a) Provide a brief description of Indigos business and what they offer customers.
b) What is Goodwill? Does Indigo have Goodwill?
c) How many common shares were issued and outstanding at the end of both years? What was the weighted average number of common shares outstanding (basic) for both years?
d) Calculate Indigos liquidity, using the current ratio for 2022 and 2021, and comment on the results.
e) Identify the cash flow patterns for 2022 and 2021. What do these patterns tell us about Indigo?
f) Evaluate the trend in the companys profitability by calculating the return on equity and the return on assets for 2022 and 2021. Comment on the results.
g) Prepare a common size analysis of the consolidated statement of earnings (loss) for 2022 and 2021. What significant trends do you observe? (see chapter 12 pages 12-16 and 12-17).
h) What is Indigos profit margin for both 2022 and 2021? Compare the results and comment.
i) Calculate the inventory turnover ratio for 2022 and 2021 and evaluate the result.
j) Summarize Indigos accounting policy for inventories and identify the cost formula that is used.
k) What are some of the actions Indigo took with regards to Covid-19 in fiscal 2022?
l) Briefly summarize Indigos revenue recognition policy.
m) What are some of the risks and uncertainties Indigo faces? Using the link to the annual report provided on page 1 of this case study, go to page 24 (25 of 78) of the annual report. The heading for this section is Risks and Uncertainties as shown below. Provide an overview of two of the risk factors you think would be important to your boss.
n) Evaluate the trend in the price/earnings ratio (P/E) comparing 2022 and 2021. You will need to look up the share price using Yahoo Finance, TMX Money or a similar financial services website. NOTE: Use March 31 when looking up the share prices. The companys stock trading symbol is IDG. Comment on the results.
o) Overall, based on your analysis above, should your boss purchase Indigo Books & Music Inc. shares? Explain your reasoning based on your above analysis.
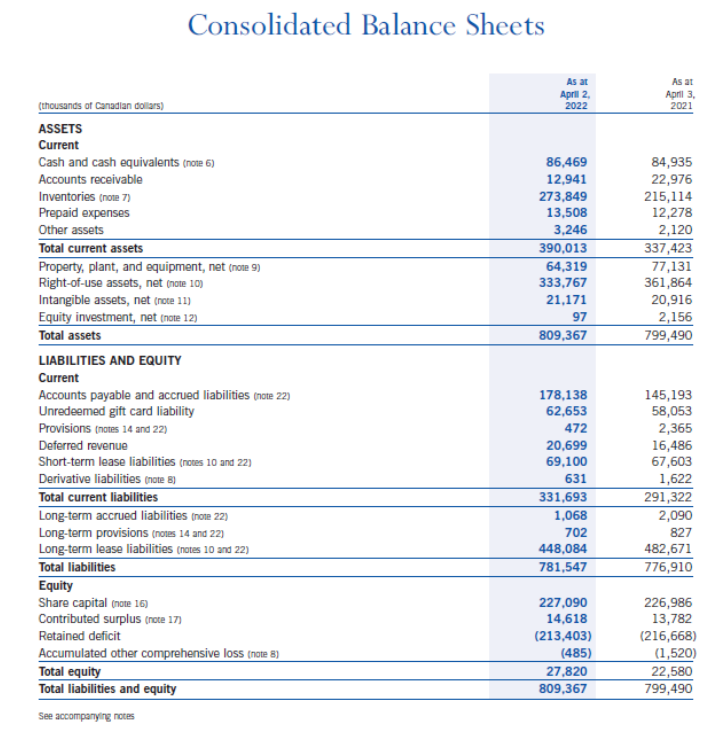
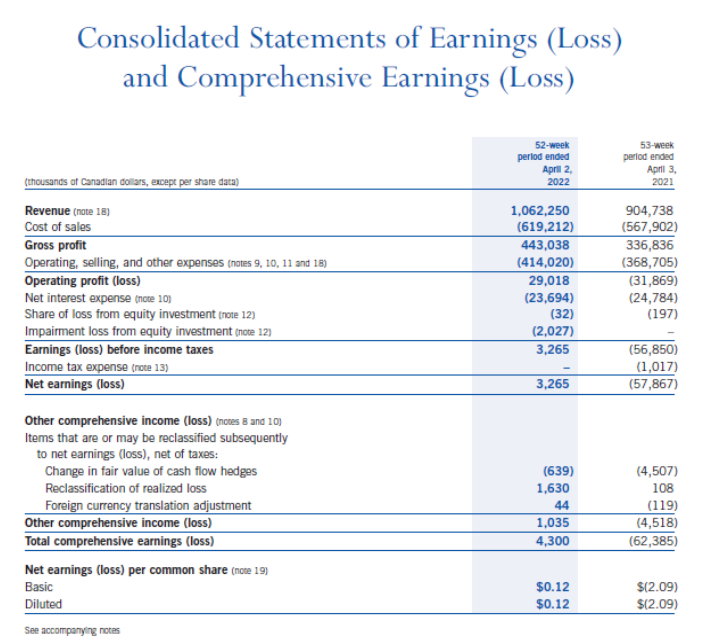
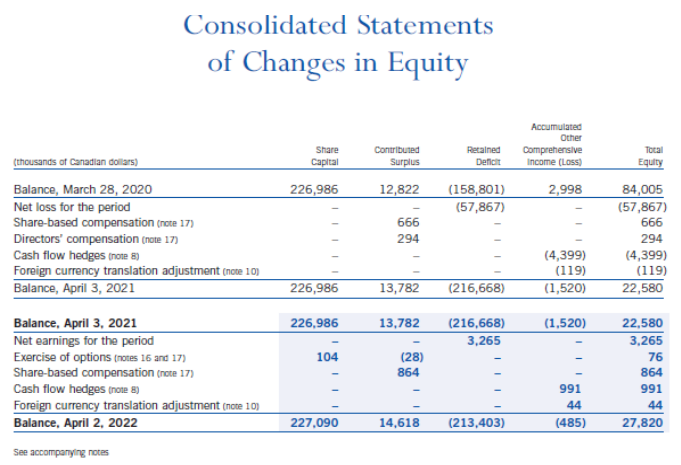
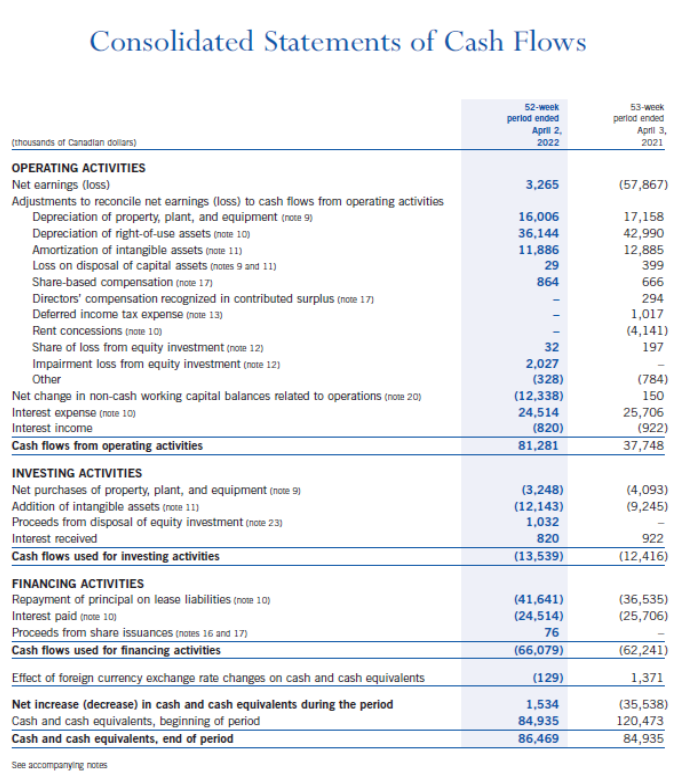




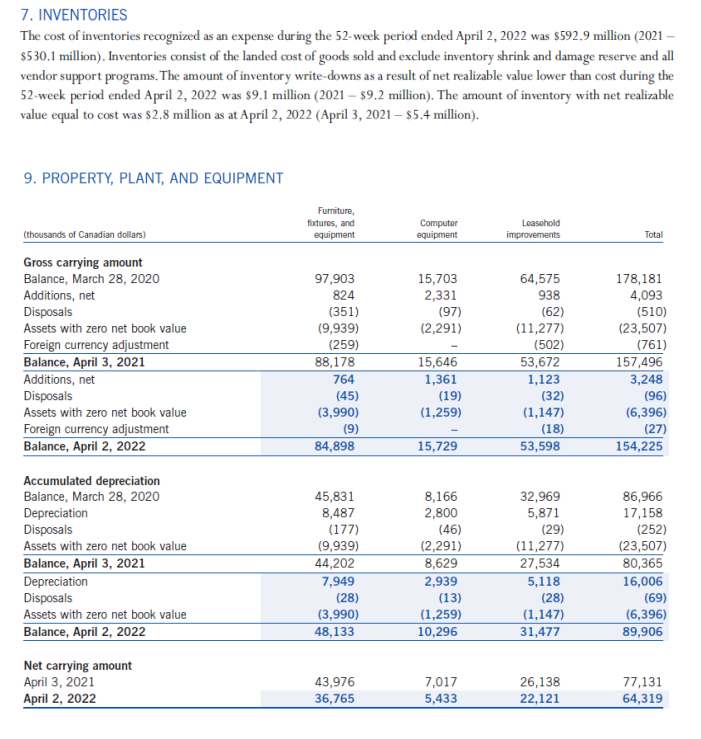
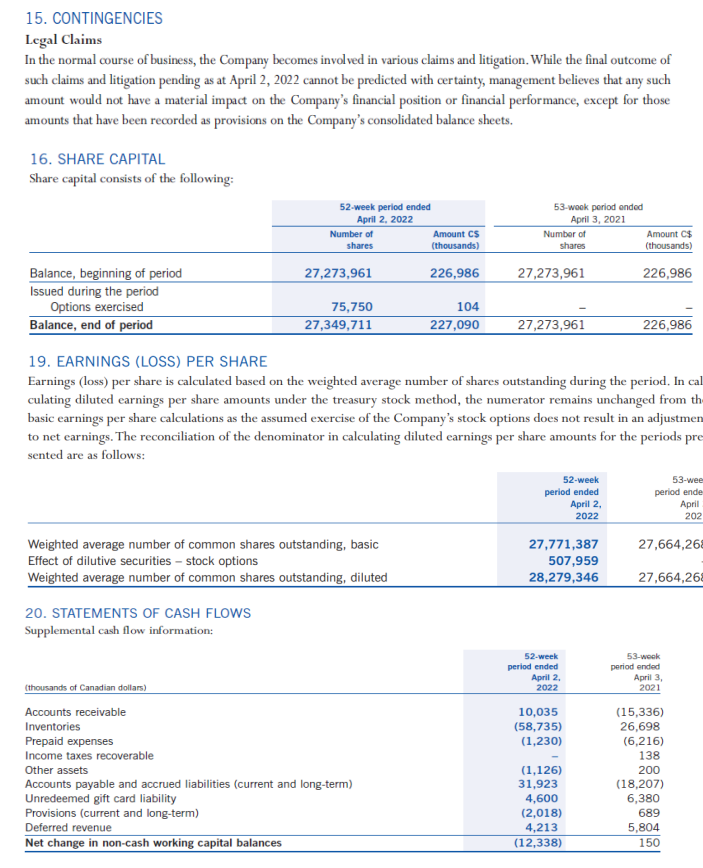


(NOTE: Where ratio calculations require averages, use year-end amounts instead. No average calculations are required. le. 2022 inventory turnover use $273,849). The Indigo Mission To inspire reading and simplify our customers' journeys to live with intention. Consolidated Balance Sheets Consolidated Statements of Earnings (Loss) and Comprehensive Earnings (Loss) Consolidated Statements of Changes in Equity Consolidated Statements of Cash Flows Notes to Consolidated Financial Statements 1. CORPORATE INFORMATION Indigo Books \& Music Inc. (the "Company" or "Indigo") is a corporation domiciled and incorporated under the laws of the Province of Ontario in Canada. The Company's registered office is located at 620 King Street West, Suite 400, Toronto, Ontario, M5V 1M6, Canada. The consolidated financial statements of the Company comprise the Company and its whollyowned subsidiaries, Indigo Design Studio Inc., Indigo Cultural Department Store Inc. ("Indigo U.S."), and YYZ Holdings Inc. ("YYZ"), along with its equity investment in Unplug Meditation, LLC ("Unplug"). The Company is the ultimate parent of the consolidated organization. 2. NATURE OF OPERATIONS Indigo is Canada's leading book and lifestyle retailer and was formed as a result of the August 2001 amalgamation of Chapters Inc. and Indigo Books \& Music Inc. The Company offers a curated assortment of books, gifts, baby, kids, wellness and lifestyle products that support customers by simplifying their journey to Living with Intention"'. The Company operates retail stores in all ten provinces and one territory in Canada, and also has retail operations in the United States through a wholly-owned subsidiary, operating one retail store in Short Hills, New Jersey. The retail network includes 88 superstores (2021 - 88) under the Indigo and Chapters names, as well as 85 small format stores (2021 - 89) under the banners Coles and Indigospirit. Retail operations are seamlessly integrated with the Company's digital channels, induding the www.indiga.ca website and the mobile applications, which are extensions of the physical stores and offer customers an expanded assor tment of book titles, along with a meaningfully curated assortment of general merchandise. The Company also offers a marketplace assortment of giftable products, experiences, services, and subscriptions on www.thoughtfull.co. The Company defines an operating segment on the same basis that it uses to evaluate performance internally and to allocate capital resources. At Indigo, this is done on an enterprise level. This holistic managerial approach is reflected in the Company's reimagined new store concept. The new store design emphasizes a central focus on enriching the lives of book lovers with core print and general merchandise products. Therefore, the Company reports as a single segment. The Company supports a separate registered charity, the Indigo Love of Reading Foundation (the "Foundation"). The Foundation provides new books and learning material to high-needs elementary schools and children across the country through donations from Indigo, its customers, its suppliers, and its employees. 3. BASIS OF PREPARATION Statement of Compliance These consolidated financial statements have been prepared using accounting policies consistent with International Financial Reporting Standards ("IFRS") as issued by the International Accounting Standards Board ("IASB"). These consolidated financial statements were approved by the Board of Directors on June 2, 2022. Fiscal Year The fiscal year of the Company ends on the Saturday closest to March 31. Under an accounting convention common in the retail industry, the Company follows a 52 -week reporting cycle, which periodically necessitates a fiscal year of 53 weeks. The year ended April 2, 2022 contained 52 weeks, while the year ended April 3, 2021 contained 53 weeks. COVID-19 Pandemic On March 11, 2020, the World Health Organization declared the outbreak of COVID-19 a pandemic, significantly impacting the Company's operations during fiscal 2022, most notably by numerous temporary mandated store closures in its first quarter, and the adverse impact of mandated pandemic restrictions to retail traffic in the Company's store network during critical holiday selling weeks in the month of December. The impact of the outbreak on the financial results of the Company will depend on future developments, induding the duration and spread of future waves of the outbreak and its impact on the overall economy and related advisories and restrictions. Further or prolonged closures of the Company's stores, or capacity restrictions, could result in the reassessment of its significant accounting estimates, including but not limited to impairment of assets. The Company is in negotiations with its landlords regarding rent abatement to address the financial impacts of the most recent wave of COVID-19 related store closures. 4. SUMMARY OF SIGNIFICANT ACCOUNTING POLICIES The accounting policies set out below have been applied consistently to all periods presented in these consolidated financial statements. Foreign Currency The functional currency for each entity included in these consolidated financial statements is the currency of the primary economic environment in which the entity operates. The consolidated financial statements are presented in Canadian dollars, which is the functional currency of the Company. Assets and liabilities of the Company's U.S. operations have a functional currency of U.S. dollars and are translated into Canadian dollars at the exchange rate in effect at the reporting date. Revenues and expenses are translated into Canadian dollars at average exchange rates during the reporting period. The resulting unrealized translation gains or losses are included in other comprehensive income (loss). Monetary assets and liabilities denominated in foreign currencies that are held at the reporting date are translated at the closing consolidated balance sheet rate. Non-monetary items are measured at historical cost and are translated using the exchange rates at the date of the transaction. Non-monetary items measured at fair value are translated using exchange rates at the date when fair value was determined. The resulting exchange gains or losses are induded in earnings. Inventorics Inventories are valued at the lower of cost, determined on a moving average cost basis, and market, being net realizable value. Costs include all direct and reasonable expenditures that are incurred in bringing inventories to their present location and condition. Net realizable value is the estimated selling price in the ordinary course of business. When the Company permanently reduces the retail price of an item and the markdown incurred brings the retail price below the cost of the item, there is a corresponding reduction in inventory recognized in the period. Vendor rebates are recorded as a reduction in the price of the products and corresponding inventories are recorded net of vendor rebates. Prepaid Expenses Prepaid expenses include store supplies, software subscription fees, rent and insurance. Store supplies are expensed as they are used while other costs are amortized over the term of the contract. Property, Plant, and Equipment All items of property, plant, and equipment are initially recognized at cost, which includes any costs directly attributable to bringing the asset to the location and condition necessary for it to be capable of operating in the manner intended by the Company. Subsequent to initial recognition, property, plant, and equipment assets are shown at cost less accumulated depreciation and any accumulated impairment losses. Depreciation of an asset begins once it becomes available for use. The depreciable amount of an asset, being the cost of an asset less the residual value, is allocated on a straight-line basis over the estimated useful life of the asset. Residual value is estimated to be nil unless the Company expects to dispose of the asset at a value that exceeds the estimated disposal costs. The residual values, useful lives, and depreciation methods applied to assets are reviewed based on relevant market information and management considerations. The following useful lives are applied: Furniture, fixtures, and equipment 510 years Computer equipment 35 years Equipment under finance leases Leasehold improvements over the shorter of useful life and lease term plus expected renewals, to a maximum of 10 years Items of property, plant, and equipment are assessed for impairment as detailed in the accounting policy note on impairment and are derecognized either upon disposal or when no future economic benefits are expected from their use. Any gain or loss arising on derecognition is induded in earnings when the asset is derecognized. Intangible Assets Intangible assets are initially recognized at cost, if acquired separately, at fair value, or as part of a business combination. After initial recognition, intangible assets are carried at cost less accumulated amor tization and any accumulated impairment losses. Amortization commences when the intangible assets are available for their intended use. The useful lives of intangible assets are assessed as either finite or indefinite. Intangible assets with finite lives are amortized over their useful economic life. Intangible assets with indefinite lives are not amortized but are reviewed at each reporting date to determine whether the indefinite life continues to be supportable. If not, the change in useful life from indefinite to finite is made on a prospective basis. Residual value is estimated to be zero unless the Company expects to dispose of the asset at a value that exceeds the estimated disposal costs. The residual values, useful lives, and amor tization methods applied to intangible assets are reviewed annually based on relevant market information and management considerations. The following useful lives are applied: There are no legal, regulatory, contractual, competitive, economic or other factors that limit the useful life of the domain name to the Company. Therefore, the useful life of the domain name is deemed to be indefinite. Intangible assets are assessed for impairment as detailed in the accounting policy note on impairment. An intangible asset is derecognized either upon disposal or when no future economic benefit is expected from its use. Any gain or loss arising on derecognition is included in earnings when the asset is derecognized. Revenue Recognition The Company recognizes revenue when control of goods has been transferred at the amount of consideration to which the Company expects to be entitled. Revenue is recorded net of sales discounts, estimated returns, sales tax, environmental fees and amounts deferred related to the issuance of plum points. Revenue is recognized when control of goods has been transferred (as described below) for each of the Company's revenue-generating activities. Retail sales Revenue for retail customers is recognized when the product is delivered to the customer, which for the majority of retail transactions occurs at time of purchase. Online and kiosk sales Revenue for online and kiosk customers is recognized when the product is shipped to customers. Gift cards The Company sells gift cards to its customers and recognizes the revenue as gift cards are redeemed for merchandise. A customer's non-refundable prepayment to the Company gives them a right to receive product in the future. However, historically customers do not exercise all of their contractual rights, which is referred to as breakage. The Company determines its average gift card breakage rate based on historical redemption rates. Breakage income represents the estimated value of gift cards that is not expected to be redeemed by customers and is determined in proportion to the pattern of rights exercised by the customer. Gift card breakage is included in revenue in the Company's consolidated statements of earnings (loss) and comprehensive earnings (loss). Changes in estimated breakage is accounted for by adjusting the contract liability to reflect the remaining rights expected to be redeemed. Indigo plum rewards program Indigo's loyalty program, plum , has two tiers: p lum , a free points-based tier; and plum PLUS, an annual fee-based tier. The plum program is an omni-channel program that allows members to earn and redeem points online and in-store, seamlessly. This program engages members through mass promotions and targeted one-to-one promotional offers, as well as invitations to exclusive events and member-only shopping experiences. The Company launched the plum PLUS membership program in fiscal 2020, replacing its former annual fee-based irewards x program. plum PLUS offers its members an immediate discount on eligible products, free shipping and the ability to earn points on almost every dollar spent at the Company's Canadian stores, as well as on its digital platforms. When a plum PLUS membership is sold, the amount is recognized in deferred revenue and amortized into revenue over the life of the membership, based on historical usage patterns. When a plum member purchases merchandise, the Company allocates consideration received between the loyalty program points and the merchandise on which the points were earned based on their relative stand-alone selling prices. The portion of revenue attributed to the merchandise is recognized at the time of purchase. Revenue attributed to the points is recorded as deferred revenue and recognized when points are redeemed. The stand-alone selling price of the points issued is determined based on the estimated reward tier value, net of points that management expects will go unredeemed. The Company continues to monitor trends in redemption patterns (redemption at each reward level), historical redemption rates (points redeemed as a percentage of points issued) and net cost per point redeemed to reduce estimation uncertainty in the consideration allocated to the loyalty contract right. Points revenue is induded as part of total revenue in the Company's consolidated statements of earnings (loss) and comprehensive earnings (loss). Interest income Interest income is reported on an accrual basis using the effective interest method and induded as part of net interest in the Company's consolidated statements of earnings (loss) and comprehensive earnings (loss). 7. INVENTORIES The cost of inventories recognized as an expense during the 52-week period ended April 2, 2022 was $592.9 million (2021 $530.1 million). Inventories consist of the landed cost of goods sold and exclude inventory shrink and damage reserve and all vendor support programs. The amount of inventory write-downs as a result of net realizable value lower than cost during the 52-week period ended April 2, 2022 was $9.1 million (2021 - \$9.2 million). The amount of inventory with net realizable value equal to cost was \$2.8 million as at April 2, 2022 (April 3, 2021$5.4 million). 9 PROPFRTY PI ANT ANN FOIIIPMFNT 15. CONTINGENCIES Legal Claims In the normal course of business, the Company becomes involved in various claims and litigation. While the final outcome of such claims and litigation pending as at April 2, 2022 cannot be predicted with certainty, management believes that any such amount would not have a material impact on the Company's financial position or financial performance, except for those amounts that have been recorded as provisions on the Company's consolidated balance sheets. 16. SHARE CAPITAL Share capital consists of the following: 19. EARNINGS (LOSS) PER SHARE Earnings (loss) per share is calculated based on the weighted average number of shares outstanding during the period. In ca culating diluted earnings per share amounts under the treasury stock method, the numerator remains unchanged from th basic earnings per share calculations as the assumed exercise of the Company's stock options does not result in an adjustme to net earnings. The reconciliation of the denominator in calculating diluted earnings per share amounts for the periods pr sented are as follows: 20. STATEMENTS OF CASH FLOWS Supplemental cash flow information: Management's Discussion and Analysis Overview Indigo is Canada's leading book and lifestyle retailer and was formed as a result of the August 2001 amalgamation of Chapters Inc, and Indigo Books \& Music Inc. The Company offers a curated assortment of books, gifts, baby, kids, wellness and lifestyle products, that supports customers by simplifying their journey to Living wtth Intention". The Company operates retail stores in all ten provinces and one territory in Canada, and also has retail operations in the United States through a wholly-owned subsidiary, operating one retail store in Short Hills, New Jersey. The retail network includes 88 superstores (2021 - 88 ) under the Indigo and Chapters names, as well as 85 small format stores (2021 - 89) under the banners Coles and Indigosptrit, Retail operations are seamlessly inte grated with the Company's digital channels, including the www. indtgo.ca website and the mobile applications, which are extensions of the physical stores and offer customers an expanded assortment of book titles, along with a meaningfully curated assortment of general merchandise. The Company also offers a marketplace assortment of giftable products, experiences, services, and subscriptions on www.thoughtfull.co. Throughout fiscal 2022, the Company employed an average of approximately 5,000 people (on a full-time, part-time, and casual hasis) and generated annual revenue of $1,062,3 million. The consolidated financial statements of the Company comprise the Company and its wholly-owned subsidiaries; Indigo Design Studio, Inc., Indigo Cultural Department Store Inc. ("Indigo U.S."), and YYZ Holdings Inc. ("YYZ"), along with its 20% equity investment in Unplug Meditation, L.L. (Unplug"). The Company supports a separate registered charity called the Indigo Love of Reading Foundation (the "Foundation"). The Foundation provides new books and learning materials to high-needs elementary schools and children across the country through donations from lndigo, its customers, its suppliers, and its employees. Statement on COVID-19 The Company, and the retail industry, continue to navigate the impacts of the COVID-19 pandemic, including government imposed restrictions, such as closures, quarantine policies and social distancing measures that negatively impact the Company's retail operations, distributions centres, head office operations and supply chain. The Company undertook the following actions in fiscal 2022: - Participated in rolling closures of its retail network, as directed by local governments and public heal th authorities. This notably included province-wide closures in Ontario that negatively impacted the Company's retail operations through the majority of the first quarter; store locations with external entrances re-opened on June 1, 2021, with remaining store locations in the province having re-opened on June 29,2021. The Company successfully executed on the reopening of 93 closed retail stores across Canarla with a focus on driving operational effectiveness. - In December 2021, the Company responded to the adverse impact of the Omicron variant on retail foot traffic patterns and implemented mandated government capadity restrictions, which most notably included a fifty percent reduction in capacity in the province of Ontario during critical selling weeks. - Recognized $7.7 million of COVID-19 occupancy expense ahatement as a direct response to the economic impact of the COVID-19 pandemic, compared to $15.5 million in the prior year. The Company continues to negotiate with landlords regarding abatement to share the finandal burden of COVID-19. - Applied for the Canada Emergency Rent Subsidy ("CERS") program and recognized rent subsidies of \$2.9 million, compared to $1,1 million in the prior year. - Applied for the Canada Emergency Wage Subsidy ("CEWS") program and recognized payroll subsidies of \$2.3 million, compared to $27.4million in the prior year. - Entered into a $25.0 million related party revolving line of credit to enhance the Company's liquidity in response to uncertainty surrounding the pandemic's financial impacts. No advances were made on the non-interest bearing facility, which matured on February 1, 2022. - Forecasted inbound inventory receipts to account for modest delays as a result of disruption to the global supply chain based on the monitored impacts of higher inbound freight costs and constrained shipping capacity. - Effectively mitigated disruption to its print business, stemming from the raw material scarcity and distribution delays experienced across the publishing industry, by shifting inventory purchases earlier in the planning season. As a result, the Company had sufficient inventory on-hand for bestselling titles and its back list catalogue to fulfill an increased demand for books during the holiday season. The Company's top priority remains the health and safety of its customers, employees and communities, and extensive health and safety measures have been employed that meet or exceed the guidance and direction from public health authorities Overview of Consolidated Balance Sheets Equity Total equity at April 2, 2022 increased $5.2 million to $27.8 million, compared to $22.6 million as at April 3, 2021, driven primarily by the net earnings of $3.3 million recognized over the past four quarters. This was furthered by an increase of $1,0 million in accumulated other comprehensive income, primarily due to the change in fair value of outstanding cash flow hedges. The weighted average number of common shares outstanding for fiscal 2022 was 27,771,387 compared to 27,664,268 in the prior year. As at June 2, 2022, the number of outstanding common shares was 27,349,711 with a book value of $227.1 million. Accounting Policies Inventories The future realization of the carrying amount of inventory is affected by future sales demand, inventory levels, and product quality. At each balance sheet date, the Company reviews its on-hand inventory and uses historical trends and current inventory mix to determine a reserve for the impact of future markdowns that will take the net realizable value of inventory on-hand below cost. Inventory valuation also incorporates a write-down to reflect future losses on the disposition of obsolete merchandise. The Company reduces inventory for estimated shrinkage that has occurred between physical inventory counts and each reporting date based on historical experience as a percentage of sales. In addition, the Company records a vendor settlement accrual to cover any disputes between the Company and its vendors. The Company estimates this reserve based on historical experience of settlements with its vendors. Property, plant, equipment, and intangible assets (collectively, "capital assets") Capital assets are depreciated and amortized over their useful lives, taking into account residual values where appropriate. Assessments of useful lives and residual values are performed on an ongoing basis and take into consideration factors such as technological innovation, maintenance programs, and relevant market information. In assessing residual values, the Company considers the remaining life of the asset, its projected disposal value, and future market conditions. Revenue The Company recognizes revenue for the estimated value of gift cards that are not expected to be redeemed by customers ("gift card breakage") in proportion to the pattern of rights exercised by the customer. The resulting gift card breakage revenue is recognized over the estimated period of redemption based on historical redemption patterns commencing when the gift cards are sold. Indigo's plume loyalty program, which includes the plume and plume PLUS membership tiers, allows customers to earn points on their purchases. The allocation of transaction price to the plum loyalty obligation, which is the estimated reward tier value of a future redemption net of points management expects will go unredeemed ("plum" breakage"), is based on a relative stand-alone selling price basis. The Company continues to monitor trends in redemption patterns (redemption at each reward level), historical redemption rates (points redeemed as a percentage of points issued) and net cost per point redeemed. Internal Controls over Financial Reporting Management is also responsible for establishing and maintaining adequate internal controls over financial reporting to provide reasonable assurance regarding the reliability of financial reporting and the preparation of consolidated financial statements for external purposes in accordance with IFRS. All internal control systems, no matter how well designed, have inherent limitations. Therefore, even those systems determined to be effective can provide only reasonable assurance with respect to consolidated financial statement preparation and presentation. Additionally, management is necessarily required to use judgment in evaluating controls and procedures. As required by National Instrument 52-109, "Certification of Disclosure in Issuers' Annual and Interim Filings," the CEO and CFO have evaluated, or caused to be evaluated under their supervision, the effectiveness of such internal controls over financial reporting using the framework established in the Internal Control - Integrated Framework ("COSO Framework") published in 2013 by the Committee of Sponsoring Organizations of the Treadway Commission. Based on that evaluation, they have conduded that the design and operation of the Company's internal controls over financial reporting were effective as at April 2, 2022



















