Question
A queue is an abstract data type that maintains the order in which elements were added to it, allowing the oldest elements to be removed
A queue is an abstract data type that maintains the order in which elements were added to it, allowing the oldest elements to be removed from the front and new elements to be added to the rear. This is called a First-In-First-Out (FIFO) data structure because the first element added to the queue (i.e., the one that has been waiting the longest) is always the first one to be removed.
A basic queue has the following operations:
- Enqueue: add a new element to the end of the queue.
- Dequeue: remove the element from the front of the queue and return it.
In this challenge, you must first implement a queue using two stacks. Then process queries, where each query is one of the following types:
-
1 x: Enqueue element into the end of the queue. -
2: Dequeue the element at the front of the queue. -
3: Print the element at the front of the queue.
Input Format
The first line contains a single integer, , denoting the number of queries. Each line of the subsequent lines contains a single query in the form described in the problem statement above. All three queries start with an integer denoting the query , but only query is followed by an additional space-separated value, , denoting the value to be enqueued.
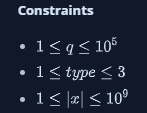
- It is guaranteed that a valid answer always exists for each query of type .
Output Format
For each query of type , print the value of the element at the front of the queue on a new line.
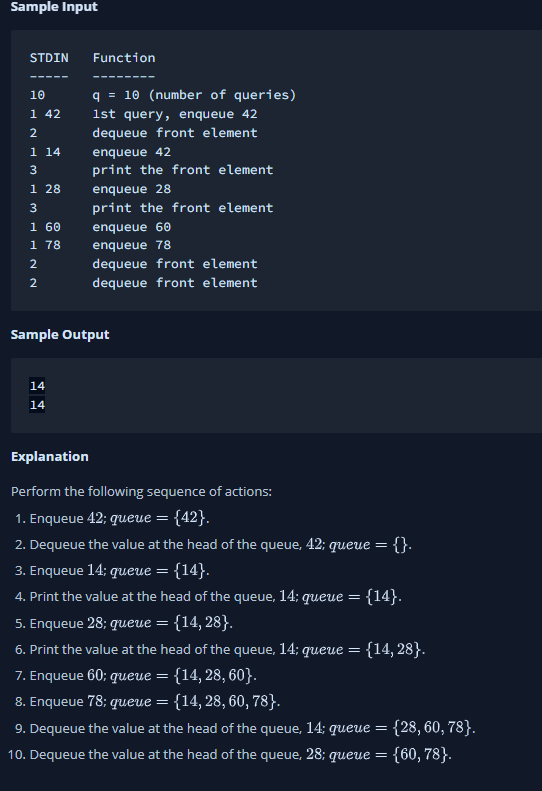
 Constraints - 1q105 - 1 type 3 - 1x109 Sample Input STDIN Function q=10 (number of queries) 1st query, enqueue 42 dequeue front element enqueue 42 print the front element enqueue 28 print the front element enqueue 60 enqueue 78 dequeue front element dequeue front element Sample Output 14 14 Explanation Perform the following sequence of actions: 1. Enqueue 42; queue ={42}. 2. Dequeue the value at the head of the queue, 42;queue={}. 3. Enqueue 14; queue ={14}. 4. Print the value at the head of the queue, 14; queue ={14}. 5. Enqueue 28 ; queue ={14,28}. 6. Print the value at the head of the queue, 14; queue ={14,28}. 7. Enqueue 60 ; queue ={14,28,60}. 8. Enqueue 78; queue ={14,28,60,78}. 9. Dequeue the value at the head of the queue, 14; queue ={28,60,78}. 10. Dequeue the value at the head of the queue, 28; queue ={60,78}. \#include scmath> \#include cstdio \#include vector \#include \#include using namespace std; int main(){ / Enter your code here. Read input from STDIN. Print output to STDOUT */ return ; \}
Constraints - 1q105 - 1 type 3 - 1x109 Sample Input STDIN Function q=10 (number of queries) 1st query, enqueue 42 dequeue front element enqueue 42 print the front element enqueue 28 print the front element enqueue 60 enqueue 78 dequeue front element dequeue front element Sample Output 14 14 Explanation Perform the following sequence of actions: 1. Enqueue 42; queue ={42}. 2. Dequeue the value at the head of the queue, 42;queue={}. 3. Enqueue 14; queue ={14}. 4. Print the value at the head of the queue, 14; queue ={14}. 5. Enqueue 28 ; queue ={14,28}. 6. Print the value at the head of the queue, 14; queue ={14,28}. 7. Enqueue 60 ; queue ={14,28,60}. 8. Enqueue 78; queue ={14,28,60,78}. 9. Dequeue the value at the head of the queue, 14; queue ={28,60,78}. 10. Dequeue the value at the head of the queue, 28; queue ={60,78}. \#include scmath> \#include cstdio \#include vector \#include \#include using namespace std; int main(){ / Enter your code here. Read input from STDIN. Print output to STDOUT */ return ; \} Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it
Step: 1

Get Instant Access to Expert-Tailored Solutions
See step-by-step solutions with expert insights and AI powered tools for academic success
Step: 2

Step: 3

Ace Your Homework with AI
Get the answers you need in no time with our AI-driven, step-by-step assistance
Get Started


