Question
A) On each of the diagram below, draw and label the forces (not components) that act on the elliptical pulley at the times indicated. To
A) On each of the diagram below, draw and label the forces (not components) that act on the elliptical pulley at the times indicated. To clearly indicate at which point on the pulley each force is exerted, draw each force as a distinct arrow starting on, and pointing away from, the point at which the force is exerted. The lengths of the arrows need not indicate the relative magnitudes of the forces. i. Time t=0 ii. Time t=4sB) In a clear, coherent, paragraph-length response, explain why the slope of the angular velocity vs. time graph changes as shown, and why the velocity vs. time graph increases and decreases as shown. Include references to specific physical principles or relationships.
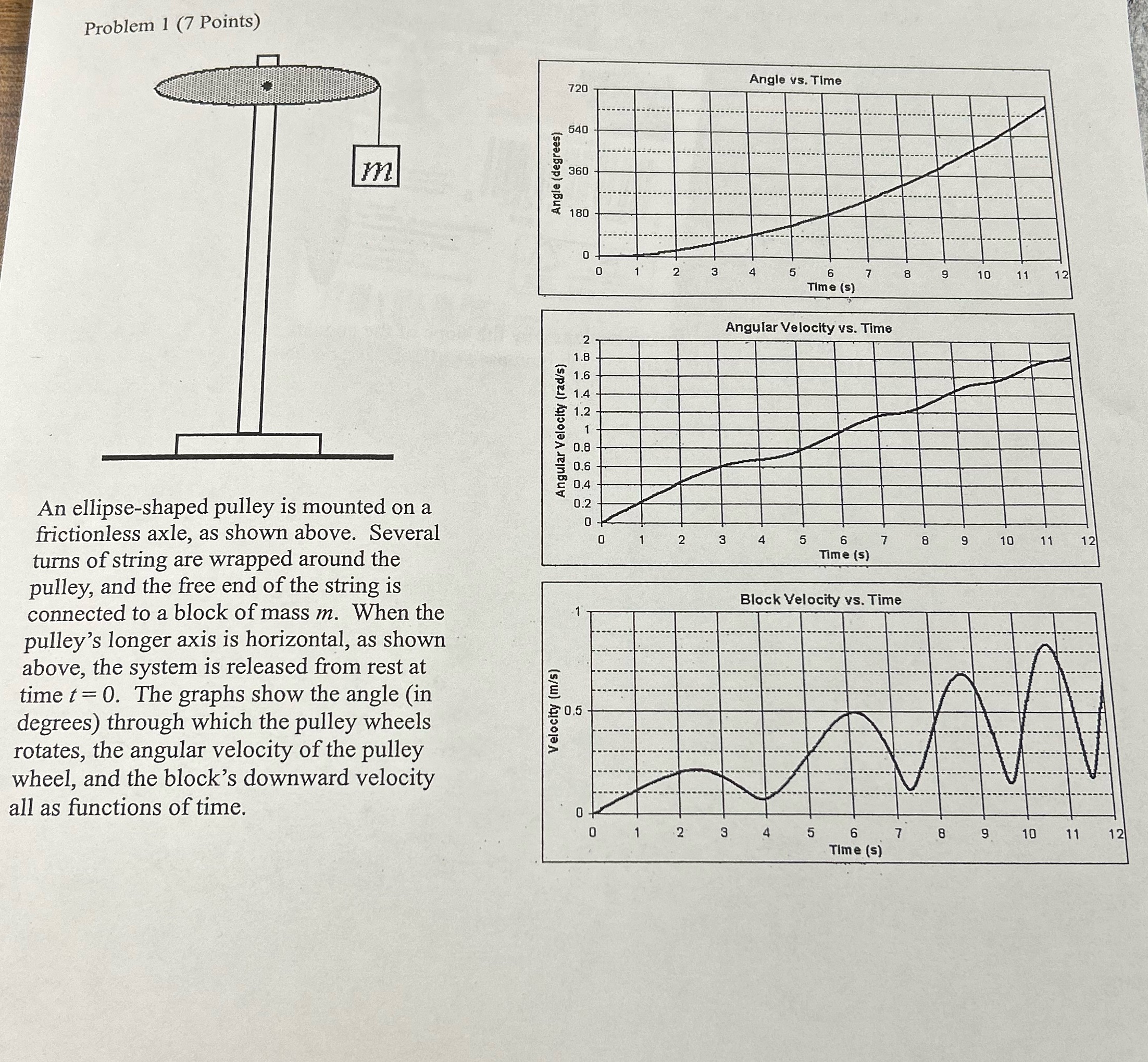
Problem 1 (7 Points) T An ellipse-shaped pulley is mounted on a frictionless axle, as shown above. Several turns of string are wrapped around the pulley, and the free end of the string is connected to a block of mass m. When the pulley's longer axis is horizontal, as shown above, the system is released from rest at time t = 0. The graphs show the angle (in degrees) through which the pulley wheels rotates, the angular velocity of the pulley wheel, and the block's downward velocity all as functions of time. Velocity (m/s) 0.5 Angular Velocity (rad/s) Angle (degrees) 2 1.8 1.6 1.4 1.2 1 B 6 0.8 0.6 Angle vs. Time 720 540 360 180 0 0 1 2 3 4 OT 5 6 Time (s) 7 8 9 10 11 12 Angular Velocity vs. Time 0.4 0.2 0 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 Time (s) 7 8 9 10 11 12 Block Velocity vs. Time 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 Time (s) 7 8 9 10 11 12
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it
Step: 1

Get Instant Access to Expert-Tailored Solutions
See step-by-step solutions with expert insights and AI powered tools for academic success
Step: 2

Step: 3

Ace Your Homework with AI
Get the answers you need in no time with our AI-driven, step-by-step assistance
Get Started


