximize revenue over the planning horizon (Suggestion: First set up the model for the March operating decisions, then modify it as necessary to extend the planning horizon to the end of June). Your model should be algebraic 2. Implement your model in GAMS and obtain an optimal solution. Your GAMS model should be algebraic too







