Question
A reaction is carried out in a well-mixed vessel fed reactant A at a concentration of 1 mol/L and volume flow rate of 1 L/min.
A reaction is carried out in a well-mixed vessel fed reactant A at a concentration of 1 mol/L and volume flow rate of 1 L/min. After a while, the reactor outflow concentration stabilizes at a value of 0.1 mol/L of A and does not change afterwards. The volume flow rate of the outflow is 1 L/min at all times, so that the reactor volume is kept constant at 10 L.
a) What is the reaction rate constant if the reaction obeys first order kinetics?
b) To optimize this process, it is decided to explore the possibility of having two 5 L reactors instead of a single 10 L reactor. The reactors are arranged in such a way that the output of the first reactor (which is labeled CAm ) becomes the input to the second reactor. Calculate the steady-state concentrations of reactant A exiting the first reactor (CAm) and second reactor (CAout)
c) Calculate the fractional conversion of A for the single reactor in part (a) and for the two-reactor system in part (b).
How do they compare? Which system gives the most fractional conversion?
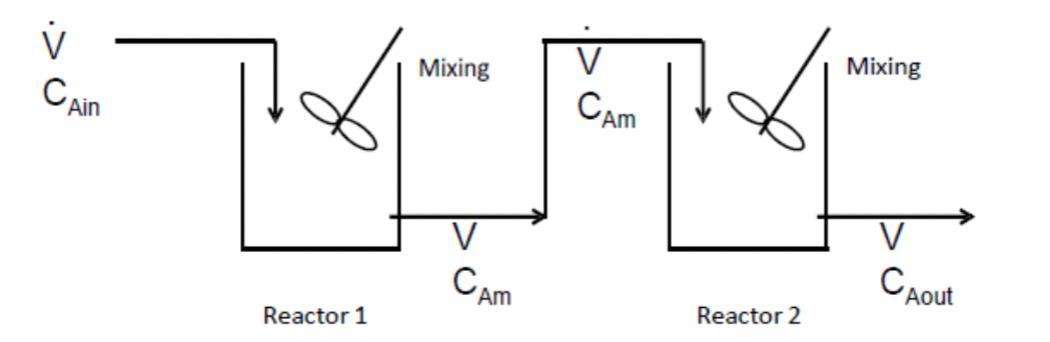
v CAin Mixing CAM Mixing Reactor 1 CAM Reactor 2 CAout
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it
Step: 1

Get Instant Access to Expert-Tailored Solutions
See step-by-step solutions with expert insights and AI powered tools for academic success
Step: 2

Step: 3

Ace Your Homework with AI
Get the answers you need in no time with our AI-driven, step-by-step assistance
Get Started


