Question
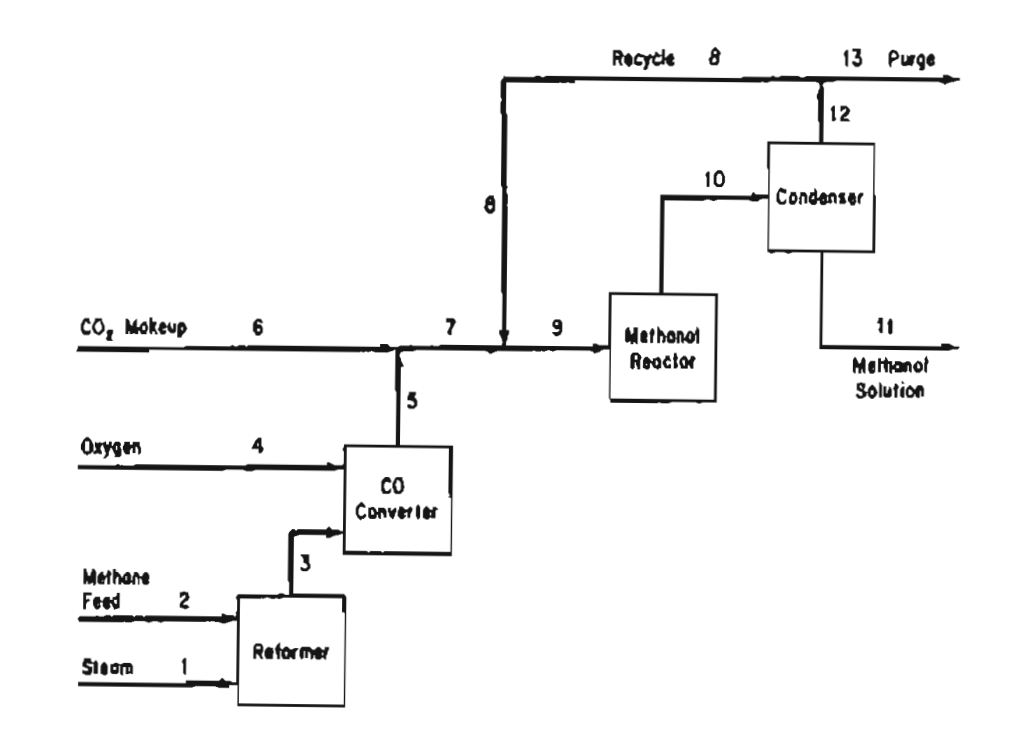
A process for methanol synthesis is shown in Figure P12.25. The pertinent chemical reactions are: 10% excess steam, based on reaction (a), is fed to
A process for methanol synthesis is shown in Figure P12.25. The pertinent chemical reactions are:

10% excess steam, based on reaction (a), is fed to the reformer, and conversion of methane is 100%, with a 90% yield of CO2. Conversion in the methanol reactor is 55% on one pass through the reactor.
A stoichiometric quantity of oxygen is fed to the CO converter, and the CO is completely converted to CO2. Additional makeup CO2 is then introduced to establish a 3 to 1 of H2 to CO2 in the feed stream to the methanol reactor.
The methanol reactor effluent is cooled to condense all the methanol and water, with the non-condensible gases recycled to the methanol reactor feed. The H2/CO2 ratio in the recycle stream is also 3 to 1.
Because the methane feed contains 1% nitrogen as an impurity, a portion of the recycle stream must be purged as shown in Fig. P12.25 to prevent the accumulation of nitrogen in the system. The purge stream analyzes 5% nitrogen.
On the basis of 100 mol of methane feed (including the N2), calculate:
a) How many moles of H2 are lost in the purge? b) How many moles of makeup CO2 are required? c) The recycle to purge ratio in mol/mol d) How much methanol solution (in kg) of what strengh (weight percent) is produced.
CH4+2H2OCO2+4H2CH4+H2OCO+3H22CO+O22CO2CO2+3H2CH3OH+H2O(mainreformerreaction)(reformersidereaction)(COconverterreaction)(methanolsynthesisreaction) (b) (d)
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it
Step: 1

Get Instant Access to Expert-Tailored Solutions
See step-by-step solutions with expert insights and AI powered tools for academic success
Step: 2

Step: 3

Ace Your Homework with AI
Get the answers you need in no time with our AI-driven, step-by-step assistance
Get Started


