Question: A Quick Recap: Propositional Logic (Equivalences) Symbols (e.g., letters, words) are used to represent facts about the world: e.g. P represents the fact Ali likes
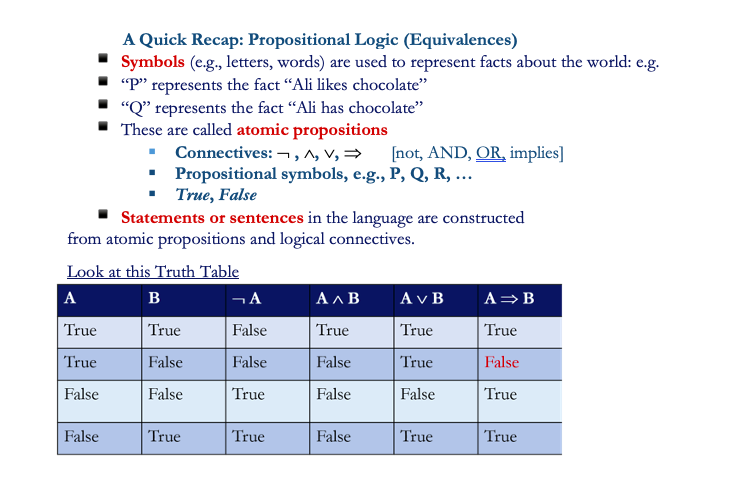

A Quick Recap: Propositional Logic (Equivalences) Symbols (e.g., letters, words) are used to represent facts about the world: e.g. P represents the fact Ali likes chocolate "Q represents the fact Ali has chocolate These are called atomic propositions . Connectives: 7,1,V, >> [not, AND, OR, implies) Propositional symbols, e.g., P, Q, R, ... True, False Statements or sentences in the language are constructed from atomic propositions and logical connectives. Look at this Truth Table A B GA AAB A B A=B True True False True True True True False False False True False False False True False False True False True True False True True Do this: Apply Truth Table to proof the following Laws: 1. Equivalences -LP) =P (PV Q) = (-P=Q) 2. The contra positive law (PQ) = (-Q-P) 3. De Morgan's law (PVQ) = (-PA-Q) and (PAQ) = (-PV-Q) 4. The commutative laws . (PAQ) = (QAP) and (PVQ) = (QVP) 5. Associative law ((PAQ) AR) = (PA (QAR)), ((P VQ) V R) = (PV (Q V R)) Distributive law PV (QAR) = (PVQ) (PVR), PA (QVR) = (PAQ) V (PAR) Apply the truth table to each of these propositional logics and submit on blackboard
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


